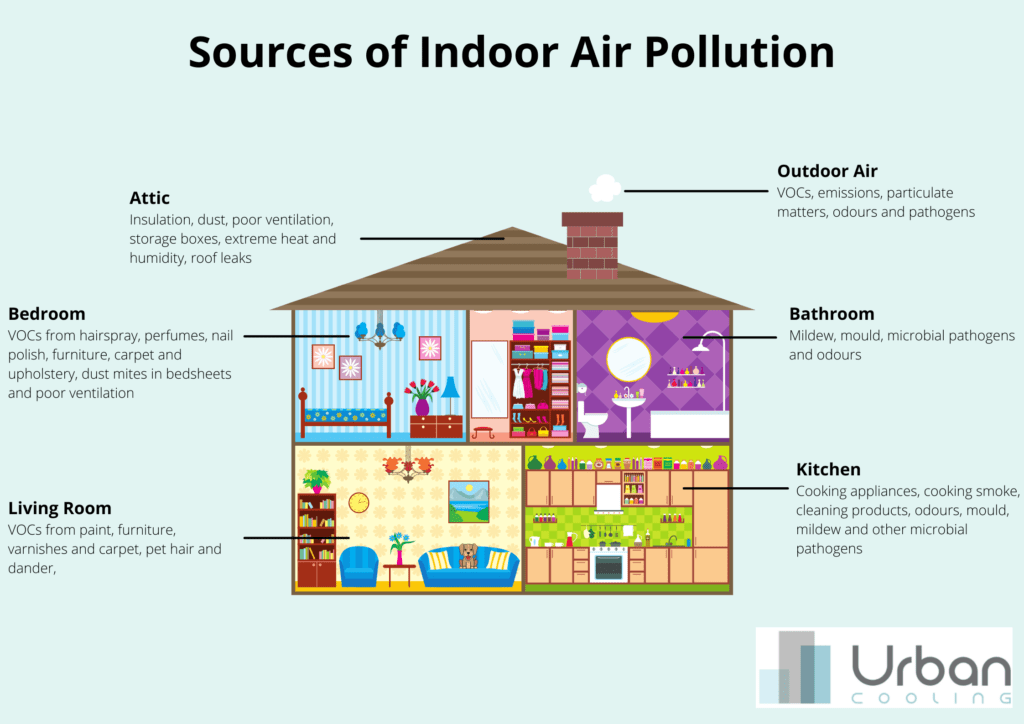
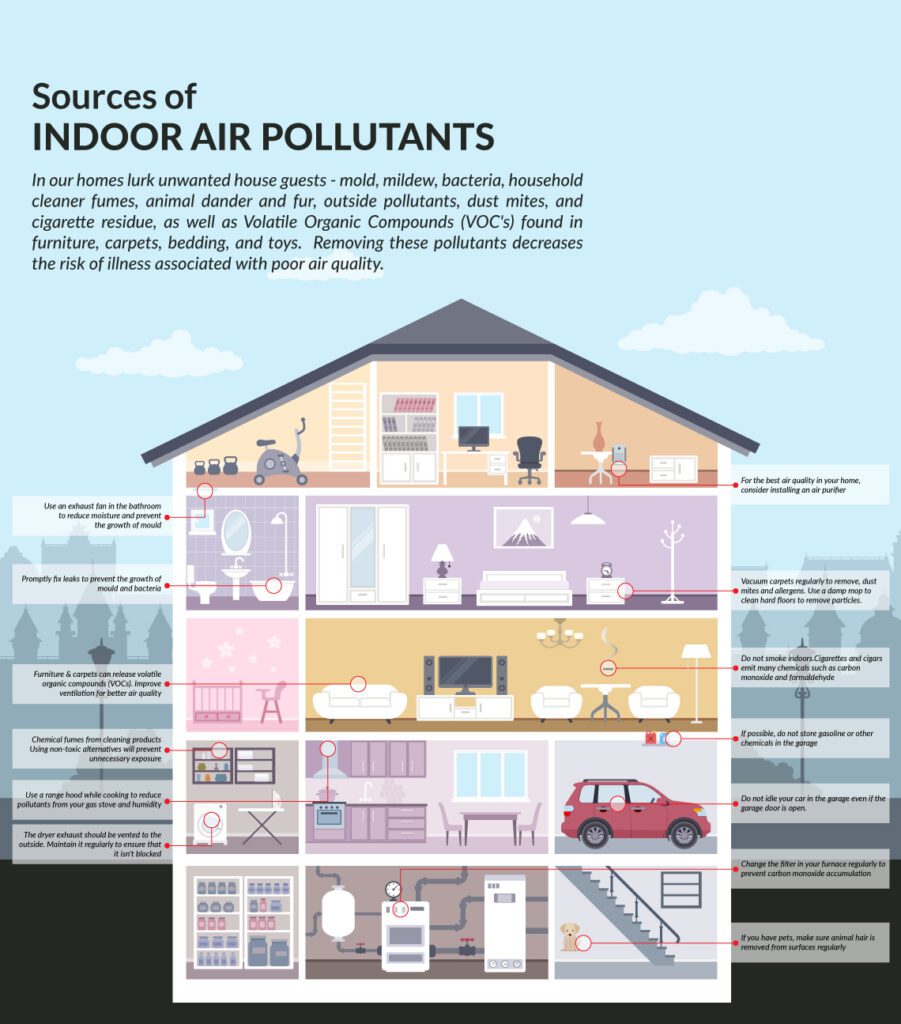
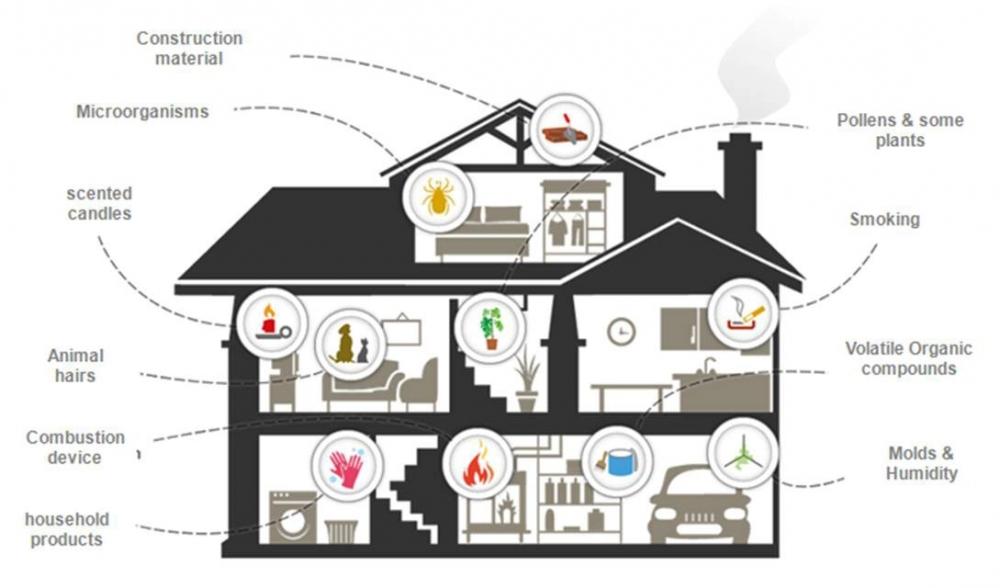
In this article, we will explore the various household items that can have an impact on indoor air quality. From the cleaning products we use to the materials in our furniture and even the candles we light, many everyday items can release harmful pollutants into our homes. By gaining a better understanding of these potential culprits, we can make informed choices to create a healthier environment for ourselves and our loved ones. So let’s take a closer look at the surprising factors that may be affecting the air we breathe inside our homes.

Cleaning Products
Chemical-based Cleaners
Chemical-based cleaners, commonly found under your kitchen or bathroom sink, can have a significant impact on indoor air quality. These cleaners often contain harsh chemicals such as ammonia, bleach, and chlorine, which can release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the air. VOCs can irritate the respiratory system and contribute to a range of health issues, including headaches, dizziness, and even long-term respiratory problems. When using chemical cleaners, it is important to ensure proper ventilation by opening windows or using exhaust fans to reduce the concentration of these harmful chemicals in your home.
Aerosol Sprays
Aerosol sprays, such as air fresheners, furniture polish, and cleaning sprays, can also negatively impact indoor air quality. These products typically contain propellants and solvents that can release harmful VOCs into the air. Additionally, the tiny particles emitted by aerosol sprays can linger in the air for extended periods, leading to respiratory irritation. To minimize the negative effects of aerosol sprays, opt for pump sprays or consider using natural alternatives like vinegar or baking soda for cleaning purposes.
Bleach and Disinfectants
While bleach and disinfectants are effective cleaners, they can have serious implications for indoor air quality. Bleach is known to emit chlorine gas when it comes into contact with other chemicals, such as ammonia or vinegar. This gas can be highly irritating to the respiratory system and cause symptoms like coughing, wheezing, and chest tightness. Disinfectants often contain potent chemicals like quaternary ammonium compounds (quats) that can cause respiratory issues and allergic reactions. When using bleach or disinfectants, ensure proper ventilation and avoid mixing them with other substances to prevent the release of harmful gases.
Air Fresheners
Plug-in Air Fresheners
Plug-in air fresheners are a popular choice for many households, but they can contribute to poor indoor air quality. These devices contain synthetic fragrances that can release harmful VOCs into the air. The constant emission of these chemicals can cause respiratory irritations, trigger allergies, and even impact cognitive function. If you must use air fresheners, consider opting for natural alternatives like essential oils or investing in air purifiers to help filter out unwanted odors.
Spray Air Fresheners
Spray air fresheners, like aerosol sprays, can also introduce harmful chemicals into your indoor environment. The release of VOCs from these products can worsen respiratory conditions, trigger asthma attacks, and even lead to long-term health problems. To improve indoor air quality, it is advisable to limit the use of spray air fresheners or explore alternatives like natural fabric sprays or homemade air fresheners using ingredients like baking soda and essential oils.
Scented Candles
While scented candles can create a cozy atmosphere, they can also release harmful pollutants into the air. Some candles, particularly those made from paraffin wax, can emit toxins like benzene and toluene when burned. These substances are known to cause respiratory irritation and may even be considered carcinogenic. If you enjoy the ambiance of candles, opt for those made from natural materials like beeswax or soy wax, which tend to produce fewer pollutants.


Cooking Appliances
Gas Stoves
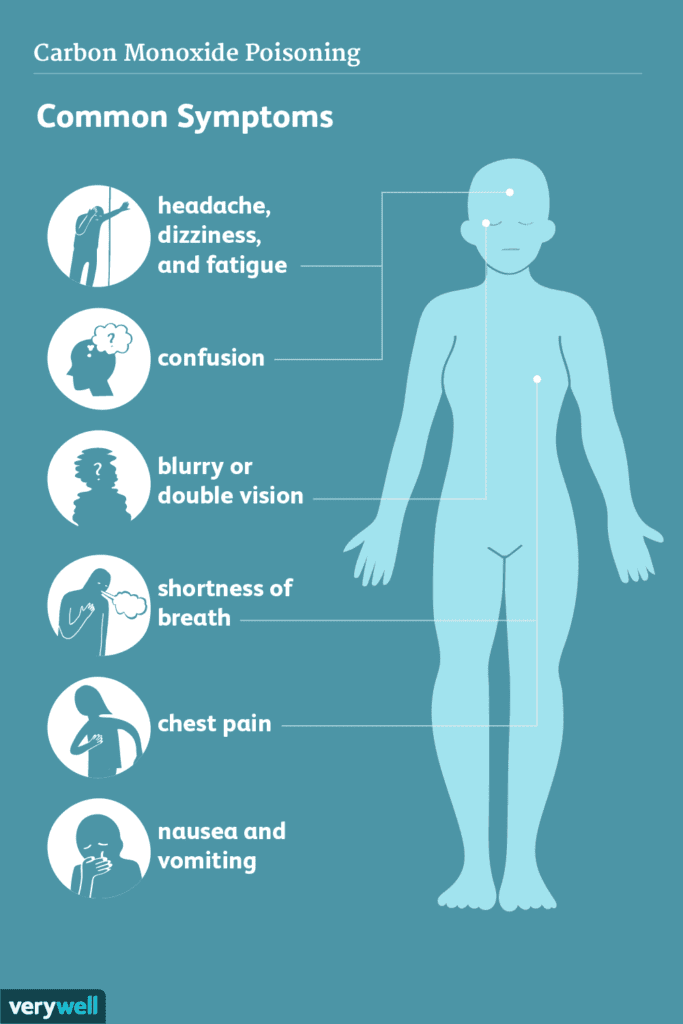
Gas stoves can be a significant source of indoor air pollutants. When natural gas is burned for cooking, it releases nitrogen dioxide and carbon monoxide. Nitrogen dioxide can cause respiratory problems, particularly in individuals with asthma or other respiratory conditions. Carbon monoxide can be particularly dangerous as it is a colorless, odorless gas that can lead to carbon monoxide poisoning, resulting in headaches, dizziness, and even death. To mitigate the impact of gas stoves on indoor air quality, ensure proper ventilation by using exhaust fans or opening windows. It is also recommended to have gas stoves regularly inspected and maintained to prevent leaks or inefficient combustion.
Electric Stoves
Electric stoves are generally considered to have less impact on indoor air quality compared to gas stoves. Since they do not burn fuel, they do not emit carbon monoxide or nitrogen dioxide. However, cooking on electric stoves can still release small amounts of particulate matter, especially when cooking at high temperatures or frying food. Good ventilation, such as using range hoods or opening windows, can help remove these particulates from the air and maintain a healthier indoor environment.
Ovens
Using ovens to bake or broil food can also affect indoor air quality. When food is heated, it can release smoke and particles into the air, which can be harmful when inhaled. Additionally, certain types of cookware, like non-stick pans, can release toxic fumes when exposed to high temperatures. To limit the impact on indoor air quality, ensure proper ventilation by using range hoods or opening windows while cooking. Avoid using non-stick cookware and opt for stainless steel or cast iron alternatives, which are generally safer.
Smoking
Cigarette Smoke
Cigarette smoke is one of the most well-known air pollutants and can have severe consequences for both smokers and non-smokers alike. When cigarettes are smoked indoors, the smoke lingers in the air and leaves behind harmful chemicals and particles. Secondhand smoke contains over 7,000 chemicals, including more than 70 known to cause cancer. The toxins in cigarette smoke can lead to respiratory issues, cardiovascular problems, and an increased risk of lung cancer. Quitting smoking and avoiding exposure to secondhand smoke are essential for maintaining good indoor air quality and protecting your health.
Secondhand Smoke
Secondhand smoke refers to the smoke exhaled by smokers as well as the smoke emitted from the burning end of a cigarette. Inhaling secondhand smoke can be just as dangerous as smoking cigarettes directly. The chemicals and fine particles in secondhand smoke can irritate the airways, trigger asthma attacks, and increase the risk of respiratory infections, especially in children and individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions. To protect yourself and others from the harmful effects of secondhand smoke, it is advisable to establish smoke-free zones in your home and encourage smokers to step outside when smoking.

Mold and Mildew
Bathrooms
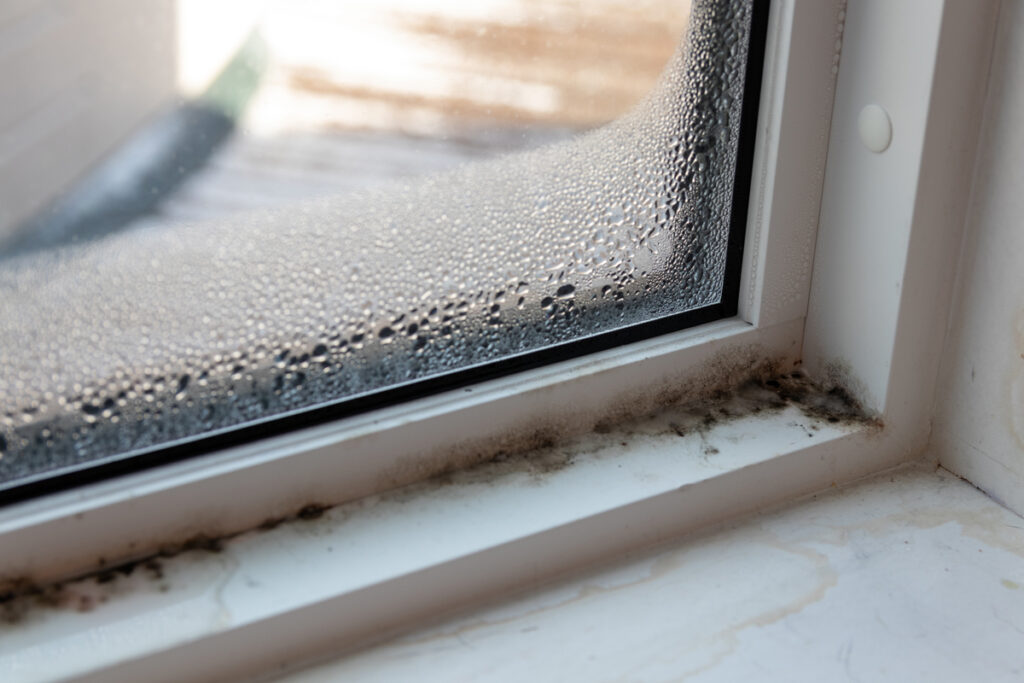
Bathrooms are notorious for their humid conditions, making them a prime breeding ground for mold and mildew. Mold spores can become airborne and cause respiratory issues, allergies, and even infections when inhaled. To prevent mold growth in your bathroom, ensure adequate ventilation by using exhaust fans or opening windows after showering or bathing. Regularly clean and disinfect surfaces prone to moisture, like shower curtains and tiles, and fix any leaks or water damage promptly to discourage mold growth.
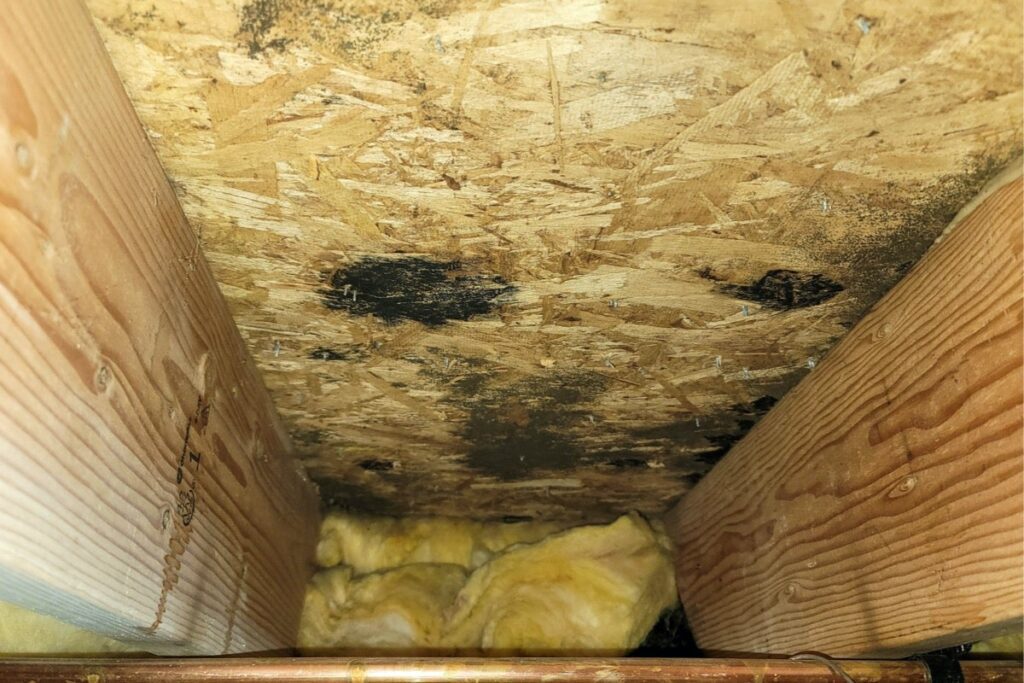
Basements
Basements can also be susceptible to mold and mildew due to their damp and poorly ventilated nature. The combination of moisture, organic materials, and insufficient air circulation creates an ideal environment for mold to thrive. If you have a basement, it is important to monitor humidity levels and use dehumidifiers if necessary. Ensure that water is properly drained away from the foundation of your home to prevent water seepage. Regularly inspect the basement for any signs of water damage or leaks and address them promptly to minimize the risk of mold growth.
Humid Areas
High humidity areas, such as kitchens and laundry rooms, are prone to mold and mildew growth if proper precautions are not taken. Excess moisture in the air can allow mold spores to settle and proliferate on surfaces. To reduce the risk of mold growth, use exhaust fans or open windows when cooking or using the washing machine. Wipe down wet surfaces promptly and fix any leaks or plumbing issues that may contribute to moisture accumulation. Regularly check for signs of mold or mildew and address them promptly to maintain good indoor air quality.
Furniture and Upholstery
Particle Board or Plywood
Particle board and plywood, commonly used in furniture construction, can release formaldehyde, a known carcinogen, into the air. Formaldehyde emissions from these materials can cause respiratory irritation and have been linked to an increased risk of cancer, particularly in high concentrations. When purchasing furniture, look for products labeled as low-emitting or free from formaldehyde. Proper ventilation can also help reduce the concentration of formaldehyde in indoor air.
Flame Retardant Chemicals
Many upholstered furniture pieces are treated with flame retardant chemicals to meet safety regulations. However, these chemicals can also contribute to indoor air pollution. Flame retardants, such as polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs), can be released into the air as dust particles and potentially accumulate in the body over time. Some flame retardants have been associated with adverse health effects, including endocrine disruption, developmental delays, and cancer. Consider choosing furniture that is made without flame retardants or inquire about the specific flame retardants used in the manufacturing process.
Upholstery Fabrics
Upholstery fabrics can also impact indoor air quality, especially if they are made from synthetic materials or treated with chemicals. Synthetic fabrics can release VOCs into the air, potentially causing respiratory irritation and allergies. Look for upholstery fabrics made from natural materials like cotton or wool, which tend to have fewer chemical additives. Consider opting for fabrics that are certified as low in VOC emissions, as they have undergone testing to ensure their safety.

Carpets and Rugs
Synthetic Fibers
Carpets and rugs made from synthetic fibers, such as nylon or polyester, can release VOCs into the air. These VOCs, which are often used in the manufacturing process, can contribute to poor indoor air quality and potential health issues. If possible, choose carpets and rugs made from natural fibers like wool or sisal, which tend to have lower VOC emissions and are generally considered more environmentally friendly. Proper ventilation and regular vacuuming can also help reduce the concentration of VOCs in carpets and rugs.
Carpet Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
In addition to synthetic fibers, carpets themselves can emit VOCs into the air. The adhesives, backing materials, and padding used in carpet installation can contain harmful chemicals that off-gas over time. These VOCs can contribute to respiratory irritation, headaches, and allergic reactions. When choosing carpets, look for products labeled as low-VOC or consider using carpet tiles, which are often easier to install and replace. Proper ventilation, such as using fans or opening windows, can also help reduce the concentration of VOCs in the air.
Paints and Varnishes
Oil-based Paints
Oil-based paints and varnishes contain high levels of VOCs, which can be released into the air during the painting process and while the paint is drying. These VOCs can contribute to poor indoor air quality and can cause a range of health issues, including respiratory irritation, headaches, and dizziness. When painting, opt for low-VOC or zero-VOC paints, which have lower emission levels of harmful chemicals. Ensure proper ventilation by opening windows or using fans to expedite the drying process and minimize exposure to potentially harmful fumes.
Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
Paints and varnishes in general, whether oil-based or water-based, can emit VOCs that significantly impact indoor air quality. VOCs are released into the air as the paint dries and can continue to off-gas for an extended period. These chemicals can cause respiratory irritation, trigger allergies, and contribute to the formation of outdoor smog. When selecting paints and varnishes, look for low-VOC or zero-VOC products that meet environmental standards. Proper ventilation, using fans or opening windows, is crucial while painting and for some time after to ensure a healthier indoor environment.


Electronic Devices
Printers and Copiers
Printers and copiers, particularly those that use laser technology, can release airborne particles and chemicals into the air during operation. The toner particles, inks, and fumes emitted can contribute to respiratory irritation and may even contain toxic substances. Ensure proper ventilation in areas with printers and copiers, such as offices or study rooms, and keep the devices clean and well-maintained. If possible, opt for printers and copiers that have low emission ratings or consider using inkjet printers that tend to produce fewer particles and chemicals.
Computers and Laptops
Computers and laptops are a staple in most households, but they can also impact indoor air quality. Electronic devices can emit small amounts of chemicals and particles into the air, particularly when they heat up during usage. Dust buildup on computer components can also contribute to poor air quality. Regular cleaning of computer equipment, proper ventilation in the workspace, and using air purifiers can help minimize the impact on indoor air quality. Additionally, keeping electronics dust-free can improve the overall performance and lifespan of your devices.
Pets
Pet Dander
Even the most beloved pets can contribute to indoor air pollution through the shedding of dander, or dead skin cells. These tiny particles can stay airborne for extended periods and trigger allergies in susceptible individuals. Regular grooming of pets can help reduce the amount of dander in the environment. Vacuuming frequently, using air purifiers, and ensuring proper ventilation can also aid in minimizing the impact of pet dander on indoor air quality.
Pet Urine and Feces
Pet urine and feces can release ammonia and other volatile organic compounds into the air, leading to unpleasant odors and potential health risks. These compounds can cause respiratory irritation and exacerbate existing respiratory conditions like asthma. Promptly cleaning up accidents, regularly replacing litter boxes, and providing proper ventilation in areas where pets spend time indoors can help mitigate the impact on indoor air quality. Using odor-absorbing materials or natural deodorizers can also help freshen the air and reduce unpleasant pet-related odors.
By being aware of the potential impacts of various household items on indoor air quality, you can take proactive steps to create a healthier environment for you and your family. Regular maintenance, proper ventilation, and considering alternatives with lower emissions can go a long way in ensuring that the air you breathe indoors is clean and safe. Remember, improving indoor air quality is a journey, and by making conscious choices, you can create a space that promotes well-being and a higher quality of life.