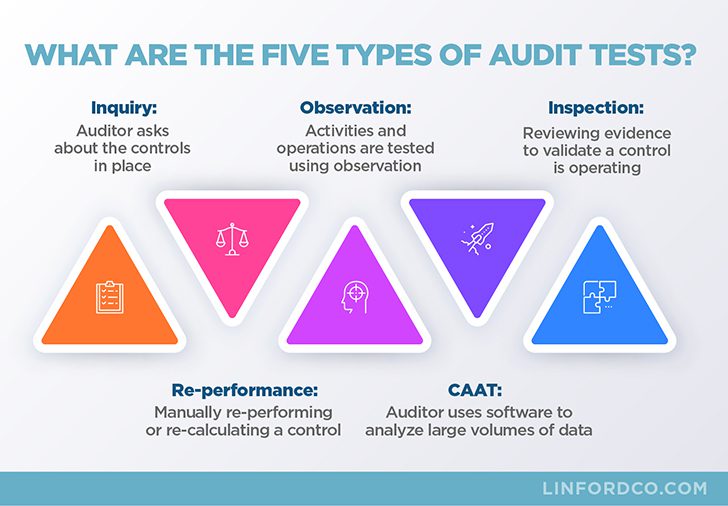
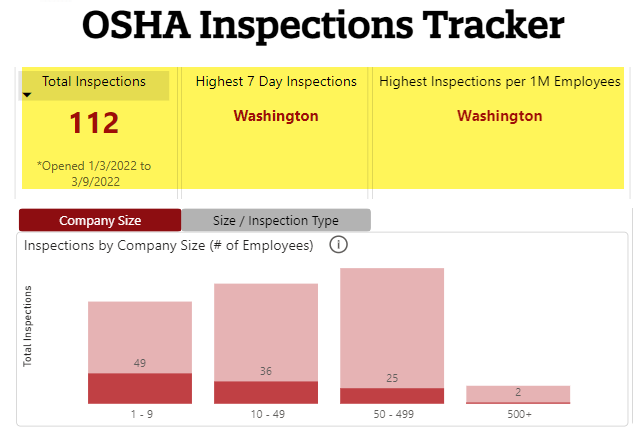
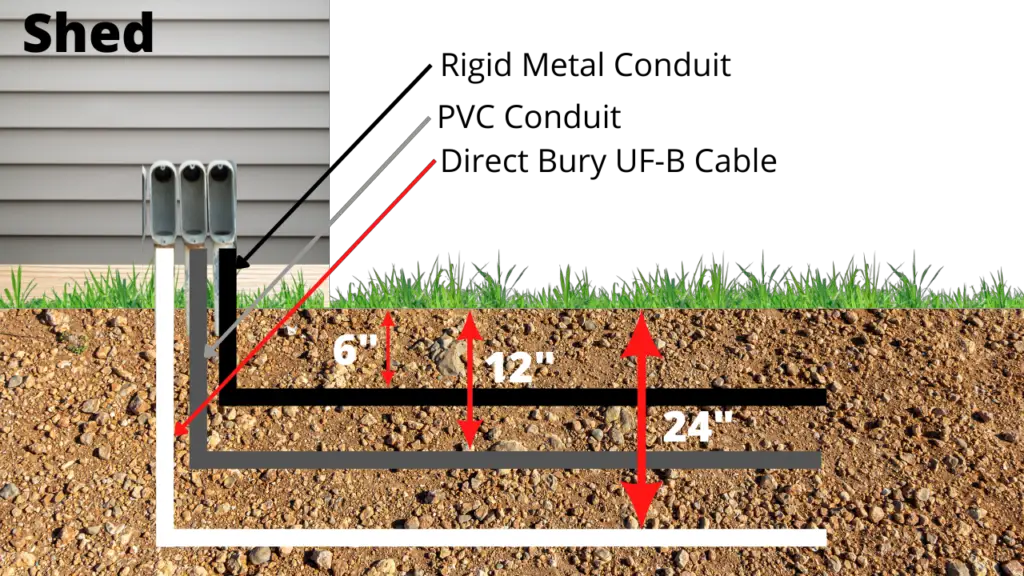
Are you curious about the various types of inspection? Wondering how they differ and what each entails? Look no further! This article will shed light on the five different types of inspection, providing you with a simple breakdown of each. From visual inspections to destructive testing, gain a better understanding of the purpose and procedures involved in these essential assessments. Let’s explore the world of inspections together!
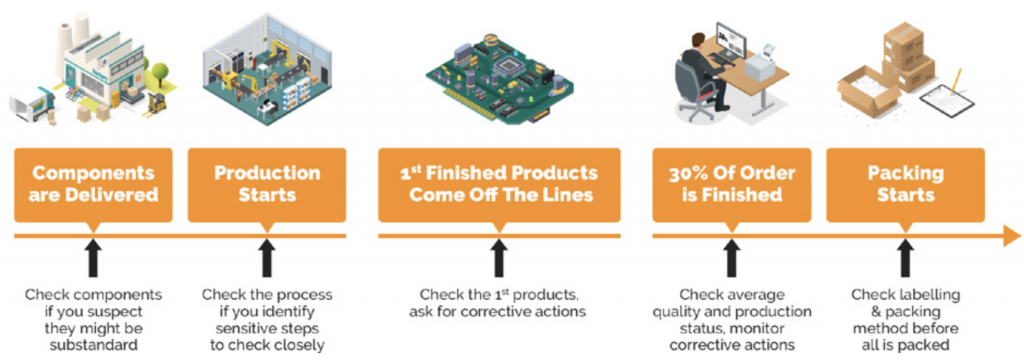

Visual Inspection
Definition of Visual Inspection
Visual inspection is a method of examining an object or system using the sense of sight. It involves a thorough examination of the physical appearance and condition of the subject to identify any defects, damages, or irregularities. This type of inspection is commonly used in various industries to assess the quality, functionality, and safety of a wide range of products, equipment, and infrastructure.
Purpose of Visual Inspection
The main purpose of visual inspection is to identify and evaluate any visible defects, damages, or abnormalities that may affect the performance, reliability, or safety of the subject. It plays a crucial role in ensuring quality control, preventing accidents or failures, and maintaining compliance with relevant regulations and standards. Visual inspection allows for early detection of potential issues, enabling timely repairs or corrective actions to be taken.
Methods Used in Visual Inspection
Visual inspection can be conducted through direct observation by trained inspectors or by using specialized equipment such as cameras, magnifying lenses, or illumination devices. It typically involves a systematic examination of the subject, looking for signs of wear and tear, corrosion, cracks, leaks, loose components, improper installation, or any other visual indications of damage or defects.
Advantages of Visual Inspection
Visual inspection offers several advantages over other inspection methods. Firstly, it is a relatively simple and cost-effective technique that does not require extensive training or specialized equipment. Additionally, visual inspection allows for immediate detection of visible defects, enabling timely interventions to prevent further damage or failures. Furthermore, it can be performed in real-time, allowing for quick assessment and decision-making.
Considerations for Visual Inspection
While visual inspection is a valuable tool, there are certain considerations that need to be taken into account. Factors such as lighting conditions, angles of observation, and the complexity of the subject may affect the accuracy and reliability of the inspection. It is important to ensure that inspectors are adequately trained and experienced in recognizing visual indicators of defects or abnormalities. In some cases, supplementary non-destructive testing methods may be necessary to complement visual inspection and provide a more comprehensive assessment.

Non-Destructive Testing
Definition of Non-Destructive Testing
Non-destructive testing (NDT) is a technique used to evaluate the properties, condition, or integrity of a material, component, or system without causing any permanent alteration or damage. It involves the use of various methods and instruments to detect and analyze potential defects, flaws, or discontinuities that may compromise the performance, reliability, or safety of the subject.
Common Techniques in Non-Destructive Testing
There are several commonly used techniques in non-destructive testing, including ultrasonic testing, magnetic particle testing, liquid penetrant testing, radiographic testing, eddy current testing, and visual inspection. Each technique has its own advantages, limitations, and areas of application. Ultrasonic testing, for example, uses high-frequency sound waves to detect internal flaws or inconsistencies in materials. Magnetic particle testing, on the other hand, uses magnetic fields and fine iron particles to identify surface cracks or defects.
Applications of Non-Destructive Testing
Non-destructive testing is widely used in various industries, including manufacturing, aerospace, automotive, construction, and energy. It is used to assess the quality and integrity of materials, components, and structures during the manufacturing process, assembly, maintenance, or inspection. NDT techniques are particularly valuable in industries where safety, reliability, and performance are critical, such as in the aerospace and nuclear sectors.
Benefits of Non-Destructive Testing
Non-destructive testing offers several benefits over destructive testing methods. Firstly, it allows for the evaluation and assessment of the subject without causing any permanent damage, minimizing the need for costly repairs or replacements. Additionally, NDT techniques can be performed relatively quickly and provide real-time results, allowing for immediate decision-making and problem-solving. Furthermore, non-destructive testing is non-intrusive, making it suitable for testing sensitive or delicate materials or components.
Limitations of Non-Destructive Testing
While non-destructive testing is a valuable tool, it is not without limitations. Certain types of defects or abnormalities may be difficult to detect using NDT techniques, particularly if they are located deep within the subject or if the material has complex geometry. Additionally, non-destructive testing requires skilled technicians who are trained in the specific techniques and interpretation of results. Furthermore, some NDT methods may be labor-intensive or require specialized equipment, which can increase the cost and time required for inspection.


Dimensional Inspection
Definition of Dimensional Inspection
Dimensional inspection involves the measurement and assessment of the physical dimensions, geometry, and tolerances of a product, component, or structure. It is used to verify that the subject conforms to the specified dimensional requirements and ensure its functionality, performance, and compatibility. Dimensional inspection is particularly important in industries where precise measurements are critical, such as manufacturing, engineering, and construction.
Methods Used in Dimensional Inspection
A variety of methods and instruments are used in dimensional inspection, depending on the complexity and size of the subject. Common techniques include coordinate measuring machines (CMM), laser scanning, optical measurement systems, and hand tools such as calipers or micrometers. These methods allow for accurate measurements of lengths, angles, diameters, shapes, and other dimensional parameters, providing objective data for comparison with design specifications.
Importance of Dimensional Inspection
Dimensional inspection plays a key role in ensuring the quality, functionality, and safety of products or structures. By verifying that the dimensions and tolerances meet the required standards, it helps prevent issues such as poor fit, misalignment, interference, or inadequate performance. Dimensional inspection is crucial in industries where precise dimensional specifications are critical, such as aerospace, automotive, or medical device manufacturing.
Applications of Dimensional Inspection
Dimensional inspection is applied in various contexts, ranging from small components to large structures. It is commonly used in manufacturing processes to ensure that parts are within the required tolerances and can be assembled correctly. In engineering or construction projects, dimensional inspection is used to verify that the dimensions of structures or components are accurate and comply with design specifications. It is also employed in quality control processes to assess the conformity of finished products.
Challenges in Dimensional Inspection
Dimensional inspection can present certain challenges, particularly when dealing with complex or large-scale subjects. Factors such as environmental conditions, material properties, or the presence of surface finishes may affect the accuracy and reliability of measurements. Additionally, the selection and calibration of measurement instruments and techniques are critical for achieving accurate and repeatable results. Proper training and experience of inspectors are also essential to ensure consistent and reliable dimensional inspection.