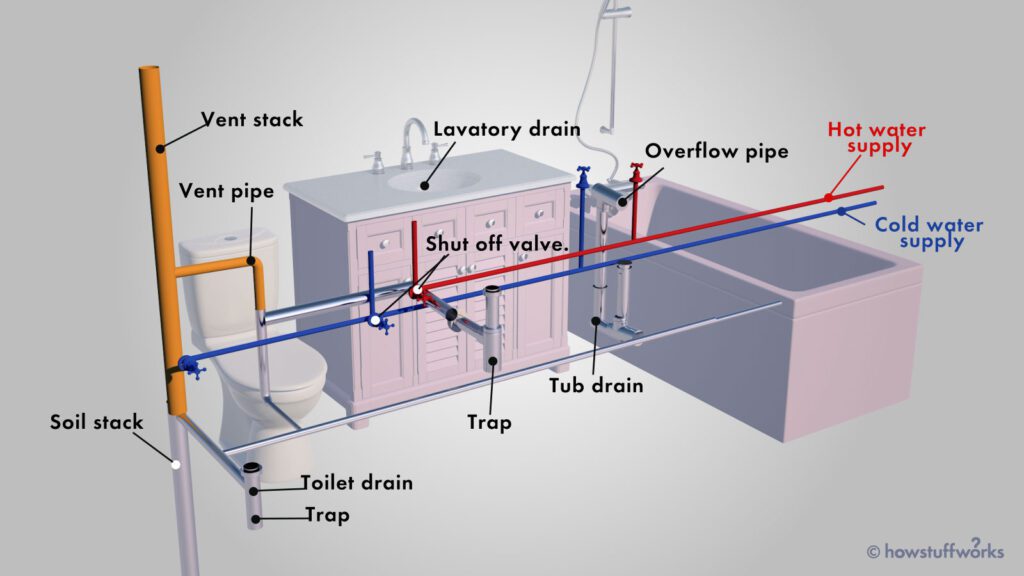
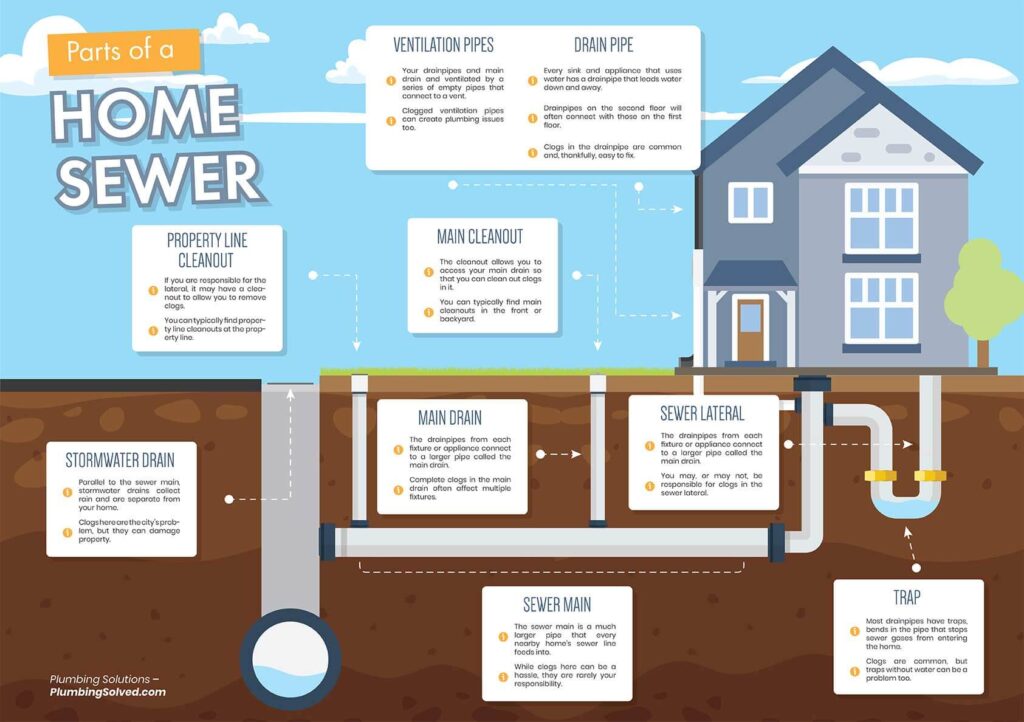
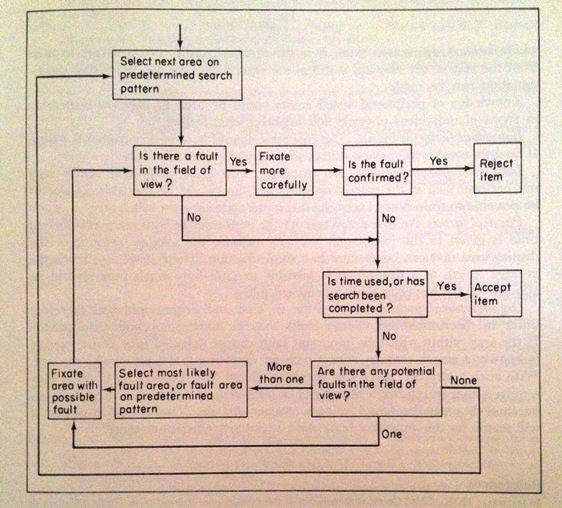
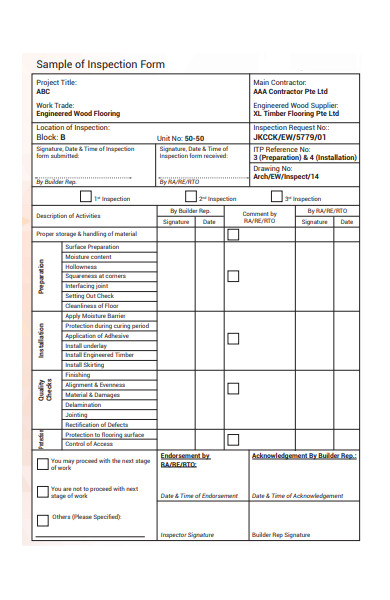
In this article, you will discover the four essential types of inspection that play a crucial role in various industries. From initial visual checks to comprehensive quality assessments, these four distinct inspection methods ensure that products and processes meet the highest standards. So, let’s explore the different types of inspection and their significance in maintaining quality and reliability.


Visual Inspection
Definition and Purpose
Visual inspection is a type of inspection that relies on the human eye to visually examine and assess the condition and quality of an object or system. It is a widely used inspection method due to its simplicity and cost-effectiveness. The purpose of visual inspection is to identify any visible defects, irregularities, or anomalies that may affect the performance, safety, or functionality of the object or system being inspected.
Methods and Techniques
In visual inspection, the inspector carefully observes and analyzes the surface, structure, components, or parts of the object or system. The inspection can be conducted at different stages, such as during manufacturing, assembly, or maintenance. The inspector looks for various signs of damage, wear and tear, corrosion, cracks, leaks, or any other indications of potential issues. The use of magnifying lenses, cameras, or remote inspection devices can also enhance the effectiveness of visual inspection.
Equipment and Tools
The primary tool for visual inspection is the human eye, although additional tools can be utilized to improve the accuracy and efficiency of the inspection. These tools may include magnifying glasses, binoculars, digital cameras, or specialized instruments designed for specific industries or applications. Lighting sources, such as flashlights or spotlights, are also essential to ensure proper visibility during the inspection process.
Advantages
Visual inspection offers several advantages. Firstly, it is a non-intrusive inspection method that does not require the object or system to be disassembled or damaged in any way. This makes it suitable for inspecting delicate or sensitive components without risking further damage. Secondly, visual inspection can be performed quickly and does not require sophisticated equipment or extensive training. It is a cost-effective method that can be easily incorporated into routine inspections or quality control processes. Lastly, visual inspection provides immediate feedback, allowing for prompt decision-making or intervention if any defects or issues are identified.
Limitations
While visual inspection is a valuable inspection method, it does have some limitations. The effectiveness of visual inspection heavily relies on the inspector’s expertise, experience, and attentiveness. Human error and subjectivity can affect the accuracy and reliability of the inspection results. Additionally, visual inspection may not detect defects or anomalies that are not easily visible or require more specialized testing methods. It is important to consider these limitations and complement visual inspection with other testing techniques when necessary for a comprehensive assessment.


Non-Destructive Testing (NDT)
Definition and Purpose
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) is a wide range of inspection techniques that enable the evaluation of the structural integrity, quality, and performance of an object or system without causing any damage to the tested material or component. The purpose of NDT is to identify and assess any defects, flaws, or irregularities that could compromise safety, functionality, or reliability.
Methods and Techniques
NDT encompasses various methods and techniques depending on the type of material or component being tested. Common NDT methods include ultrasonic testing, radiographic testing, magnetic particle testing, eddy current testing, and liquid penetrant testing. Each method uses different physical principles to inspect and analyze the properties and characteristics of the material or component. NDT techniques can be applied to different stages, such as during manufacturing, assembly, maintenance, or repair.
Equipment and Tools
Non-Destructive Testing requires specialized equipment and tools specific to each testing method. Ultrasonic testing, for example, uses ultrasonic transducers and receivers to emit and detect sound waves. Radiographic testing involves X-ray machines or gamma ray sources along with imaging equipment to capture radiographic images. Magnetic particle testing uses magnetic fields and magnetic particles to detect defects, while eddy current testing utilizes electromagnetic induction. The appropriate equipment and tools are selected based on the testing requirements and the material or component being inspected.
Advantages
NDT offers several advantages as an inspection method. Firstly, it allows for the evaluation of an object or system without causing any damage, making it particularly suitable for critical components or structures. NDT can detect both surface and subsurface defects, ensuring a comprehensive assessment. Secondly, NDT techniques can be highly sensitive and provide precise measurements, enabling accurate identification and characterization of defects. Additionally, NDT is versatile and can be applied to various materials, including metals, composites, ceramics, or even concrete.
Limitations
Despite its many advantages, Non-Destructive Testing does have some limitations. Depending on the specific NDT method, certain factors such as material composition, thickness, or geometry may affect the effectiveness of the inspection. NDT techniques often require skilled and trained personnel to ensure accurate interpretation of test results. Furthermore, NDT can be time-consuming and more costly compared to visual inspection. It is crucial to carefully choose the appropriate NDT method and consider potential limitations specific to each application or industry to ensure a reliable inspection.

Dimensional Inspection
Definition and Purpose
Dimensional inspection focuses on assessing the physical dimensions, geometrical features, or tolerances of an object or component to ensure it meets the specified requirements. The purpose of dimensional inspection is to verify that the object or component conforms to the desired measurements, ensuring proper fit, form, and functionality.
Methods and Techniques
Dimensional inspection can be performed using various methods and techniques, depending on the complexity and accuracy requirements. Common techniques include coordinate measuring machines (CMM), laser scanning, optical measurement, or manual measuring tools such as calipers, micrometers, or gauges. These methods allow for precise measurements of lengths, diameters, angles, surface profiles, or other dimensional parameters.
Equipment and Tools
The equipment and tools employed in dimensional inspection depend on the chosen measurement technique. Coordinate measuring machines consist of a moving probe or sensor that collects measurement data, along with a computer system for analysis and reporting. Laser scanners capture 3D data by projecting laser lines or dots onto the object and recording their reflection. Optical measurement systems utilize cameras and advanced algorithms to record and analyze images of the object. Manual measuring tools, such as calipers or gauges, are used for simple and quick measurements.
Advantages
Dimensional inspection provides various advantages, ensuring the quality and conformity of an object or component. Accurate measurements help identify any dimensional variations or deviations from the desired specifications. By verifying tolerances and dimensions, dimensional inspection ensures that parts fit together correctly, minimizing assembly issues and potential defects. It also enables the detection of manufacturing errors, such as incorrect setups or machine malfunctions, allowing for timely corrective actions. Moreover, dimensional inspection can aid in quality control, contributing to the overall product reliability and customer satisfaction.
Limitations
Dimensional inspection does have certain limitations that need to be considered. The accuracy and reliability of measurements are highly dependent on the chosen measurement technique and the skill of the operator. Complex geometries or objects with intricate features may pose challenges for accurate dimensional inspection. Additionally, dimensional inspection alone may not provide a complete assessment of a component’s performance or integrity. It is important to integrate dimensional inspection with other inspection methods, such as NDT or functional testing, for comprehensive evaluation.

Functional Inspection
Definition and Purpose
Functional inspection focuses on evaluating the performance, functionality, or operational capabilities of an object or system. It aims to verify whether the object or system functions as intended, meets specified requirements, and performs the desired tasks effectively.
Methods and Techniques
Functional inspection involves simulating real-life conditions or scenarios to assess the performance and capabilities of the object or system. It may require the object or system to be operated, tested, or subjected to specific loads, pressures, temperatures, or other environmental conditions. Functional testing can be performed using manual procedures, automated testing equipment, or specialized test setups, depending on the complexity of the object or system being inspected.
Equipment and Tools
The equipment and tools used in functional inspection depend on the specific requirements of the testing. They may range from simple manual controls, switches, or gauges to more advanced instrumentation, data acquisition systems, or custom-designed test rigs. Functional inspection often involves the use of sensors, actuators, electronic or mechanical components, and testing software for accurate data collection and analysis.
Advantages
Functional inspection offers several advantages in assessing the performance and functionality of an object or system. By subjecting the object or system to realistic operating conditions, functional inspection provides a comprehensive evaluation of its capabilities and limitations. It allows for the detection of functional defects, malfunctions, or inconsistent performance that may not be apparent through visual or dimensional inspection alone. Functional inspection ensures that the object or system meets the required specifications and performs its intended tasks efficiently and reliably.
Limitations
Functional inspection does have some limitations that should be taken into account. Replicating the exact conditions of operation or simulating all possible scenarios may be challenging and time-consuming. Testing complex systems may require substantial planning and coordination to ensure accurate and meaningful results. Additionally, functional inspection may not detect hidden or dormant defects that only manifest under certain conditions or during extended operation. It is essential to consider the limitations and potential risks when designing and executing functional inspections for critical or safety-critical systems.