Have you ever wondered how large of a space a 4-ton AC unit can effectively cool? In this article, we will explore the cooling capabilities of a 4-ton AC unit and determine the approximate square footage it can effectively cool. Whether you are considering installing a new AC unit or trying to determine if your current unit is sufficient for your space, this article will provide you with the information you need to make an informed decision.

Factors affecting the cooling capacity of an AC unit
Air conditioning units are crucial for providing comfort and relief during hot summer months. However, the cooling capacity of an AC unit is influenced by several factors that need to be considered before making a purchase or determining the appropriate size for your space. Understanding these factors will ensure that your AC unit performs optimally and meets your cooling needs effectively.
BTU rating of the AC unit
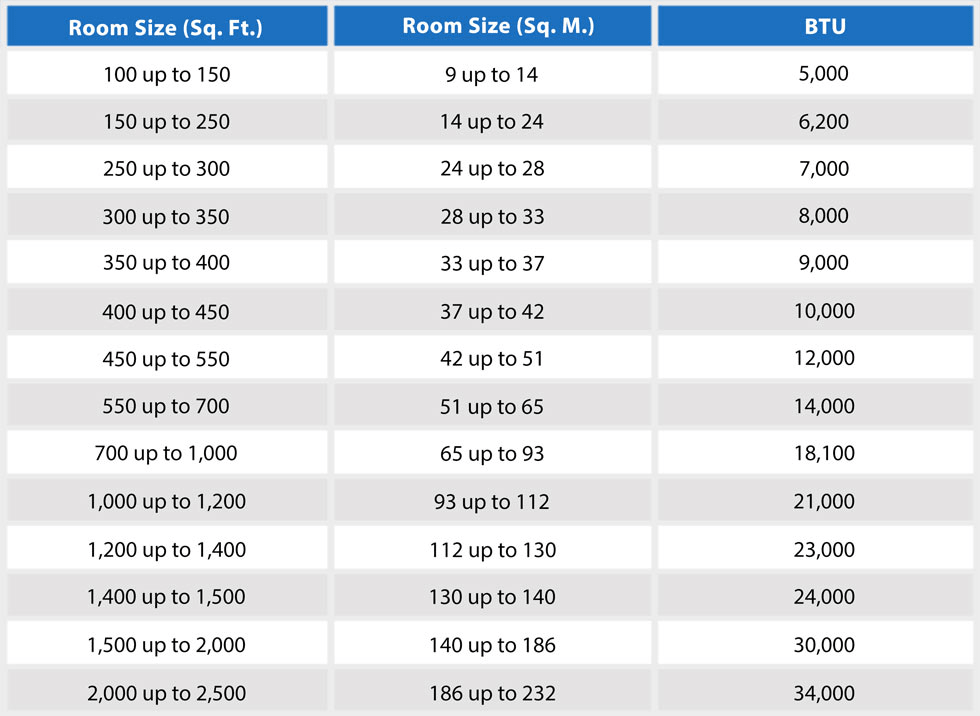
BTU (British Thermal Units) is the unit used to measure the cooling capacity of an AC unit. The higher the BTU rating, the greater the cooling capacity of the AC unit. When selecting an AC unit, it is essential to consider the required BTU based on the size of your space. A higher BTU rating is suitable for larger areas, while smaller spaces can be adequately cooled with a lower BTU rating.
Insulation and energy efficiency of the building
The insulation and energy efficiency of your building can significantly impact the cooling capacity of your AC unit. Proper insulation ensures that cooled air remains inside, while also preventing heat from entering your space. Additionally, energy-efficient buildings reduce overall energy consumption, allowing your AC unit to cool more effectively without excessive strain.
Climate and geographic location
The climate and geographic location of your area play a significant role in determining the cooling capacity required for your AC unit. Hotter and more humid climates require higher cooling capacities to maintain comfortable indoor temperatures. On the other hand, cooler and less humid climates may require lower cooling capacities. It is important to consider these factors to ensure your AC unit can handle the demands of your specific climate and geographic location.
Ceiling height and attic space
Ceiling height and attic space also affect the cooling capacity of an AC unit. Higher ceilings and larger attic spaces require higher BTU ratings to effectively cool the entire area. This is because taller spaces and attics have more cubic footage that needs to be cooled. It is crucial to take these measurements into account when determining the appropriate AC unit size for your space.
Number of windows and their orientation
Windows play a significant role in the cooling capacity of an AC unit. The number of windows and their orientation affect the amount of heat that enters your space. South and west-facing windows receive the most direct sunlight, leading to increased heat gain. In contrast, windows facing north or east receive less direct sunlight and experience reduced heat gain. The size, type, and quality of windows also contribute to heat transfer. Proper window coverings and insulation can help minimize heat gain and improve the cooling capacity of your AC unit.
Heat generating appliances and electronics
The heat generated by appliances and electronics can impact the cooling capacity of your AC unit. Appliances such as ovens, stoves, refrigerators, and washing machines produce heat that can make your space warmer. Similarly, electronic devices such as computers, televisions, and gaming consoles generate heat when in use. It is crucial to consider the heat load generated by these appliances and electronics when determining the cooling capacity needed for your AC unit.
Number of occupants
The number of occupants in your space can also affect the cooling capacity required for your AC unit. Each person emits body heat, which can increase the overall heat load. Additionally, the presence of more people may require more airflow to maintain comfort. It is important to account for the number of occupants in your space when selecting the appropriate cooling capacity for your AC unit.
Airflow and ventilation
Adequate airflow and ventilation are essential for optimizing the cooling capacity of your AC unit. Efficient airflow ensures that cool air is evenly distributed throughout your space, preventing any hot spots. Proper ventilation also helps remove stale air and promote healthier indoor air quality. By ensuring good airflow and ventilation, you can enhance the cooling performance of your AC unit.
Indoor air quality
Indoor air quality can impact the cooling capacity of your AC unit. Dust, allergens, and pollutants in the air can clog air filters and decrease the efficiency of your AC system. Regularly changing air filters and maintaining clean indoor air will help your AC unit cool more effectively and efficiently.
Maintenance and servicing
Regular maintenance and servicing of your AC unit are vital for preserving its cooling capacity. Over time, dust and debris can accumulate in the unit’s components, hindering its efficiency. The condenser coils, evaporator coils, and air filters should be cleaned or replaced regularly as recommended by the manufacturer. Professional servicing can also identify potential issues and ensure your AC unit operates at its full cooling capacity.
Understanding AC tonnage
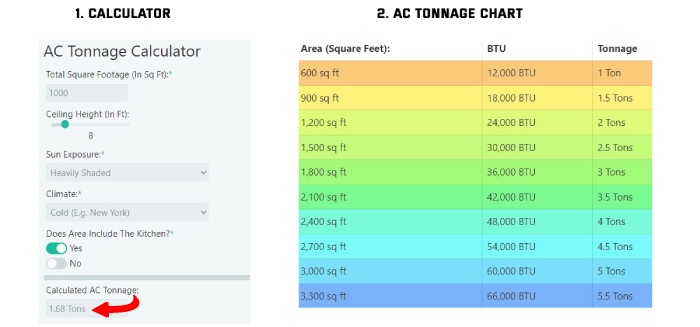
AC tonnage is an important measurement to consider when determining the cooling capacity of your AC unit. Understanding the relationship between tonnage and cooling capacity will help you make an informed decision when selecting the appropriate AC unit for your space.
Definition of AC tonnage
AC tonnage refers to the cooling capacity of an air conditioning unit and is expressed in tons. One ton of cooling capacity is equivalent to the amount of heat needed to melt one ton (2000 pounds) of ice in a 24-hour period. The higher the tonnage, the greater the cooling capacity of the AC unit.
Relationship between tonnage and cooling capacity
The cooling capacity of an AC unit is directly proportional to its tonnage. A higher-tonnage AC unit has a greater cooling capacity and can effectively cool larger spaces. Conversely, a lower-tonnage AC unit is suitable for smaller areas with lower cooling requirements.
4-ton AC unit example
To illustrate the relationship between tonnage and cooling capacity, let’s consider a 4-ton AC unit. A 4-ton AC unit has a cooling capacity of 48,000 BTUs per hour (12,000 BTUs per ton x 4 tons). This capacity is suitable for cooling spaces that range from approximately 1500 to 2500 square feet, depending on other factors such as insulation, climate, and heat load.

Determining the cooling capacity needed for your space
To determine the appropriate cooling capacity for your space, it is essential to calculate the square footage, consider the heat load, and utilize the Manual J calculation.
Calculating the square footage of the area
Measure the length and width of each room or area in your space and multiply them to calculate the square footage. Add the square footage of all the rooms or areas together to get the total square footage of your space.
Determining the heat load
The heat load of your space refers to the amount of heat that needs to be removed by the AC unit to maintain a comfortable temperature. This includes factors such as the number of occupants, heat-generating appliances, and windows. Calculate the heat load based on these factors to determine the cooling capacity required for your AC unit.
Using the Manual J calculation
The Manual J calculation is a widely accepted method used by HVAC professionals to determine the cooling capacity needed for a space. This calculation takes into account various factors such as square footage, insulation, heat load, and other specifics of your space. Consulting with a professional to perform a Manual J calculation can ensure accurate results and help determine the appropriate cooling capacity for your AC unit.
Considering other factors
In addition to square footage and heat load, it is important to consider other factors such as insulation quality, climate, geographical location, ceiling height, attic space, and the number of windows. Each of these factors can impact the cooling capacity needed for your AC unit.
Consulting with a professional
If you are unsure about the cooling capacity needed for your space, it is recommended to consult with a professional HVAC technician. They can assess your specific requirements and provide guidance on selecting the right AC unit size to effectively cool your space.
Approximate cooling capacity of a 4-ton AC unit
A 4-ton AC unit has an approximate cooling capacity suitable for spaces ranging from 1500 to 2500 square feet, depending on various factors. However, the cooling capacity of a 4-ton AC unit can be influenced by other specific factors unique to your space.
Dependence on other factors
While a 4-ton AC unit can generally provide adequate cooling for a certain square footage range, it is important to consider other factors such as insulation, climate, ceiling height, and heat load. These factors can either increase or decrease the cooling capacity required for your space.
Average square footage coverage
On average, a 4-ton AC unit can cool approximately 2000 square feet of space. However, this coverage may vary depending on the specific factors discussed earlier. It is recommended to perform a thorough assessment of your space and consult with a professional to determine the exact cooling capacity required.
Example scenarios
To provide a better understanding, let’s consider a couple of example scenarios. In a well-insulated and energy-efficient home located in a moderate climate, a 4-ton AC unit may effectively cool a space of 2500 square feet. However, in a poorly insulated home located in a hot and humid climate, the same 4-ton AC unit may struggle to cool a space of 1500 square feet.

Effect of insulation and energy efficiency
The insulation and energy efficiency of your building significantly impact the cooling capacity of your AC unit. By improving insulation and energy efficiency, you can enhance the cooling performance and reduce the load on your AC unit.
Impact on cooling capacity
Insufficient insulation allows heat to seep into your space, making it harder for the AC unit to cool effectively. By improving insulation in walls, ceilings, and windows, you can minimize heat transfer and optimize your AC unit’s cooling capacity. Similarly, an energy-efficient building ensures that less energy is wasted, resulting in a more efficient cooling process.
Improving insulation and energy efficiency
To improve insulation, consider adding insulation material to walls, ceilings, and floors. Ensure that windows are properly sealed and install energy-efficient windows if possible. Additionally, weatherstripping doors and sealing any air leaks will further enhance insulation. Energy efficiency can be improved by using LED lighting, energy-efficient appliances, and a programmable thermostat. By taking these measures, you can maximize the cooling capacity of your AC unit and reduce energy consumption.
Influence of climate and geographic location
The climate and geographic location of your area have a significant influence on the cooling capacity required for your AC unit. Understanding how different climates impact cooling needs will help you determine the appropriate AC unit size for your space.
Hot and humid climates
In hot and humid climates, cooling requirements are typically higher due to the higher temperatures and humidity levels. To adequately cool your space in these climates, you may need a higher-tonnage AC unit or additional cooling solutions such as dehumidifiers or multiple AC units.
Mild and temperate climates
Mild and temperate climates have relatively lower cooling requirements compared to hot and humid climates. A lower-tonnage AC unit may be sufficient to cool your space in these climates. However, it is still important to consider factors such as insulation and heat load to ensure optimal cooling performance.
Dry and arid climates
Dry and arid climates have unique cooling challenges compared to other climates. While the temperatures may be high, the absence of humidity can make spaces feel cooler and reduce the cooling load. A lower-tonnage AC unit may be suitable for these climates, but it is important to consider other factors such as insulation and window orientation.
Cooler climates with moderate summers
In cooler climates, where summers are moderate and temperatures are not excessively high, a lower-tonnage AC unit may be sufficient to cool your space. However, it is essential to consider insulation and other factors that may impact cooling capacity.

Ceiling height and attic space considerations
Ceiling height and attic space are often overlooked factors that can impact the cooling capacity of your AC unit. Proper consideration of these elements will help you select the right size AC unit for your space.
Effect on cooling capacity
Higher ceilings and larger attic spaces require a higher cooling capacity as they have more cubic footage that needs to be cooled. The extra space in high ceilings and attics adds to the overall heat load, requiring a higher-tonnage AC unit to compensate for the increased cooling demand.
Increasing ceiling height or attic insulation
If you have high ceilings or a large attic space, it may be beneficial to increase the insulation and install proper ventilation systems to maintain an efficient cooling process. Adequate insulation and ventilation will minimize heat transfer and ensure that cold air is effectively distributed throughout your space. Properly insulating the attic and increasing attic ventilation can help optimize your AC unit’s cooling capacity.
Impact of windows and their orientation
Windows have a significant impact on the cooling capacity of an AC unit. The number of windows and their orientation can affect the heat gain in your space, requiring a higher cooling capacity.
Heat gain through windows
Windows allow heat from sunlight to enter your space, leading to increased heat gain. South and west-facing windows receive the most direct sunlight and are susceptible to higher heat gain. In contrast, north and east-facing windows receive less direct sunlight and experience reduced heat gain. The size, type, and quality of windows also contribute to heat transfer.
Strategies for reducing heat gain
To minimize heat gain through windows, consider using window coverings such as blinds, curtains, or shades. Installing window films or applying reflective coatings to windows can also help reduce heat transfer. Additionally, planting trees or shrubs outside south and west-facing windows can provide natural shade and further reduce heat gain.

Heat generating appliances and electronics
The heat generated by appliances and electronics in your space can impact the cooling capacity required for your AC unit.
Calculating heat load from appliances
To calculate the heat load from appliances, consider their power consumption and runtime. Appliances such as ovens, stoves, refrigerators, washing machines, and dryers produce heat while operating. Determining the heat output of these appliances will help you accurately assess the cooling capacity needed to counteract the additional heat load.
Reducing heat generation
To minimize the heat generated by appliances and electronics, ensure that they are well-maintained and operating efficiently. Regularly clean air vents and filters to prevent dust buildup, as this can hinder proper cooling. Additionally, consider using energy-efficient appliances and practicing energy-saving habits to reduce overall heat generation in your space.
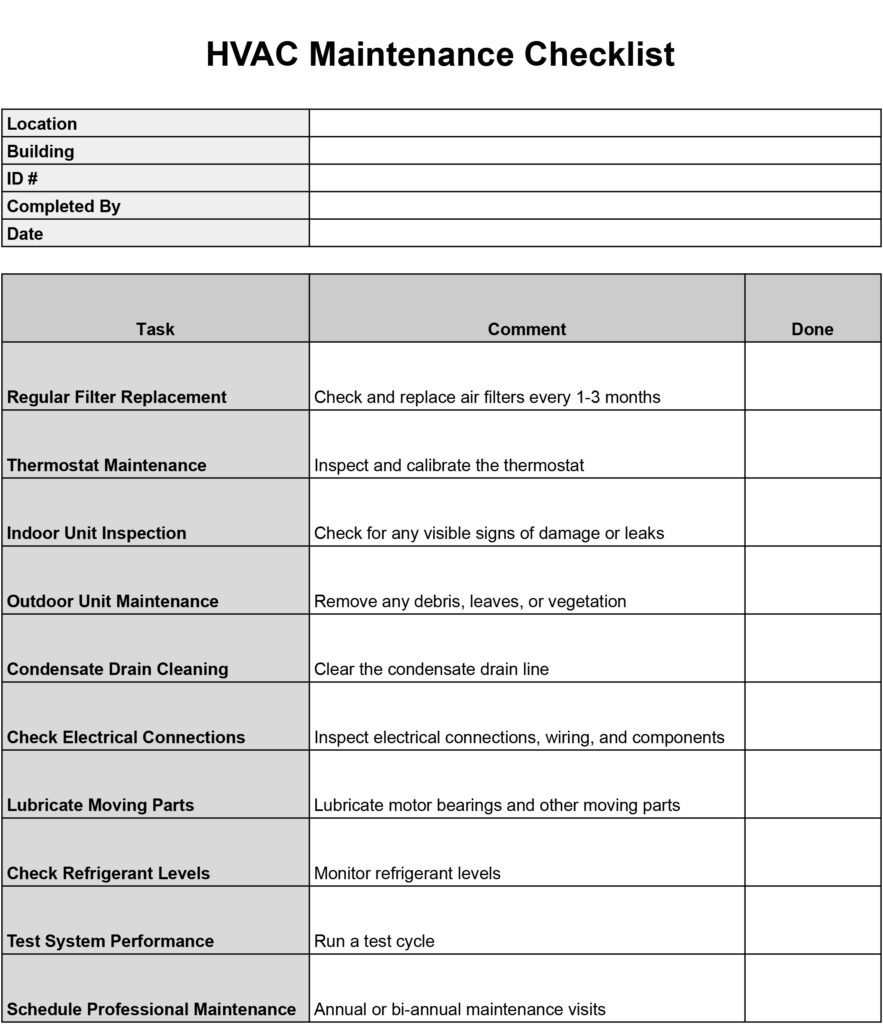
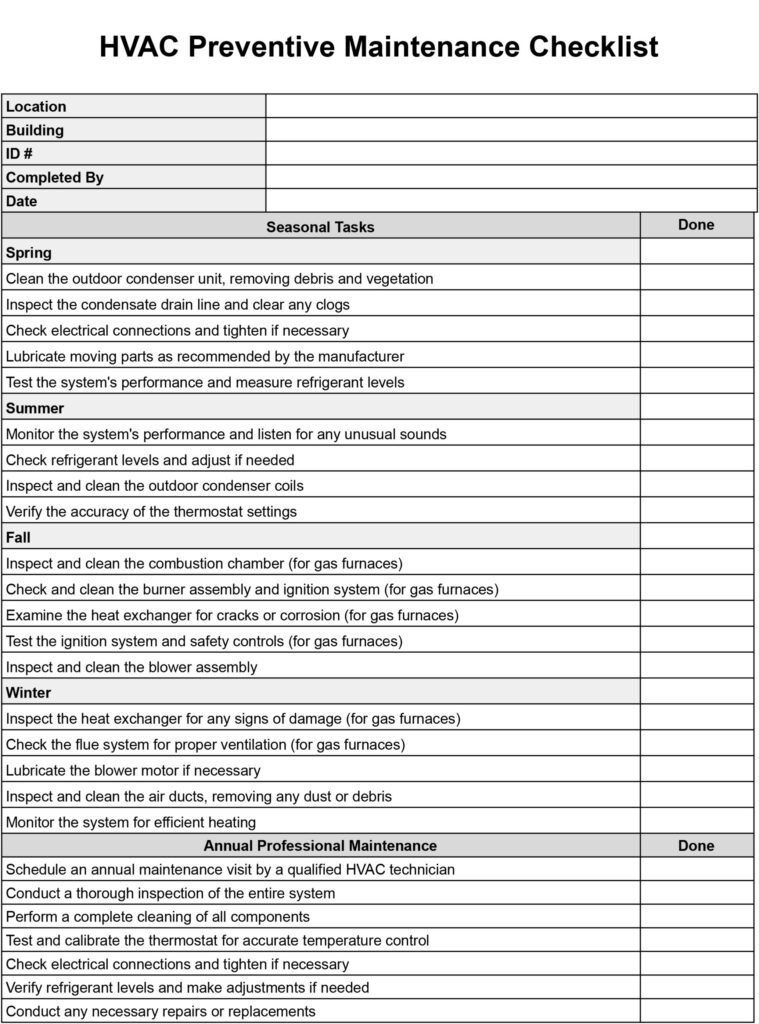
Maintenance and servicing of the AC unit
Regular maintenance and servicing of your AC unit are essential to preserve its cooling capacity and ensure optimal performance.
Effects on cooling capacity
Over time, dust and debris can accumulate in the AC unit’s condenser coils, evaporator coils, and air filters, reducing the efficiency of the cooling process. Regular maintenance helps ensure that these components are clean and functioning properly, allowing for maximum cooling capacity.
Regular maintenance tasks
Maintaining your AC unit involves regular tasks such as cleaning or replacing air filters, checking and cleaning condenser coils, inspecting refrigerant levels, and lubricating moving parts. These tasks should be performed as recommended by the manufacturer or by a professional HVAC technician.
Professional servicing recommendations
In addition to regular maintenance, it is recommended to schedule professional servicing of your AC unit once or twice a year. A professional servicing includes a thorough inspection of the unit, identifying any potential issues, and performing necessary repairs or adjustments. Professional servicing helps extend the lifespan of your AC unit and ensures that it operates at its full cooling capacity.
In conclusion, several factors affect the cooling capacity of an AC unit. Factors such as the BTU rating, insulation, climate, ceiling height, windows, heat-generating appliances, number of occupants, airflow, indoor air quality, and maintenance all play a crucial role in determining the cooling capacity needed for your space. By understanding and considering these factors, you can select the right AC unit size and optimize its performance to provide optimal cooling and comfort in your space.