In this article, we will discuss the process of testing for mold in indoor air. Detecting mold in your home or workplace is crucial to ensure a healthy living environment. By understanding the various methods and techniques used to test for mold, you can take the necessary steps to prevent its growth and potential health hazards. Let’s explore the different approaches you can take to effectively test for mold in your indoor air.


Understanding Mold
Mold is a common type of fungus that can grow and thrive in various environments, including indoor spaces. It reproduces by creating spores that can float through the air and land on surfaces, where they have the potential to grow and multiply. Mold can be found almost anywhere, both indoors and outdoors, but it becomes a concern when it starts growing indoors and poses health risks.
What is mold?
Mold is a type of fungus that exists in our everyday environment. It can be found both indoors and outdoors, and it plays an important role in breaking down dead plant and animal matter. Mold spores are always present in the air, but they usually remain at a low level that is not harmful to humans. However, when mold spores find a damp environment with suitable conditions for growth, they can quickly multiply and create colonies.
The dangers of mold
While mold plays a crucial role in our ecosystem, it can become a health hazard when it grows indoors. Mold reproduces by releasing spores into the air, and these spores can trigger allergic reactions in some individuals. Common symptoms of mold exposure include sneezing, coughing, watery eyes, and skin rashes. In people with pre-existing respiratory conditions or compromised immune systems, exposure to mold can lead to more severe health problems such as respiratory infections and asthma attacks.
Mold can also cause structural damage to buildings. It can rot wood, deteriorate drywall, and compromise the integrity of the structure. Additionally, it can leave unsightly stains and produce musty odors that can be challenging to eliminate.
Common signs of mold in indoor air
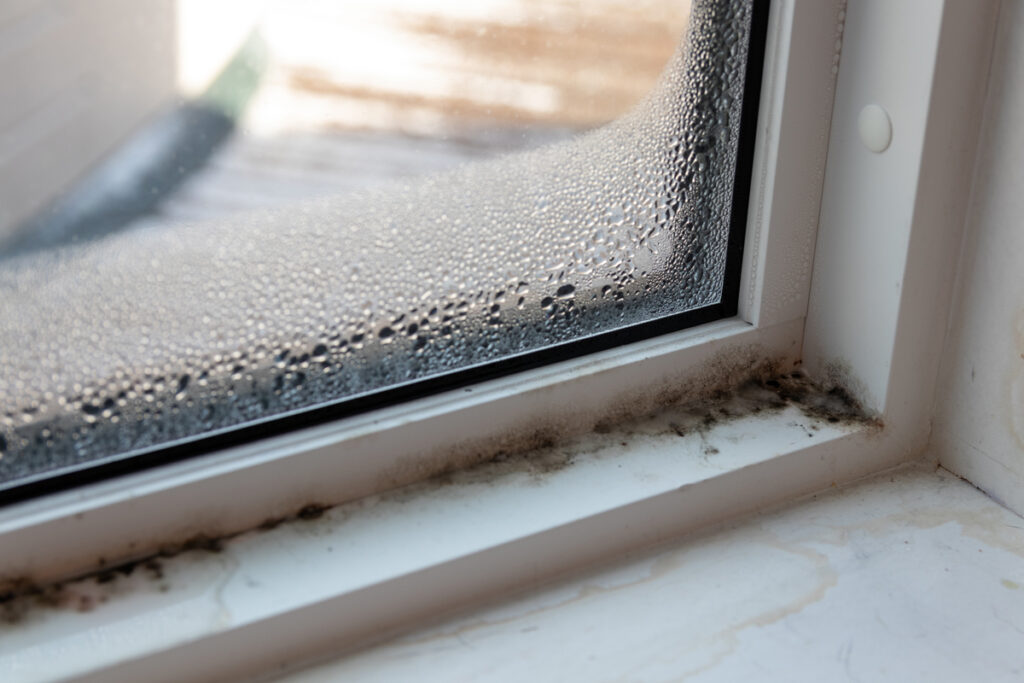
If you suspect that mold might be present in your indoor air, there are some common signs to look out for. These include a musty odor that seems to persist despite cleaning efforts, visible signs of mold growth such as dark spots or patches on walls or ceilings, and experiencing symptoms of allergies or respiratory issues when spending time indoors. It is important to note that not all signs of mold are visible, as mold can grow behind walls, under carpets, and in other hidden areas. Therefore, it is crucial to conduct proper mold testing to determine the extent of the problem and take appropriate action.
Professional Mold Testing
If you suspect that you have a mold problem in your home or workplace, it is advisable to hire a qualified mold inspector to conduct professional mold testing. Mold testing is a specialized process that involves the collection and analysis of samples to determine the presence and type of mold in the indoor environment.
Hiring a qualified mold inspector
When hiring a mold inspector, it is crucial to choose a qualified and experienced professional. Look for certifications such as the Certified Mold Inspector (CMI) or Certified Indoor Environmentalist (CIE) to ensure that the inspector has undergone proper training and has the necessary expertise in mold assessment and testing. Additionally, consider checking references and reading reviews from previous clients to get an idea of their reputation and level of service.
Types of professional mold tests
There are several types of professional mold tests that can be performed to assess mold levels in indoor air. These tests include air sampling, surface sampling, and bulk sampling. Each type of test has its own advantages and limitations, and the choice of the test method depends on various factors such as the suspected location of mold growth and the desired level of detail in the analysis.
Costs associated with professional mold testing
The cost of professional mold testing can vary depending on various factors such as the size of the property, the number of samples needed, and the specific tests being performed. On average, homeowners can expect to pay anywhere between $300 and $1,000 for professional mold testing. While this may seem like a significant expense, it is important to consider the potential health and structural risks associated with mold growth. Investing in professional mold testing can help identify the problem at an early stage and prevent further damage and potential health issues.


DIY Mold Testing Kits
If you prefer to take a more hands-on approach and want to test for mold yourself, there are several DIY mold testing kits available in the market. These testing kits provide homeowners with the tools necessary to collect samples and send them to a laboratory for analysis.
What are DIY mold testing kits?
DIY mold testing kits are designed to be user-friendly and provide a convenient way for homeowners to collect samples and assess the presence of mold in their indoor environment. These kits typically include instructions on how to collect samples, sample collection materials (such as swabs or adhesive tapes), and prepaid envelopes for sending the samples to a laboratory for analysis.
How do DIY mold testing kits work?
Using a DIY mold testing kit is generally a straightforward process. The kit will provide step-by-step instructions on how to collect samples from different surfaces or air. Typically, the samples are collected by swabbing or using adhesive tapes to gather mold particles from surfaces or by capturing air samples using specialized devices. The collected samples are then sent to a laboratory for analysis, where they are examined under a microscope to identify the presence of mold and determine the type and concentration of mold spores.
Pros and cons of using DIY mold testing kits
Using a DIY mold testing kit has some advantages, such as convenience and cost-effectiveness. These kits are readily available and relatively affordable compared to hiring a professional inspector. DIY testing kits can provide a basic assessment of the presence of mold, which can be useful for preliminary evaluations.
However, it is important to note that DIY mold testing kits have limitations. They may not be as accurate or reliable as professional mold testing, as the analysis is typically performed by a homeowner rather than a trained professional. Additionally, DIY kits may not identify all types of mold or provide detailed information about mold levels, which could impact the effectiveness of remediation efforts.
Air Sampling
Air sampling is a common method used to assess the levels of mold spores in indoor air. By collecting air samples, it is possible to determine the concentration of mold spores and compare it to outdoor air to evaluate the extent of mold contamination.
What is air sampling for mold?
Air sampling for mold involves collecting samples of the air in a specific area to measure the concentration of mold spores. This method is useful for assessing the airborne mold levels and determining if there is an elevated mold presence in the indoor environment. Air sampling can also help identify the types of mold spores present, which can provide valuable information when assessing potential health risks.
Methods of air sampling
There are two main methods of air sampling for mold: spore trap sampling and viable air sampling.
Spore trap sampling: This method involves using a specialized cassette or filter to capture mold spores present in the air. The cassette or filter is then sent to a laboratory, where the captured mold spores are examined under a microscope. This method provides information about the total concentration and types of mold spores present in the air.
Viable air sampling: Viable air sampling involves collecting air samples using a specialized device, such as an impactor or a slit sampler. The collected samples are then cultured in a laboratory to determine if the captured mold spores are viable (able to grow and reproduce). This method provides information not only about the concentration and types of mold spores but also about their potential to cause mold growth.
Interpreting air sampling results
Interpreting air sampling results requires the expertise of a trained professional. The results will provide information about the concentration and types of mold spores present in the air. A higher concentration of mold spores compared to outdoor air samples may indicate a mold problem, especially if specific types of mold spores associated with indoor mold growth are present. However, it is important to note that mold spore levels can fluctuate depending on various factors such as ventilation, temperature, and recent activities in the area. Therefore, it is crucial to interpret the results in conjunction with other tests and observations to get a comprehensive understanding of the mold situation.


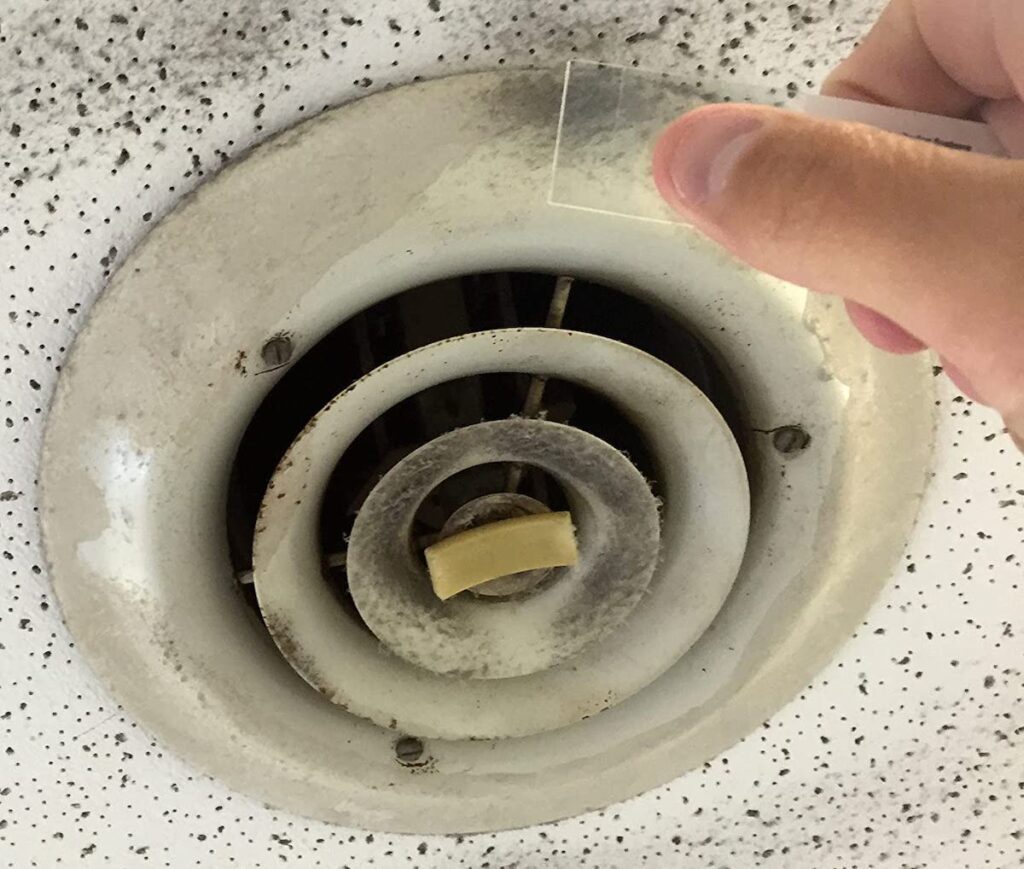
Surface Sampling
Surface sampling is another method used to assess mold contamination in indoor environments. By collecting samples from various surfaces, it is possible to determine the presence of mold and the type of mold species present.
What is surface sampling for mold?
Surface sampling for mold involves collecting samples from various surfaces, such as walls, ceilings, floors, and furniture, to determine if mold is present. This method helps identify areas of visible mold growth and assess the extent of mold contamination. Surface sampling is particularly useful when the presence of mold is suspected but not visually confirmed.
Methods of surface sampling
There are several methods of surface sampling for mold, including tape lift, swab, and bulk sampling.
Tape lift sampling: This method involves pressing a clear adhesive tape against a surface with suspected mold growth and then carefully peeling it off. The tape is then placed on a glass slide or a petri dish and sent to a laboratory for analysis. This method is effective for collecting samples from flat surfaces.
Swab sampling: Swab sampling involves using a sterile swab to collect samples from surfaces with suspected mold growth. The swab is then placed in a vial or a tube and sent to a laboratory for analysis. This method is useful for collecting samples from irregular surfaces or areas where tape lift sampling is not feasible.
Bulk sampling: Bulk sampling involves collecting a piece of material or a portion of a surface with suspected mold growth. The collected sample is then placed in a container and sent to a laboratory for analysis. This method is useful for determining the extent of mold contamination in a particular area.
Interpreting surface sampling results
Interpreting surface sampling results requires the expertise of a trained professional. The laboratory analysis of surface samples can provide information about the presence of mold, the type of mold species, and the extent of mold contamination. The results will help identify areas that require remediation and provide guidance on the appropriate remediation techniques to be used. It is important to note that surface sampling may not be able to detect mold growth behind walls or in hidden areas, so it should be used in conjunction with other testing methods to get a comprehensive assessment of the mold situation.
Bulk Sampling
Bulk sampling is a method used to assess the extent and severity of mold contamination in a specific area. By collecting larger samples of materials or surfaces, it is possible to determine the concentration of mold and the type of mold species present.
What is bulk sampling for mold?
Bulk sampling for mold involves collecting larger samples of materials or surfaces to determine the extent and severity of mold contamination. This method provides a more detailed analysis of the mold situation and helps identify areas that require remediation. Bulk sampling is particularly useful when assessing areas with visible mold growth, such as water-damaged materials or heavily contaminated surfaces.
Methods of bulk sampling
There are several methods of bulk sampling for mold, including cutting out a section of a material, using a coring tool, or collecting dust or debris from surfaces.
Material sampling: This method involves cutting out a section of a material, such as drywall or carpet, that shows signs of mold growth. The collected sample is then placed in a container and sent to a laboratory for analysis. Material sampling provides valuable information about the type and concentration of mold present in the contaminated material.
Coring sampling: Coring sampling involves using a coring tool to collect samples from materials such as wood or concrete. The coring tool drills a small hole into the material, and the collected sample is then placed in a container and sent to a laboratory for analysis. This method helps assess the extent of mold contamination within the material.
Dust or debris sampling: Dust or debris sampling involves collecting samples of dust or debris from surfaces that may contain mold spores. The collected samples are placed in a container and sent to a laboratory for analysis. This method can provide information about the presence of mold spores and their potential to cause mold growth.
Interpreting bulk sampling results
Interpreting bulk sampling results requires the expertise of a trained professional. The laboratory analysis of bulk samples provides information about the concentration and types of mold present in the collected materials. The results help determine the severity of mold contamination and identify areas that require remediation. It is important to note that bulk sampling may not be able to detect hidden mold growth or provide a comprehensive assessment of the entire indoor environment. Therefore, it should be used in conjunction with other testing methods to get a complete understanding of the mold situation.


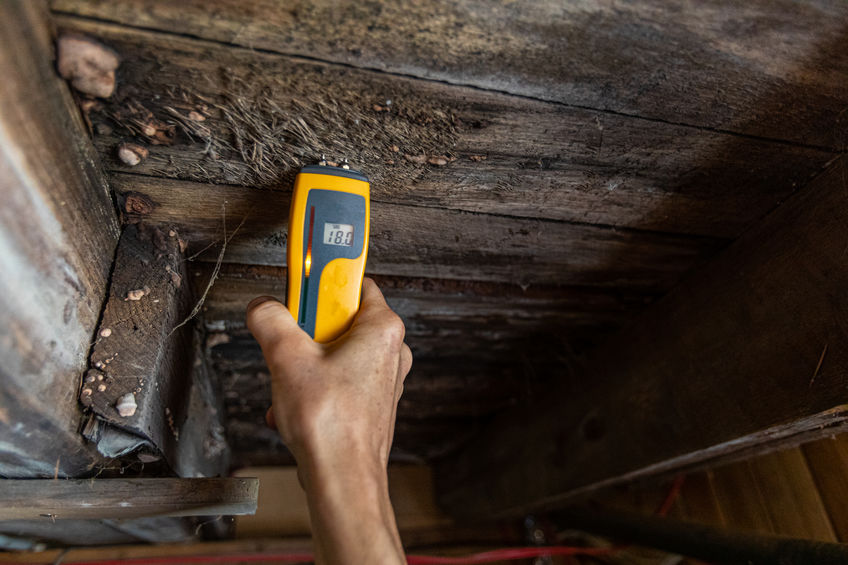
Testing Hidden Areas
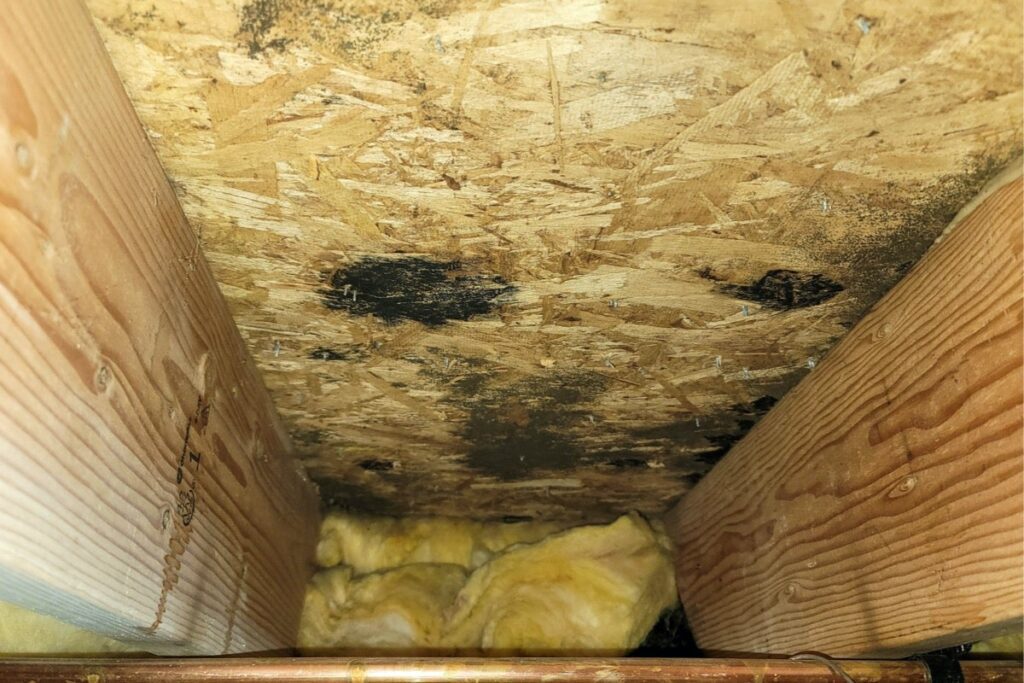
Testing hidden areas for mold is crucial to identify and address mold growth that may not be immediately visible. Mold can thrive in hidden spaces, such as behind walls, under flooring, and in ceiling cavities, making it important to include these areas in the testing process.
Common hidden areas to test for mold
There are several common hidden areas in buildings that are prone to mold growth. These include:
- Behind walls, especially in areas with water or moisture damage.
- Underneath flooring, especially in areas where water or moisture may have seeped through.
- In ceiling cavities or crawl spaces, particularly if there has been a roof leak or plumbing issue.
- Inside HVAC systems or air ducts, where moisture can accumulate and create an ideal environment for mold growth.
- Behind appliances or fixtures, such as refrigerators, washing machines, or sink cabinets, where water leakage or condensation may occur.
Testing these hidden areas is essential to ensure that mold is not silently spreading and causing damage in areas that may not be easily accessible or immediately visible.
Methods for testing hidden areas
Testing hidden areas for mold can be more challenging than testing visible surfaces. Depending on the specific area to be tested, different methods may be used.
-
Wall cavities: In order to test for mold behind walls, it may be necessary to create small openings in the wall to access the area. This can be done by cutting small inspection holes or using borescopes or fiber optic cameras to visually inspect the wall cavity for mold growth.
-
Ceiling cavities and crawl spaces: For hard-to-reach areas like ceiling cavities and crawl spaces, air sampling or bulk sampling methods can be employed. Air sampling devices or bulk sampling tools can be inserted into these areas to collect samples for analysis.
-
HVAC systems and air ducts: To test for mold in HVAC systems or air ducts, specialized sampling methods can be utilized. This may involve using air pumps to collect air samples from the ducts or using swabs to collect samples from the surfaces inside the system.
-
Appliances or fixtures: Testing for mold behind appliances or fixtures can involve visual inspection and surface sampling. By carefully inspecting these areas for signs of mold growth and using tape lift, swab, or bulk sampling methods, samples can be collected for laboratory analysis.
Importance of testing hidden areas
Testing hidden areas for mold is crucial because mold growth in these areas can go unnoticed for extended periods. Mold colonies can thrive in dark, damp, and hidden spaces, spreading spores and potentially causing significant damage to the structure and air quality of a building. By including hidden areas in the testing process, potential mold issues can be identified and addressed promptly, preventing further damage and potential health risks.
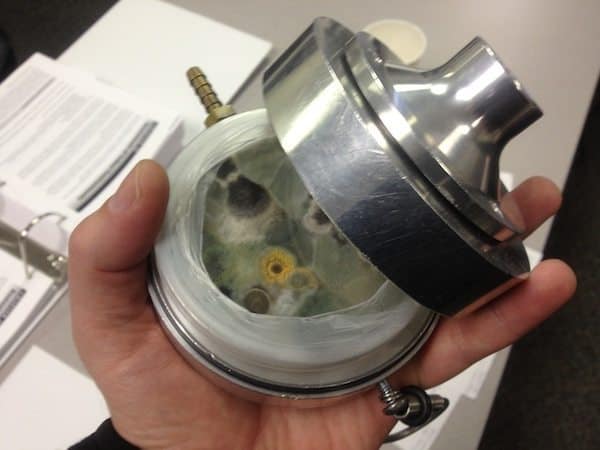
Interpreting Test Results
After conducting mold testing, it is essential to interpret the results accurately to understand the severity of the mold contamination and determine the appropriate actions and remediation measures.
Understanding spore counts
Spore counts refer to the number of mold spores detected in a sample. Interpretation of spore counts should take into account the specific type of mold and the concentration of spores compared to outdoor air samples. High spore counts compared to outdoor air may indicate a mold problem, particularly if the specific mold species is associated with indoor mold growth. However, it is important to note that spore counts can vary depending on factors such as weather conditions, time of year, and recent activities in the area. Therefore, interpretation of spore counts should be done by a trained professional using established guidelines and taking into consideration other testing results and observations.
Comparing results to outdoor air
Comparing the results of indoor mold testing to outdoor air samples can provide valuable information about the extent of mold contamination. Outdoor air samples serve as a reference point for normal mold levels in the environment. If the indoor spore counts are significantly higher than outdoor levels, it indicates a potential indoor mold problem that needs to be addressed. However, it is important to note that outdoor mold levels can also fluctuate, so this comparison should be used as a general guideline and not the sole determinant of a mold issue.
Analyzing the presence of specific mold species
Analyzing the presence of specific mold species in test results can provide additional insights into the severity and potential health risks of the mold contamination. Some mold species are more commonly associated with indoor mold growth and can pose greater health risks than others. Identifying the specific mold species can help determine the appropriate remediation measures and guide decisions related to occupant safety and health.


Taking Action Based on Results
Once mold testing results have been obtained and interpreted, it is important to take appropriate action based on the findings. The actions may vary depending on the severity of the mold contamination, the type of mold species present, and the specific circumstances of the building.
When to hire a professional remediation company
In cases where the mold contamination is extensive, the mold species present are known to be hazardous, or the remediation process requires specialized equipment and expertise, it is advisable to hire a professional mold remediation company. Professional remediation companies have the knowledge, experience, and resources to safely and effectively remove mold and prevent further contamination. Additionally, they can provide recommendations for preventing future mold growth.
Tips for DIY mold removal
For minor mold problems that can be addressed without professional help, there are some tips to keep in mind for DIY mold removal:
-
Wear appropriate personal protective equipment, such as gloves, goggles, and a mask, to protect yourself from mold spores and cleaning chemicals.
-
Contain the affected area by sealing off the space with plastic sheets or tarps to prevent the spread of mold spores to other areas of the building.
-
Remove and dispose of any mold-infested materials, such as drywall or carpet, following proper guidelines for handling and disposal.
-
Clean surfaces with a mold-specific cleaner or a mixture of water and detergent. Scrub the affected areas thoroughly, ensuring that all visible mold is removed.
-
Dry the area completely and address the moisture source that caused the mold growth. Fix any leaks or water damage and improve ventilation in the area to prevent future mold problems.
Preventing future mold growth
Preventing future mold growth is essential to maintain a healthy indoor environment. Here are some preventive measures to consider:
- Control moisture levels by promptly repairing any leaks, addressing water damage, and maintaining proper ventilation in areas prone to dampness.
- Keep indoor humidity levels below 50% to discourage mold growth. Consider using dehumidifiers in high-humidity areas.
- Insulate cold surfaces, such as pipes and windows, to prevent condensation and moisture buildup.
- Regularly clean and dry areas that are prone to moisture, such as bathrooms, kitchens, and basements.
- Regularly inspect hidden areas, such as behind appliances and inside HVAC systems, for potential mold growth.
- Ensure proper drainage around your property to prevent water from seeping into the foundation.
By following these preventive measures and maintaining a vigilant approach to moisture control and regular inspections, you can significantly reduce the risk of future mold growth.
Conclusion
Understanding mold and the importance of mold testing is crucial for maintaining a healthy indoor environment. Mold can pose health risks and cause structural damage if left unchecked. Professional mold testing provides the expertise and accuracy needed to assess mold contamination comprehensively, while DIY mold testing kits offer a convenient option for initial evaluations. Air sampling, surface sampling, bulk sampling, and testing hidden areas are all valuable methods to identify the presence of mold and determine the appropriate actions. By interpreting the test results accurately and taking prompt and appropriate action, you can effectively address mold problems, mitigate health risks, and prevent future mold growth. Remember, when in doubt, it is always advisable to seek the assistance of professionals for a thorough assessment and remediation. With proper knowledge and proactive measures, you can create a mold-free environment for you and your loved ones.