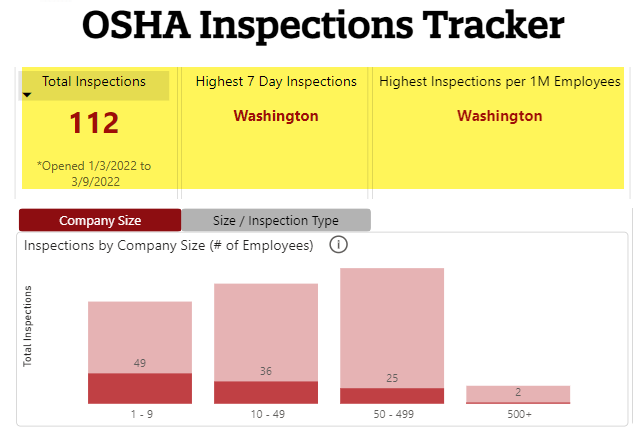
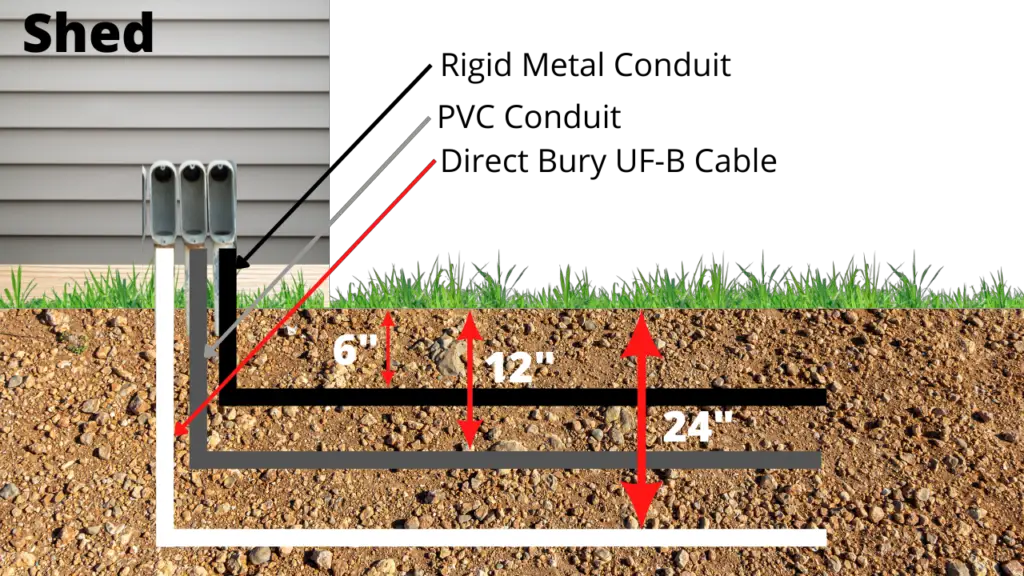
You have probably heard the term “inspection schedule” before, but do you know what it really means? In a nutshell, an inspection schedule is a planned timeline or calendar that outlines when inspections will be conducted for a particular purpose, such as ensuring safety standards or maintaining the quality of a product or service. It helps organizations stay organized and proactive in identifying and addressing any potential issues or areas of improvement. By following an inspection schedule, businesses can ensure compliance, reduce risks, and ultimately enhance their overall operations.
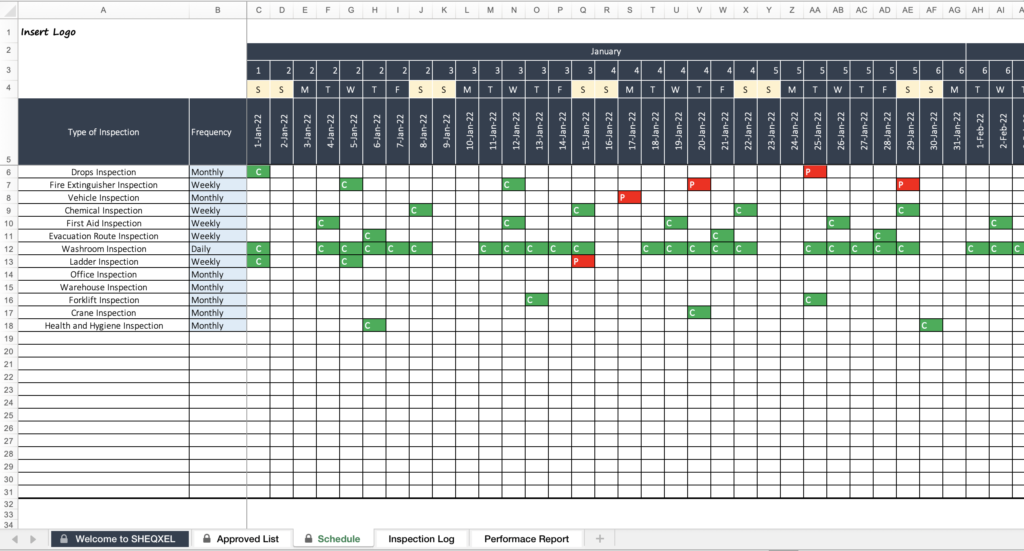

What is an Inspection Schedule?
An inspection schedule is a planned and structured approach to regularly assess and evaluate the condition and performance of equipment, facilities, or processes. It involves a systematic review of designated areas, assets, or tasks to ensure compliance with regulations, identify potential hazards or risks, and maintain overall operational efficiency. By implementing an inspection schedule, organizations can prevent costly repairs, minimize downtime, enhance workplace safety, and comply with legal and regulatory requirements.
Definition of Inspection Schedule
Basic Explanation of Inspection Schedules
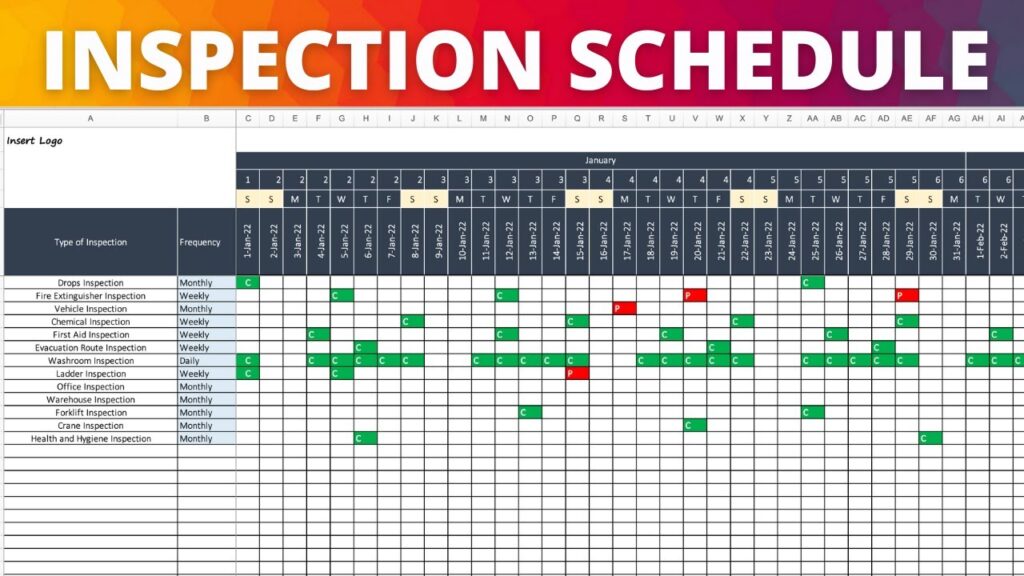
An inspection schedule is a predetermined plan that outlines when and how inspections should be conducted to ensure that all necessary areas are thoroughly examined. It sets the framework for systematic inspections and serves as a guide for performing routine checks, preventive maintenance inspections, safety inspections, compliance inspections, and quality inspections. The schedules can be created for various assets, such as machinery, equipment, vehicles, buildings, or systems.
Purpose and Objectives of an Inspection Schedule
The primary purpose of an inspection schedule is to maintain the optimal functioning and safety of assets within an organization. By conducting inspections at regular intervals, potential issues or deficiencies can be identified in a timely manner before they escalate into larger problems. The objectives of an inspection schedule include:
-
Ensuring compliance with regulations and standards: Regular inspections help organizations adhere to legal requirements and industry standards, minimizing the risk of penalties or non-compliance.
-
Identifying and preventing potential hazards or risks: By regularly inspecting equipment, facilities, or processes, organizations can proactively identify any potential safety hazards and take appropriate preventive measures.
-
Maintaining equipment and facility performance: Inspections allow for early detection of any issues that might negatively impact the performance or efficiency of equipment or facilities. Timely maintenance or repairs can be carried out to prevent further deterioration.
-
Minimizing downtime and costly repairs: Scheduled inspections help identify problems before they become significant, resulting in reduced downtime and the need for extensive repairs. This helps save both time and money for organizations.
-
Enhancing workplace safety and employee well-being: Through routine inspections, organizations can create and maintain a safe working environment, reducing the risk of accidents, injuries, or occupational hazards.
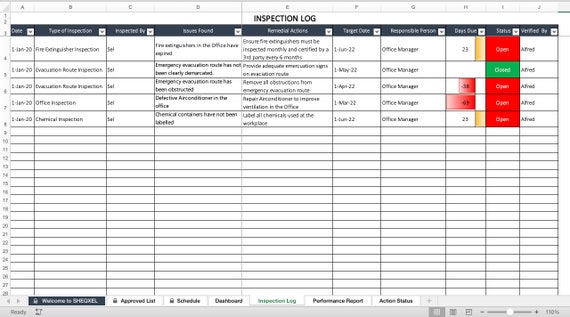

Components of Inspection Schedule
Identification of Inspection Areas
The first step in creating an inspection schedule is to identify the areas or assets that need to be included in the inspection process. This may involve various aspects such as machinery, equipment, facility components, or specific processes.
Listing of Specific Inspection Tasks
Once the inspection areas are identified, the next step is to define the specific tasks that need to be performed during inspections. These tasks can vary depending on the nature of the asset or area being inspected and may include visual checks, measurements, testing, or sampling.
Assigning Responsible Personnel or Teams
To ensure accountability and effective execution of inspections, it is important to assign responsible personnel or teams. These individuals or teams should have the necessary knowledge, skills, and training to perform the inspections accurately and efficiently.
Establishing Inspection Frequencies
Inspection frequencies should be determined based on various factors such as regulatory requirements, equipment criticality, historical performance, or industry best practices. This involves deciding how often inspections should be conducted, whether it is daily, weekly, monthly, or annually.
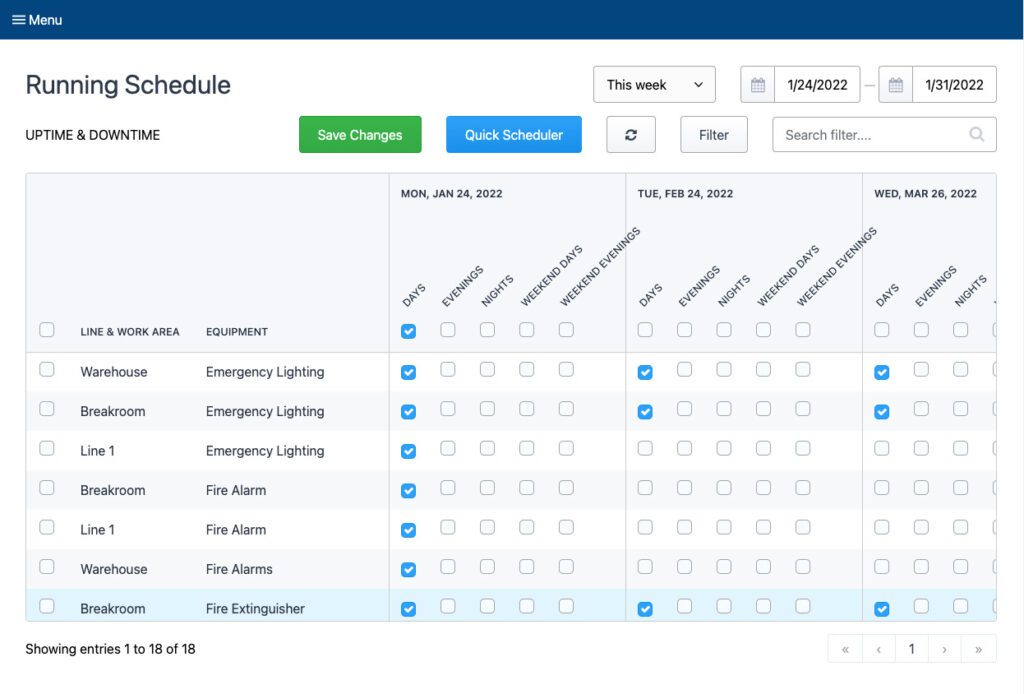
Documentation and Record-Keeping
To maintain a comprehensive record of inspections, it is essential to establish a system for documentation and record-keeping. This may involve documenting inspection findings, recording corrective actions, and storing relevant reports or data for future reference and analysis.
Types of Inspections
Routine Inspections
Routine inspections are regularly scheduled assessments performed to ensure the smooth operation and maintenance of equipment, machinery, or facilities. These inspections are typically carried out at predetermined intervals and encompass visual checks, basic measurements, or functional verifications.
Preventive Maintenance Inspections
Preventive maintenance inspections aim to identify and address potential issues or risks that may arise due to regular usage or wear and tear. By conducting these inspections, organizations can proactively perform maintenance tasks, such as lubrication, filter replacement, or calibration, to prevent breakdowns or significant failures.
Safety Inspections
Safety inspections focus on identifying potential hazards, risks, or non-compliance with safety regulations within a workplace. These inspections evaluate factors such as ergonomic conditions, availability and functionality of safety equipment, electrical safety, or fire prevention measures.
Compliance Inspections
Compliance inspections ensure that organizations are following relevant regulations, guidelines, or industry standards. These inspections are conducted to verify adherence to legal requirements concerning environmental protection, workplace safety, product quality, or data privacy.
Quality Inspections
Quality inspections involve the systematic examination of products, services, or processes to assess their adherence to specific quality standards or customer requirements. These inspections may include checks for defects, presence of desired features, or compliance with established quality benchmarks.


Creating an Inspection Schedule
Assessing Inspection Requirements
Before creating an inspection schedule, organizations must assess their unique inspection requirements. This involves evaluating the assets, areas, or processes that need to be inspected, considering factors such as criticality, safety implications, and regulatory compliance.
Identifying Critical Areas and Assets
To prioritize inspections, it is important to identify critical areas and assets that are crucial to the organization’s operations and performance. This helps determine the level of thoroughness required during inspections and ensure that resources are allocated accordingly.
Establishing Priorities
Based on the criticality assessment, organizations should establish priorities for inspections. This allows them to focus on areas or assets that pose the highest risk or have the greatest impact on operations, safety, or compliance.
Setting Inspection Frequencies
Once the priorities are defined, inspection frequencies can be established. This should take into account relevant regulations, the asset’s history and performance, and the level of risk associated with potential failures.
Developing Checklists or Protocols
To ensure consistency and standardization during inspections, checklists or protocols can be developed. These documents provide step-by-step guidance for inspectors, ensuring that all necessary tasks are performed and records are accurately maintained.
Allocating Necessary Resources
Organizations need to allocate the necessary resources for inspections, including personnel, equipment, and time. Adequate resources ensure that inspections are executed effectively and that any identified issues can be addressed promptly.
Frequency of Inspections
Determining Inspection Intervals
The frequency of inspections depends on various factors, including regulatory requirements, equipment criticality, and industry standards. Some inspections may need to be conducted on a daily or weekly basis to ensure ongoing operation, while others may require monthly or annual assessments.
Factors Influencing Inspection Frequency
Several factors influence the frequency at which inspections should be conducted. These factors include the criticality and complexity of the asset or process being inspected, historical performance and failure data, regulatory requirements, and the availability of resources.
Balancing Frequency and Practicality
When determining inspection frequencies, organizations must strike a balance between conducting inspections frequently enough to identify potential issues and the practicality of performing the inspections without interrupting operations or incurring excessive costs.

Factors to Consider
Legal and Regulatory Requirements
Organizations must consider the legal and regulatory requirements applicable to their industry or operations. Compliance with these requirements is crucial to avoid penalties or legal consequences.
Industry Standards and Guidelines
In addition to legal requirements, organizations should also consider industry-specific standards and guidelines. These provide best practices and benchmarks for inspections, ensuring that organizations operate at an optimal level.
Equipment or Asset Criticality
The criticality of an asset or piece of equipment influences the importance and frequency of inspections. Critical assets require more frequent inspections to mitigate the risk of failures that could have severe consequences.
History of Incidents or Failures
The history of incidents, failures, or maintenance issues should be taken into account when determining inspection requirements. Assets that have a higher likelihood of problems may require more frequent and comprehensive inspections.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors, such as temperature, humidity, or exposure to corrosive substances, can impact the condition and performance of assets. Inspections should consider these factors and assess their potential effects on equipment or facilities.
Operational Conditions
The nature and intensity of operations can affect the inspection requirements. Assets subject to heavy usage, extreme conditions, or continuous operation may require more frequent inspections to ensure their reliability and safety.
Budget Limitations
Organizations must consider budget limitations when developing an inspection schedule. It may be necessary to prioritize inspections based on asset criticality or regulatory requirements to optimize resource allocation.
Availability of Resources
The availability of qualified personnel, equipment, and time is critical in implementing an effective inspection schedule. Organizations must ensure that sufficient resources are allocated to perform inspections accurately and in a timely manner.
Benefits of Using an Inspection Schedule
Improved Maintenance Planning and Execution
By having a structured inspection schedule, organizations can plan and execute maintenance activities more effectively. Inspections provide valuable information on the condition of assets, helping organizations prioritize and schedule maintenance tasks efficiently.
Timely Identification and Resolution of Issues
Regular inspections allow for the early detection of issues or abnormalities, enabling organizations to intervene promptly and prevent more significant problems from occurring. Timely identification and resolution of issues lead to increased overall reliability and performance.
Reduced Equipment Downtime
Proactive inspections help identify potential problems before they lead to unexpected breakdowns or failures. By addressing these issues in a planned manner, organizations can reduce equipment downtime and minimize the potential impact on operations.
Enhanced Operational Efficiency
Well-maintained equipment and facilities perform more efficiently, resulting in improved operational productivity. Regular inspections ensure that assets are functioning optimally, reducing energy consumption, waste, and inefficiencies.
Extended Equipment Lifespan
Through systematic inspections, organizations can identify and address issues that could shorten the lifespan of their assets. Timely maintenance and repairs extend the lifespan of equipment, maximizing return on investment.
Cost Savings through Proactive Maintenance
Inspections help organizations detect issues that, if left unattended, may lead to costly repairs or replacements. By proactively addressing these issues, organizations can minimize the financial burden associated with unexpected failures.
Increased Workplace Safety
Inspections play a crucial role in ensuring workplace safety. By identifying and addressing potential hazards or risks, organizations create a safer environment for employees, reducing the likelihood of accidents or injuries.
Compliance with Legal and Regulatory Requirements
Regular inspections help organizations comply with legal and regulatory requirements. By identifying and rectifying any non-compliance issues promptly, organizations avoid penalties or legal consequences.

Challenges in Implementing an Inspection Schedule
Implementing an effective inspection schedule may present some challenges. These challenges include:
-
Resistance to change: Employees might resist adopting new processes or systems, leading to difficulties in implementing an inspection schedule effectively.
-
Lack of resources: Insufficient resources, such as personnel, equipment, or time, can hinder the proper execution of inspections and maintenance activities.
-
Coordination and communication: Coordinating inspection schedules and communicating relevant information to all involved parties can be challenging, especially in large organizations.
-
Training and skill gaps: Inspectors may require specific training to perform inspections effectively and understand the importance of their role.
-
Compliance complexity: Meeting the requirements of multiple legal and regulatory frameworks can be complex, especially in industries with stringent regulations.
Best Practices for an Effective Inspection Schedule
To ensure the success of an inspection schedule, organizations should consider the following best practices:
-
Involving all relevant stakeholders: Engage stakeholders throughout the process, including personnel responsible for inspections, maintenance teams, and management, to ensure a comprehensive and collaborative approach.
-
Regularly reviewing and updating the schedule: Inspection schedules should be reviewed periodically to assess their effectiveness and relevance. Necessary updates can be made based on changes in regulations, equipment performance, or organizational priorities.
-
Ensuring clear communication and reporting: Establish clear communication channels for reporting inspection findings, corrective actions, and any changes to the schedule. This promotes transparency and accountability.
-
Implementing a system for tracking and documenting inspections: Utilize digital tools or software to track inspections, maintain records, and generate reports. These systems help ensure consistency, accuracy, and accessibility of inspection data.
-
Providing adequate training and support to inspectors: Train inspectors on inspection protocols, techniques, and any relevant regulatory requirements. Support them by providing necessary resources, such as equipment, tools, and ongoing training opportunities.
-
Encouraging a culture of accountability and responsibility: Foster a culture where everyone understands the importance of inspections and takes responsibility for the equipment or areas under their care. Promote a proactive approach to maintenance and safety.
-
Conducting periodic audits or evaluations: Regularly assess the effectiveness of the inspection schedule through audits or evaluations. Identify areas for improvement and implement necessary changes to enhance the inspection process.
By implementing and following these best practices, organizations can establish an effective inspection schedule that promotes maintenance, safety, and compliance while optimizing operational performance.