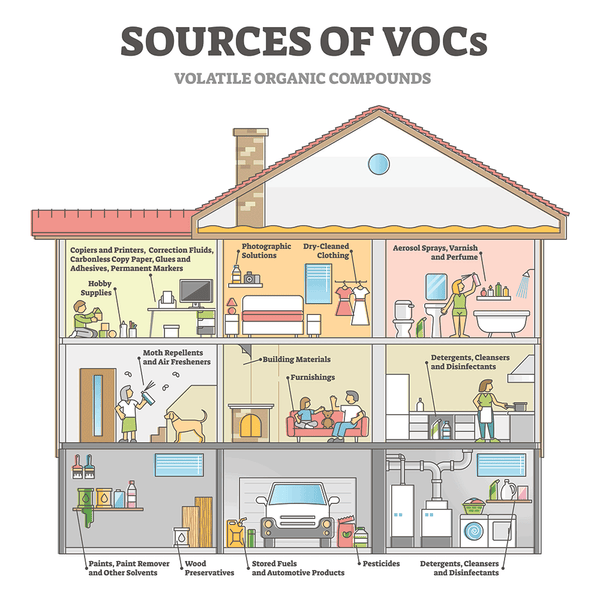
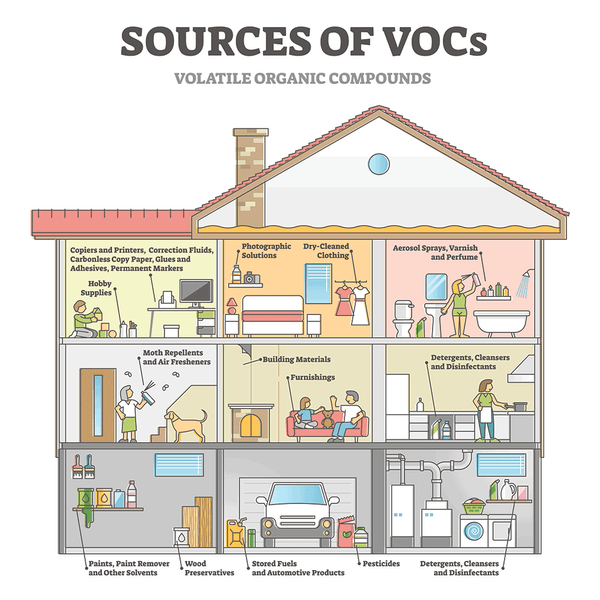
Have you ever wondered what could be the reason behind the presence of high VOC levels in your home? VOCs, or volatile organic compounds, are invisible chemicals that can be released into the air from various sources within your house. These compounds can have a significant impact on your indoor air quality and overall health. In this article, we will explore some common culprits that contribute to high VOC levels in homes, helping you understand and address this potentially harmful issue.

Overview
Volatile Organic Compounds, commonly known as VOCs, refer to a group of carbon-based chemicals that easily evaporate at room temperature. They can be found in many everyday household items, such as building materials, cleaning products, furnishings, and air fresheners. VOCs can also be released during common indoor activities like cooking, smoking, and using certain personal care products. Poor ventilation and a lack of proper air circulation can further contribute to high VOC levels in homes. New construction and renovation activities can also release VOCs, posing health risks to occupants. High levels of VOCs can cause a range of health effects, from respiratory problems to headaches and increased risk of certain cancers. It is important to be aware of these sources and take steps to prevent and reduce VOC levels in our homes. In this article, we will explore the various sources of VOCs, the health effects they can have, and methods for testing and reducing VOC levels.
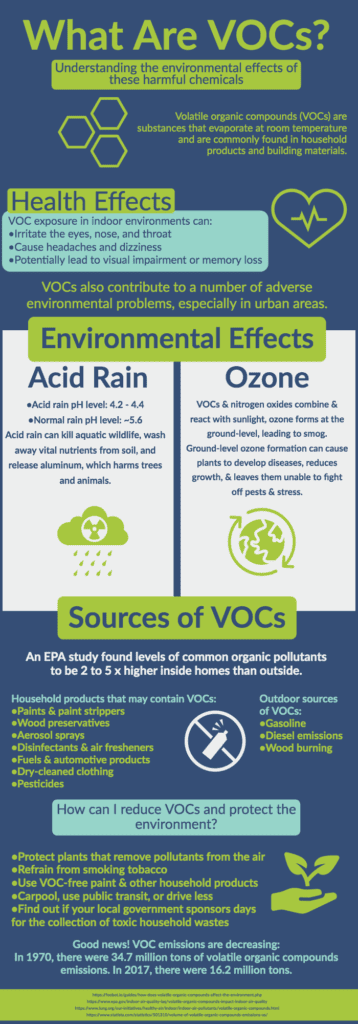
Sources of VOC
Building Materials
Many building materials used in homes, such as plywood, particleboard, and laminate flooring, contain formaldehyde, a common VOC. Other materials, such as insulation, carpet, and adhesives, can also release VOCs. The off-gassing of these materials can contribute to high VOC levels indoors, especially in newly constructed or renovated homes.
Cleaning Products
Cleaning products, including household cleaners, disinfectants, and laundry detergents, often contain VOCs. These chemicals can be released into the air during use and can linger even after cleaning is complete. Common VOCs found in cleaning products include benzene, toluene, ethanol, and formaldehyde.
Paints and Coatings
Traditional paints and coatings contain high levels of VOCs, mainly in the form of solvents. These solvents help the paint spread smoothly and then evaporate as the paint dries. However, they can release harmful VOCs into the air, contributing to poor indoor air quality. Low VOC or zero VOC paints and coatings are available as an alternative.
Furnishings and Upholstery
Furnishings and upholstery made from materials like foam, fabric, and synthetic materials can emit VOCs, particularly when they are new. These VOCs, often from flame retardants or formaldehyde-based adhesives, may be released into the air and contribute to high levels of indoor pollution. Choosing furniture and upholstery made from natural or organic materials can help reduce VOC emissions.
Air Fresheners
While air fresheners are designed to make our homes smell pleasant, many of them contain high levels of VOCs. These VOCs are often released in the form of fragrance compounds, such as limonene and formaldehyde. Air fresheners can contribute to poor indoor air quality and should be used sparingly, if at all. Natural alternatives like essential oils or open windows for fresh air are preferable.
Personal Care Products
Many personal care products we use daily, such as perfumes, hairsprays, deodorants, and nail polish removers, contain VOCs. These VOCs can be released into the air, especially in poorly ventilated spaces like bathrooms. Choosing personal care products with low VOC content or opting for natural alternatives can help reduce VOC exposure.
Pesticides and Insecticides
Pesticides and insecticides used inside the home, such as bug sprays, mothballs, and rodent repellents, can contain high levels of VOCs. These chemicals are designed to kill or repel pests, but they can also contribute to poor indoor air quality. It is important to use these products sparingly, according to the manufacturer’s instructions, and to ensure proper ventilation when applying them.


Indoor Activities
Cooking
Cooking, especially when using gas stoves and ovens, can release VOCs into the air. The burning of natural gas can produce nitrogen dioxide and formaldehyde, both of which are harmful VOCs. Proper ventilation, such as using exhaust fans and opening windows, can help remove the pollutants generated during cooking.
Smoking
It is well known that smoking cigarettes indoors is harmful to both the smoker and non-smokers. Cigarette smoke contains thousands of chemicals, including a significant amount of VOCs. These VOCs can accumulate indoors and linger in the air long after smoking has ceased, posing health risks to occupants. It is important to establish a smoke-free environment indoors to reduce VOC exposure.
Using Solvent-based Products
Using solvent-based products, such as adhesives, glue, and paint thinners, indoors can release high levels of VOCs into the air. These products are often used for DIY projects or repairs but can contribute to poor indoor air quality if not used in a well-ventilated area. It is important to use these products sparingly and in a well-ventilated space, or consider switching to low VOC or solvent-free alternatives.
Using Personal Care Products
As mentioned earlier, personal care products like perfumes, hairsprays, and nail polish removers can release VOCs into the air. Applying these products in a poorly ventilated space, such as a small bathroom, can lead to higher VOC concentrations. It is recommended to use these products in well-ventilated areas or switch to low VOC options.
Dry Cleaning Clothes Indoors
Bringing dry-cleaned clothes or items into the home can introduce VOCs into the indoor environment. Dry cleaning chemicals like perchloroethylene, commonly known as perc, can evaporate from the clothes and contribute to indoor air pollution. It is advisable to air out dry-cleaned items outdoors before bringing them indoors or opt for alternative cleaning methods.
Poor Ventilation
Inadequate Ventilation Systems
Homes with inadequate ventilation systems can have a higher risk of indoor air pollution. Without proper airflow and ventilation, VOCs can accumulate indoors and lead to increased exposure. It is important to have a well-designed ventilation system that helps remove indoor pollutants and brings in fresh outdoor air.
Closed Windows and Doors
Keeping windows and doors closed for extended periods, especially in airtight homes, can trap VOCs indoors. Without proper ventilation, VOCs released from various sources can accumulate and contribute to poor indoor air quality. Opening windows and doors periodically, especially when the outdoor air is clean, can help remove VOCs and refresh the indoor environment.
Improper Use of HVAC Systems
Improper use of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems can also contribute to high VOC levels indoors. Closing off vents or not properly maintaining HVAC systems can result in poor air circulation and an accumulation of VOCs. It is important to ensure that HVAC systems are clean, well-maintained, and used properly to prevent the build-up of indoor pollutants.

New Construction and Renovation
Off-gassing of New Furniture and Materials
When new furniture, flooring, or other building materials are brought into a home, they can release VOCs through a process known as off-gassing. Off-gassing occurs when VOC-containing materials slowly release chemicals into the air over time. This can be a significant source of VOCs in newly constructed or renovated homes. Allowing new items to off-gas in well-ventilated areas or opting for low VOC or natural alternatives can help reduce exposure.
Freshly Painted Walls and Surfaces
The strong smell often associated with freshly painted walls is a result of the release of VOCs. Traditional paints contain solvents that evaporate as the paint dries, releasing VOCs into the air. Proper ventilation and choosing low VOC or zero VOC paints can help minimize the levels of VOCs during and after painting.
Renovation and Remodeling Activities
Any renovation or remodeling activities that involve the use of construction materials, paints, adhesives, or other chemicals can release high levels of VOCs. These activities can lead to a sudden increase in VOC levels and should be carried out in a well-ventilated space. It is important to minimize exposure by using low VOC materials whenever possible and ensuring proper ventilation during and after the renovation process.
Health Effects of High VOC Levels
Exposure to high levels of VOCs can have various adverse health effects. Some common health effects associated with high VOC levels include:
Irritation of Respiratory System
VOCs can irritate the respiratory system, leading to symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. Individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions, such as asthma or bronchitis, may experience exacerbated symptoms when exposed to high levels of VOCs.
Headaches and Dizziness
Inhaling high levels of VOCs can cause headaches, dizziness, and lightheadedness. These symptoms can be particularly noticeable upon entering a space with high VOC concentrations or after prolonged exposure to VOC-emitting sources.
Eye and Nose Irritation
VOCs can also cause eye and nose irritation, leading to redness, itching, watering eyes, and a runny or stuffy nose. These symptoms can occur immediately upon exposure to VOCs or develop gradually over time.
Allergies and Asthma
For individuals with allergies or asthma, high levels of VOCs can trigger or worsen symptoms. VOCs can act as respiratory irritants and exacerbate allergic reactions or asthma attacks.
Increased Risk of Cancer
Some VOCs, such as benzene and formaldehyde, have been classified as carcinogens by reputable organizations like the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). Prolonged exposure to high levels of these VOCs may increase the risk of developing certain types of cancer, including lung, liver, and bladder cancer.

Testing for VOC Levels
To determine the levels of VOCs in your home, there are several testing options available:
VOC Monitoring Devices
VOC monitoring devices, such as indoor air quality monitors, can provide real-time measurements of VOC levels in your home. These devices typically use sensors to detect and measure the concentration of various VOCs in the air. Some models also provide additional information about temperature, humidity, and particulate matter.
Professional Indoor Air Quality Testing
Hiring a professional indoor air quality testing service can provide a more comprehensive assessment of VOC levels and other indoor pollutants. These professionals use specialized equipment and techniques to collect air samples and analyze them in a laboratory. They can provide detailed reports and recommendations based on the findings.
Home VOC Test Kits
There are also DIY home VOC test kits available for purchase. These kits typically come with sampling materials and instructions on how to collect air samples. The samples can then be sent to a laboratory for analysis, and the results are typically provided along with recommendations on how to address any detected VOC issues.
Preventing and Reducing VOC in Homes
There are several steps you can take to prevent and reduce VOC levels in your home:
Choose Low VOC Products
When purchasing building materials, furnishings, cleaning products, or personal care products, look for those labeled as low VOC or zero VOC. These products have lower levels of harmful chemicals and can help reduce indoor VOC concentrations.
Proper Ventilation
Ensuring proper ventilation in your home is crucial for maintaining good indoor air quality. Open windows and doors when weather permits, use exhaust fans in areas prone to high VOC emissions, and consider installing a ventilation system if necessary. Regularly ventilating your home can help remove VOCs and introduce fresh outdoor air.
Regular Cleaning and Maintenance
Regularly cleaning your home, including dusting and vacuuming, can help reduce VOC levels. Dust and dirt can accumulate VOCs, so removing them can minimize exposure. Proper maintenance of HVAC systems, including regular filter changes, can also contribute to healthier indoor air quality.
Use Air Purifiers
Air purifiers with activated carbon filters can be effective in removing VOCs from the air. These filters are designed to trap and absorb VOC molecules, reducing their presence in the indoor environment. Place air purifiers in frequently used areas or where VOC-emitting sources are present for the best results.
Keep Indoor Plants
Certain indoor plants, such as spider plants, Boston ferns, and peace lilies, can help absorb VOCs and improve indoor air quality. These plants act as natural air purifiers and can help reduce VOC levels in your home. Be sure to choose plants that are safe for pets and children if applicable.
Avoid Smoking Indoors
Smoking indoors is not only harmful to your health but also contributes to high VOC levels in your home. Establishing a smoke-free environment can greatly reduce VOC exposure and improve indoor air quality for both smokers and non-smokers alike.


Regulations and Standards
Various regulations and standards are in place to address VOC emissions and promote healthier indoor environments:
EPA Regulations
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has implemented regulations to limit VOC emissions from various sources, including building materials, paints, and cleaning products. These regulations aim to protect air quality and reduce the health risks associated with VOC exposure.
VOC Limits for Building Materials
Some countries and regions have established limits on the amount of VOCs allowed in building materials. These limits are often defined by law or specific green building certifications. Choosing building materials that meet or exceed these limits can help ensure lower VOC emissions in your home.
Green Building Certifications
Green building certifications, such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) and BREEAM (Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method), have specific criteria for VOC emissions. Homes that meet these certifications have undergone rigorous testing and selection of low VOC materials and products, resulting in healthier indoor air quality.
Conclusion
Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) can be found in numerous sources within our homes, including building materials, cleaning products, furnishings, and personal care items. Indoor activities such as cooking, smoking, and the use of solvents and personal care products can also contribute to high VOC levels. Poor ventilation, new construction, and renovation activities further exacerbate the issue. The health effects of high VOC levels range from respiratory irritation to headaches, allergies, and increased cancer risk. Testing for VOC levels can help identify potential problems, and steps can be taken to prevent and reduce VOC levels, such as choosing low VOC products, ensuring proper ventilation, regular cleaning, and using air purifiers. Regulations and standards have been established to promote healthier indoor environments by limiting VOC emissions. By being aware of the sources of VOCs and taking proactive measures, we can create homes with better indoor air quality and promote the well-being of ourselves and our loved ones.