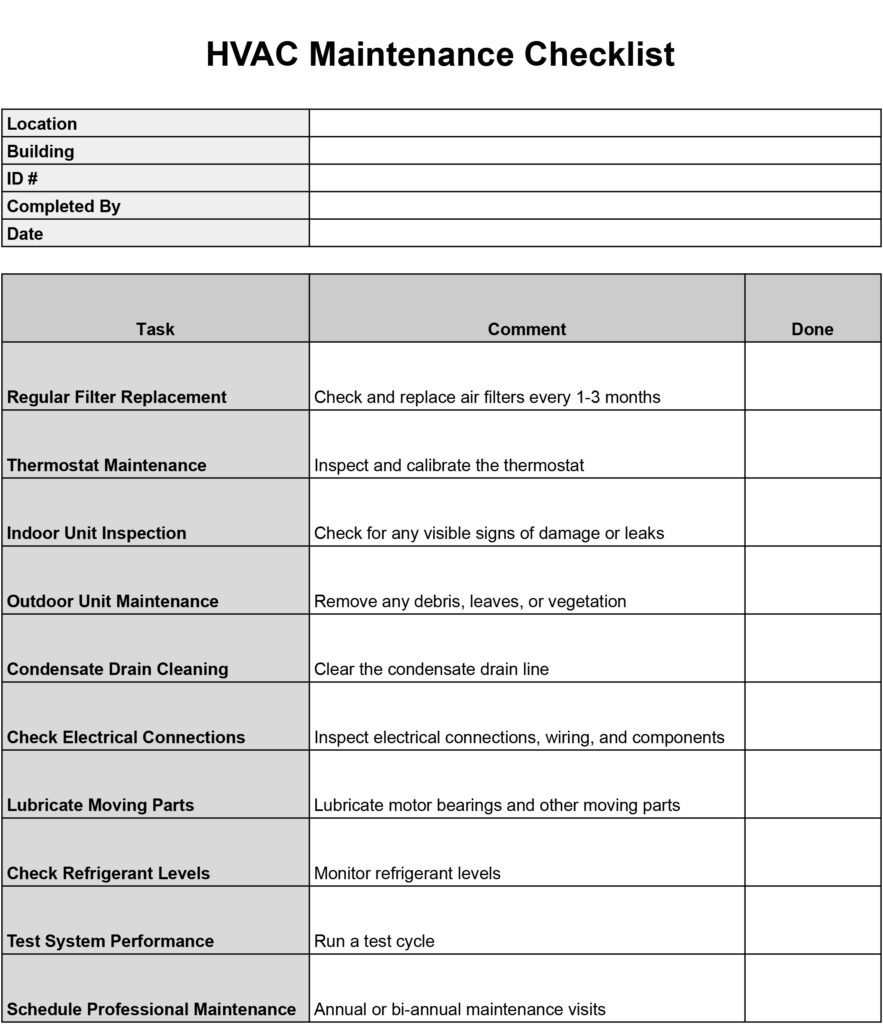
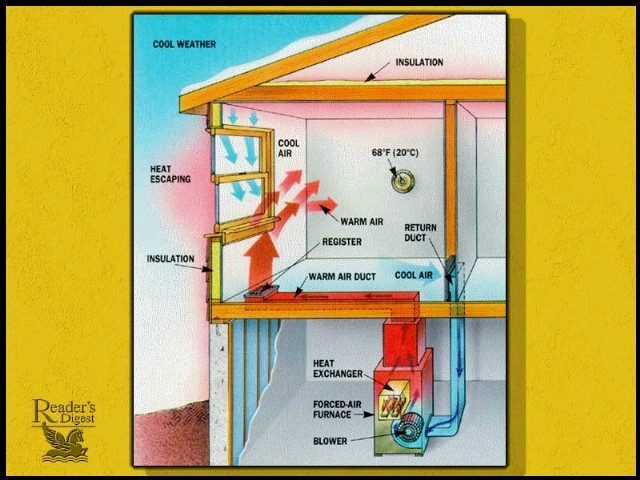
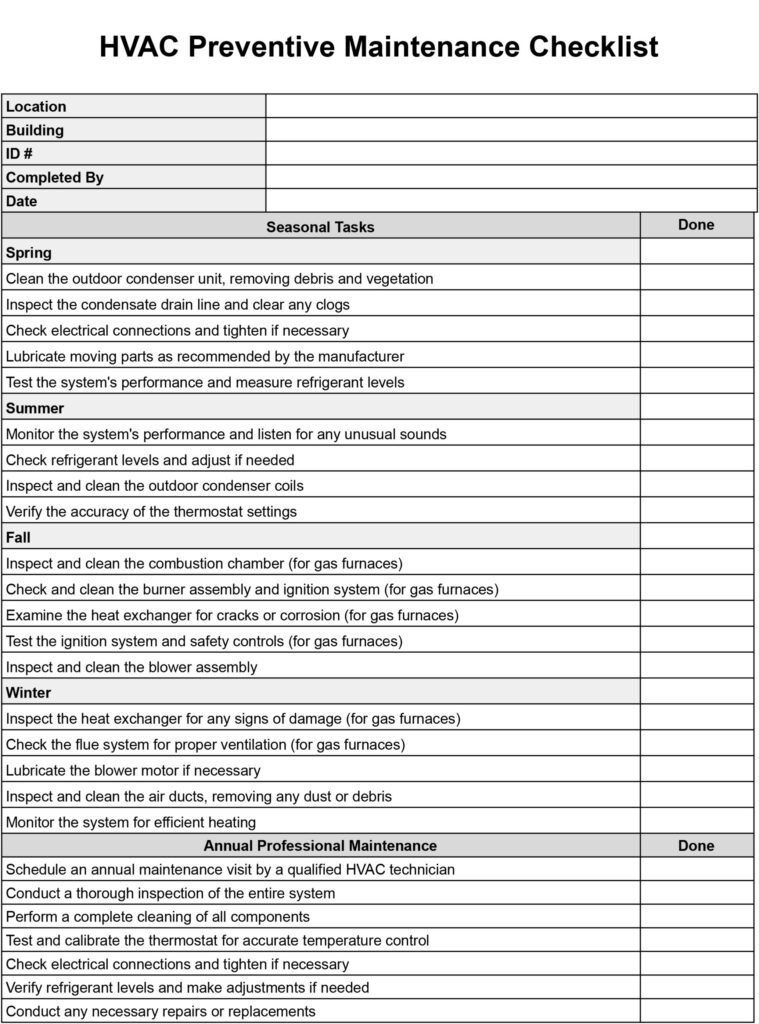
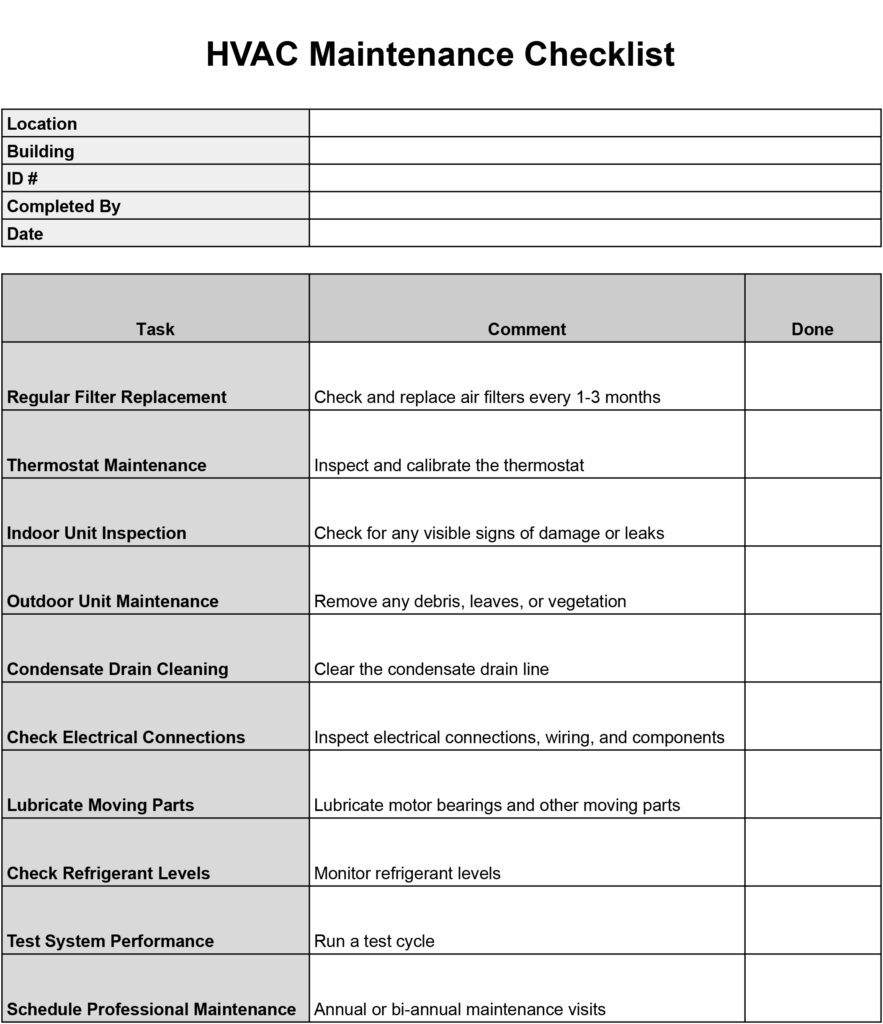
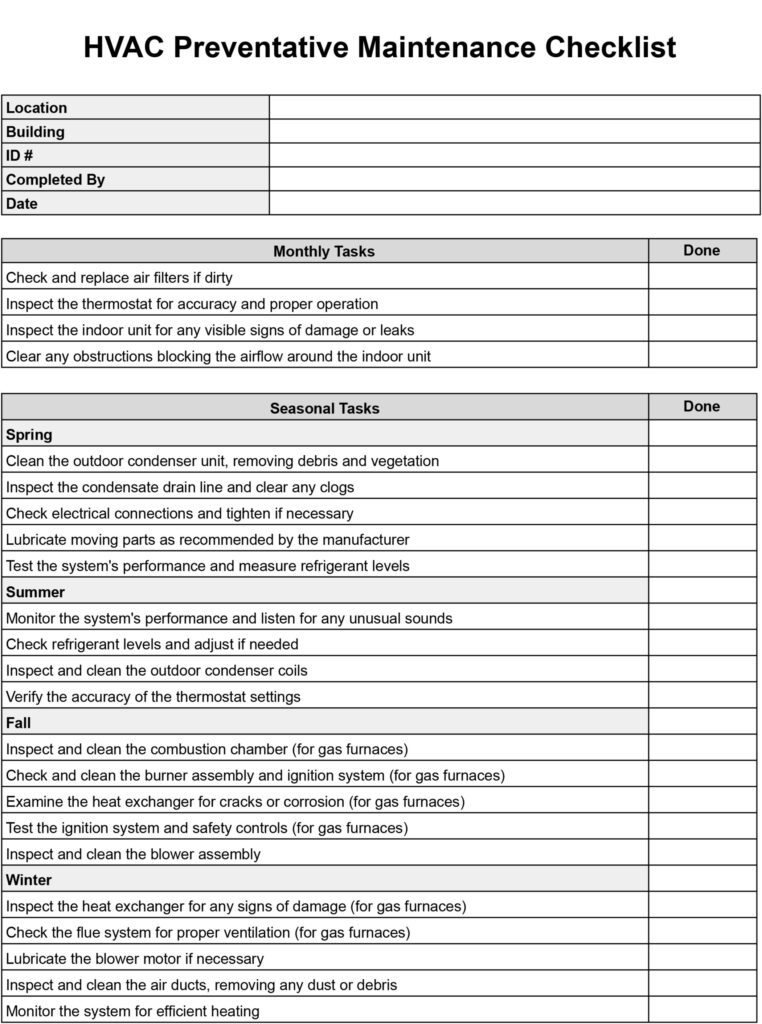
When conducting an HVAC inspection, it is crucial to have a comprehensive checklist that covers all the necessary parameters. From checking the air filters and ductwork to inspecting electrical connections and airflow, a well-designed HVAC inspection checklist ensures that all aspects of the system are thoroughly evaluated. By following a systematic approach and including key parameters in the checklist, you can ensure that your HVAC system is in optimal condition and operating efficiently.

1. Air Conditioning System
The air conditioning system is an essential component of any HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) system. It plays a crucial role in regulating the temperature and humidity of indoor spaces, ensuring comfort and maintaining indoor air quality. Understanding the different components of the air conditioning system is essential for effective maintenance and troubleshooting.
1.1. Thermostat
The thermostat is the control panel of the air conditioning system. It allows you to set the desired temperature and activate or deactivate the cooling function. During an inspection, it is important to ensure that the thermostat is calibrated correctly, responds accurately to temperature changes, and is free from any damage or malfunction.
1.2. Air Filter
The air filter is responsible for trapping dust, pollen, and other airborne particles, preventing them from entering the air conditioning system. Regularly inspecting and replacing the air filter is crucial for maintaining proper airflow and preventing the buildup of pollutants that can affect indoor air quality.
1.3. Evaporator Coil
The evaporator coil absorbs heat from indoor air, cooling it down in the process. Inspecting the evaporator coil involves checking for dust or debris accumulation, signs of corrosion, and ensuring proper airflow around the coil.
1.4. Condenser Coil
The condenser coil releases the heat absorbed by the evaporator coil to the outdoor air. During an inspection, it is important to check for any debris or dirt buildup on the condenser coil and ensure that it is clean and free from obstructions.
1.5. Refrigerant Level
The refrigerant is the substance responsible for absorbing and releasing heat in the air conditioning system. Inspecting the refrigerant level involves checking for any leaks, ensuring proper pressure, and replenishing the refrigerant if necessary.
1.6. Ductwork
The ductwork is responsible for distributing cooled air throughout the building. Inspecting the ductwork involves checking for any leaks, obstructions, or damage that may affect the airflow and efficiency of the air conditioning system.
1.7. Electrical Connections
Inspecting the electrical connections of the air conditioning system involves checking for any loose or damaged wires, ensuring proper grounding, and verifying that all connections are secure.
1.8. Capacitors
Capacitors are electrical components that store and release electrical energy. During an inspection, it is important to check the capacitors for any signs of damage or leakage, as faulty capacitors can affect the performance of the air conditioning system.
1.9. Compressor
The compressor is the heart of the air conditioning system. Inspecting the compressor involves checking for any signs of damage, leakage, or abnormal noises, ensuring proper lubrication, and verifying that the compressor is functioning efficiently.
1.10. Fan Motor
The fan motor is responsible for circulating the air within the air conditioning system. Inspecting the fan motor involves checking for any signs of damage, ensuring proper lubrication, and verifying that the fan motor is operating smoothly and quietly.
2. Heating System
The heating system is another important component of an HVAC system, providing warmth and comfort during colder months. Understanding the different elements of the heating system is crucial for maintaining efficient and safe operation.
2.1. Furnace
The furnace is the main heat-generating component of the heating system. Inspecting the furnace involves checking for any signs of damage or malfunction, ensuring proper ignition, and verifying that the furnace is operating within safe parameters.
2.2. Heat Exchanger
The heat exchanger is the part of the furnace that transfers heat from the combustion process to the air. Inspecting the heat exchanger involves checking for any cracks or damage, as a compromised heat exchanger can pose a safety hazard.
2.3. Ignition System
The ignition system is responsible for initiating the combustion process in the heating system. Inspecting the ignition system involves checking for proper ignition, ensuring that the pilot light or igniter is functioning correctly, and verifying that there are no issues with the ignition sequence.
2.4. Burner Assembly
The burner assembly is where the fuel is burned to generate heat. Inspecting the burner assembly involves checking for any signs of damage, ensuring proper ignition and flame quality, and verifying that there are no issues with combustion efficiency.
2.5. Combustion Air Supply
The combustion air supply is essential for the combustion process in the heating system. Inspecting the combustion air supply involves checking for any obstructions or blockages, ensuring that there is an adequate supply of fresh air, and verifying that there are no issues with the combustion air intake.
2.6. Gas/Oil Connections
Inspecting the gas or oil connections involves checking for any leaks, ensuring that the connections are secure, and verifying that there are no issues with the fuel supply.
2.7. Flue Pipe
The flue pipe is responsible for safely venting the combustion byproducts to the outside. Inspecting the flue pipe involves checking for any signs of damage or blockages, and ensuring proper venting of the combustion gases.
2.8. Ventilation System
The ventilation system is important for maintaining indoor air quality and removing stale air. Inspecting the ventilation system involves checking for any issues with the exhaust fans, ensuring proper ventilation rates, and verifying that there are no obstructions or blockages in the ventilation ducts.
2.9. Blower Motor
The blower motor is responsible for circulating the heated air within the heating system. Inspecting the blower motor involves checking for any signs of damage, ensuring proper lubrication, and verifying that the blower motor is operating efficiently.
2.10. Safety Controls
The safety controls in the heating system are designed to ensure safe operation and prevent any potential hazards. Inspecting the safety controls involves checking for any issues with the limit switches, pressure switches, or other safety devices, and verifying that they are functioning correctly.

3. Ventilation System
The ventilation system plays a crucial role in maintaining indoor air quality and ensuring proper airflow throughout the building. Inspecting the ventilation system is important for identifying any issues that may affect air exchange and ventilation.
3.1. Air Intake
The air intake is responsible for bringing fresh air into the building. Inspecting the air intake involves checking for any obstructions or blockages, ensuring that there is an adequate supply of fresh air, and verifying that there are no issues with the intake vents.
3.2. Air Exhaust
The air exhaust is responsible for removing stale air from the building. Inspecting the air exhaust involves checking for any signs of blockages or restrictions, ensuring proper venting of the exhaust air, and verifying that there are no issues with the exhaust vents.
3.3. Ductwork
The ductwork is responsible for distributing fresh air and removing stale air from different areas of the building. Inspecting the ductwork involves checking for any leaks or damage, ensuring proper insulation, and verifying that there are no restrictions or obstructions in the ducts.
3.4. Vents and Registers
The vents and registers are the points of entry and exit for the air in the ventilation system. Inspecting the vents and registers involves checking for any blockages or obstructions, ensuring proper airflow, and verifying that there are no issues with the airflow direction.
3.5. HRV/ERV Units
HRV (Heat Recovery Ventilation) and ERV (Energy Recovery Ventilation) units are designed to recover heat or energy from the exhaust air and transfer it to the fresh air entering the building. Inspecting the HRV/ERV units involves checking for proper operation, cleaning or replacing filters, ensuring proper air exchange rates, and verifying that there are no issues with the unit’s ventilation controls.
3.6. Air Filters
Air filters in the ventilation system are responsible for trapping dust, pollen, and other airborne particles. Inspecting the air filters involves checking for any signs of dirt or debris accumulation, ensuring that the filters are clean and free from obstructions, and verifying that they are the correct type and size for the ventilation system.
3.7. Fan Motor
The fan motor in the ventilation system is responsible for circulating the air. Inspecting the fan motor involves checking for any signs of damage or malfunction, ensuring proper lubrication, and verifying that the fan motor is operating efficiently.
3.8. Damper Controls
Damper controls in the ventilation system are used to control the airflow and redirect air to specific areas of the building. Inspecting the damper controls involves checking for any issues with the damper actuators or controls, ensuring proper operation, and verifying that there are no obstructions or restrictions in the damper mechanisms.
3.9. Balancing
Balancing the airflow in the ventilation system is essential for maintaining proper air exchange rates and ensuring comfort. Inspecting the balancing of the ventilation system involves checking for any areas of the building with inadequate airflow, adjusting the dampers or registers to achieve proper balancing, and verifying that the airflow is evenly distributed throughout the building.
3.10. Heating/Cooling Medium
In some cases, the ventilation system may be integrated with the heating or cooling system to provide additional temperature control. Inspecting the heating/cooling medium involves checking for any issues with the heat exchangers or cooling coils, ensuring proper heat transfer or cooling efficiency, and verifying that there are no leaks or malfunctions in the heating or cooling components.
4. Controls and Electrical System
The controls and electrical system of an HVAC system are responsible for regulating and controlling the various components of the system. Inspecting the controls and electrical system is important for ensuring safe and efficient operation.
4.1. Thermostat
The thermostat is the control panel of the HVAC system, allowing you to set the desired temperature and activate or deactivate the heating or cooling functions. Inspecting the thermostat involves checking for proper calibration, accurate temperature sensing, and verifying that all the functions are working correctly.
4.2. Electrical Connections
Inspecting the electrical connections involves checking for any loose or damaged wires, ensuring that all connections are secure, and verifying proper grounding of the electrical system.
4.3. Control Panel
The control panel is responsible for controlling and monitoring the different components of the HVAC system. Inspecting the control panel involves checking for any issues with the control relays, switches, or circuit boards, and verifying that the control panel is functioning correctly.
4.4. Wiring
Inspecting the wiring of the HVAC system involves checking for any signs of damage, ensuring proper insulation, and verifying that all the wiring is correctly connected and secured.
4.5. Safety Switches
Safety switches in the HVAC system are designed to protect against potential hazards or malfunctions. Inspecting the safety switches involves checking for proper operation, ensuring that the switches are not bypassed or malfunctioning, and verifying that all the safety features are functioning correctly.
4.6. Circuit Breakers/Fuses
Inspecting the circuit breakers or fuses involves checking for any signs of damage or malfunction, ensuring that the correct amperage is used, and verifying that the circuit breakers or fuses are correctly sized for the HVAC system.
4.7. Motor Starters/Contactors
Motor starters or contactors are responsible for controlling the operation of the motors in the HVAC system. Inspecting the motor starters or contactors involves checking for any signs of damage or malfunction, ensuring proper operation, and verifying that the motors are starting and stopping correctly.
4.8. Relays
Relays in the HVAC system are used to control the flow of electrical current to different components. Inspecting the relays involves checking for any signs of damage or malfunction, ensuring proper operation, and verifying that the relays are functioning correctly.
4.9. Transformers
Transformers in the HVAC system are responsible for stepping up or stepping down the voltage. Inspecting the transformers involves checking for any signs of damage or malfunction, ensuring proper voltage output, and verifying that the transformers are functioning correctly.
4.10. Grounding
Proper grounding of the HVAC system is essential for electrical safety. Inspecting the grounding involves checking for any issues with grounding connections, ensuring proper grounding of the electrical system, and verifying that all the grounding components are correctly installed and functional.

5. Overall System Performance
Inspecting the overall system performance of the HVAC system involves evaluating its efficiency, effectiveness, and comfort level. Several parameters need to be considered to assess the system’s performance.
5.1. Airflow
Airflow is a crucial component of the HVAC system. Inspecting the airflow involves checking for any restrictions or obstructions in the ductwork, ensuring proper duct sizing, and verifying that the air is being distributed evenly throughout the building.
5.2. Temperature Differential
The temperature differential refers to the difference between the supply air temperature and the return air temperature. Inspecting the temperature differential involves measuring the temperature at different points in the HVAC system, ensuring that it falls within the recommended range, and verifying that there are no issues with heat transfer or cooling efficiency.
5.3. Humidity Level
Maintaining the proper humidity level is important for comfort and indoor air quality. Inspecting the humidity level involves measuring the relative humidity in different areas of the building, ensuring that it falls within the recommended range, and verifying that the humidification or dehumidification components are functioning correctly.
5.4. Noise Level
Excessive noise from the HVAC system can be disruptive and indicate potential issues. Inspecting the noise level involves listening for any abnormal or excessive noises during operation, identifying the source of the noise, and verifying that there are no issues with the fan motors, compressors, or other components.
5.5. System Cycling
System cycling refers to the frequency and duration of the HVAC system’s operation. Inspecting the system cycling involves monitoring the on/off cycles of the system, ensuring that they are within the recommended range, and verifying that there are no issues with the thermostat, sensors, or other control components.
5.6. Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency is an essential aspect of HVAC systems, as it directly affects operational costs and environmental impact. Inspecting the energy efficiency involves evaluating the system’s energy consumption, comparing it to industry standards, and identifying any areas for improvement, such as insulation, control settings, or equipment upgrades.
5.7. Indoor Air Quality
Maintaining good indoor air quality is crucial for occupant health and comfort. Inspecting the indoor air quality involves evaluating air pollutants, such as dust, pollen, or volatile organic compounds (VOCs), measuring carbon dioxide levels, and verifying that the air filters, ventilation system, and other components are effectively removing or diluting contaminants.
5.8. Comfort Level
Comfort is a key factor in assessing the performance of an HVAC system. Inspecting the comfort level involves considering factors such as temperature, humidity, airflow, and noise, and evaluating whether the system provides consistent and comfortable conditions throughout the building.
5.9. System Capacity
The system capacity refers to the ability of the HVAC system to meet the heating or cooling demands of the building. Inspecting the system capacity involves evaluating the size of the system in relation to the building’s requirements, verifying that the equipment is correctly sized, and ensuring that there are no issues with undersizing or oversizing.
5.10. Air Balance
Air balance refers to the distribution of airflow throughout the building. Inspecting the air balance involves measuring airflow at different supply and return vents, ensuring that the air is evenly distributed, and verifying that there are no areas with inadequate or excessive airflow.
6. Safety and Compliance
Safety and compliance are paramount when it comes to HVAC systems. Inspecting safety and compliance involves checking for adherence to industry standards, codes, and regulations to ensure a safe and healthy environment.
6.1. Carbon Monoxide Detection
Carbon monoxide is a colorless and odorless gas that can be produced by combustion devices. Inspecting carbon monoxide detection involves checking for the presence of carbon monoxide detectors, ensuring that they are properly placed, and verifying that they are functioning correctly.
6.2. Combustion Analysis
Combustion analysis involves evaluating the combustion process in combustion-based heating systems. Inspecting the combustion analysis involves measuring combustion efficiency, checking for any issues with the burner assembly, heat exchanger, or other combustion components, and verifying that there are no signs of incomplete combustion or production of harmful byproducts.
6.3. Gas Leak Detection
Gas leak detection involves checking for any leaks in the gas piping or connections. Inspecting gas leak detection involves using gas detectors or other methods to identify the presence of gas leaks, ensuring that gas shut-off valves are properly installed and functioning correctly, and verifying that there are no signs of gas leaks.
6.4. Electrical Safety
Electrical safety is crucial for the safe operation of the HVAC system. Inspecting electrical safety involves checking for any exposed or damaged electrical wires, ensuring that electrical connections are properly insulated and grounded, and verifying that there are no signs of electrical hazards or malfunctions.
6.5. Ventilation Standards
Ventilation standards refer to the guidelines and regulations pertaining to air exchange rates and ventilation systems. Inspecting ventilation standards involves evaluating the ventilation system’s compliance with these standards, ensuring that the ventilation rates are appropriate for the building’s occupancy, and verifying that there are no issues with the air intake or exhaust systems.
6.6. Refrigerant Leak Detection
Refrigerant leak detection involves checking for any leaks in the refrigerant piping or connections. Inspecting refrigerant leak detection involves using refrigerant leak detectors or other methods to identify the presence of refrigerant leaks, ensuring that refrigerant lines are properly insulated and secured, and verifying that there are no signs of refrigerant leaks.
6.7. Indoor Air Quality Testing
Indoor air quality testing involves evaluating the levels of pollutants and contaminants in the indoor air. Inspecting indoor air quality involves conducting air quality tests, measuring parameters such as particulate matter, volatile organic compounds, and carbon dioxide levels, and verifying that the HVAC system is effectively removing or diluting contaminants.
6.8. Fire Safety
Fire safety is crucial for the safe operation of the HVAC system. Inspecting fire safety involves checking for the presence of fire dampers, ensuring that they are properly installed and functioning correctly, and verifying that there are no signs of fire hazards or potential ignition sources near the HVAC system.
6.9. Permit and Code Compliance
Permit and code compliance involves ensuring that the HVAC system meets the requirements set forth by local authorities and regulatory bodies. Inspecting permit and code compliance involves reviewing documentation, permits, and certifications, ensuring that the system installation or modifications were done in accordance with the applicable codes, and verifying that there are no outstanding compliance issues.
6.10. Documentation and Record-Keeping
Proper documentation and record-keeping are important for tracking system performance, maintenance, and compliance. Inspecting documentation and record-keeping involves reviewing maintenance records, inspection reports, and other relevant documentation, ensuring that all necessary records are up to date, and verifying that the HVAC system has been adequately documented for future reference.

7. Maintenance and Cleaning
Regular maintenance and cleaning are essential for ensuring the longevity, efficiency, and reliability of the HVAC system. Inspecting the maintenance and cleaning aspects involves evaluating the condition of various components and performing necessary tasks to keep the system in optimal working condition.
7.1. Cleaning Coils
Cleaning the coils involves removing any dirt, debris, or other accumulations that may affect heat transfer or cooling efficiency. Inspecting coil cleaning involves checking for any signs of dirt or debris buildup, ensuring that the coils are clean and free from obstructions, and verifying that the coil cleaning process is performed correctly and on a regular basis.
7.2. Lubricating Bearings
Lubricating bearings in the HVAC system ensures smooth and efficient operation of motorized components. Inspecting bearing lubrication involves checking for proper lubrication, ensuring that the correct lubricants are used, and verifying that the bearings are free from signs of wear or damage.
7.3. Tightening Electrical Connections
Ensuring that electrical connections are tight and secure is important for electrical safety and proper operation of the HVAC system. Inspecting the tightening of electrical connections involves checking for any loose or damaged wires, ensuring that all connections are properly secured, and verifying that the electrical connections are tightened to the manufacturer’s specifications.
7.4. Cleaning Drains
Cleaning the drains in the HVAC system ensures that condensate water can flow freely and prevent issues such as water leakage or mold growth. Inspecting drain cleaning involves checking for any signs of clogged or blocked drains, ensuring that the drains are clean and unrestricted, and verifying that the condensate removal system is functioning correctly.
7.5. Inspecting and Replacing Belts
Belts in the HVAC system are responsible for transmitting power to fans or other components. Inspecting and replacing belts involves checking for signs of wear or damage, ensuring proper tension, and verifying that the belts are correctly aligned and in good condition.
7.6. Cleaning and Adjusting Fan Blades
Cleaning and adjusting the fan blades ensure smooth and efficient airflow in the HVAC system. Inspecting fan blades involves checking for any signs of dirt or debris accumulation, ensuring that the blades are clean and free from obstructions, and verifying that the fan blades are correctly balanced and adjusted.
7.7. Cleaning Condensate Pump
Cleaning the condensate pump ensures proper operation and prevents water backups or failures. Inspecting the condensate pump involves checking for any signs of dirt or debris accumulation, ensuring that the pump is clean and free from obstructions, and verifying that the condensate pump is functioning correctly.
7.8. Cleaning Air Filters
Cleaning or replacing air filters ensures proper airflow and indoor air quality in the HVAC system. Inspecting air filters involves checking for signs of dirt or debris accumulation, ensuring that the filters are clean and free from obstructions, and verifying that the air filters are the correct type and size for the HVAC system.
7.9. Inspecting and Cleaning Ductwork
Inspecting and cleaning the ductwork helps maintain proper airflow and minimize the accumulation of dirt or contaminants. Inspecting and cleaning the ductwork involves checking for any signs of leaks, damage, or obstructions, ensuring that the ducts are clean and free from debris, and verifying that the ductwork is properly sealed and insulated.
7.10. Inspecting and Cleaning Vents and Registers
Inspecting and cleaning the vents and registers ensures proper airflow and prevents the buildup of dust or dirt. Inspecting and cleaning vents and registers involves checking for any signs of dirt or debris accumulation, ensuring that the vents and registers are clean and unrestricted, and verifying that the airflow direction is correct.
Regular maintenance and cleaning tasks should be performed according to the manufacturer’s recommendations and industry guidelines to ensure optimal HVAC system performance and longevity. Keeping a detailed maintenance and cleaning schedule, along with documentation of performed tasks, is crucial for effective system management and ongoing maintenance efforts.
In conclusion, a comprehensive HVAC inspection checklist covers various parameters and components of the air conditioning system, heating system, ventilation system, controls and electrical system, overall system performance, safety and compliance, and maintenance and cleaning. By thoroughly inspecting these aspects, HVAC professionals can identify any issues, perform necessary repairs or maintenance, and ensure the safe, efficient, and reliable operation of HVAC systems in residential, commercial, and industrial settings.