Have you ever wondered if the air you breathe can affect your mental health? The connection between air quality and physical well-being is well-established, but what about its impact on our emotions? In this article, we will explore the question of whether bad air quality can potentially cause anxiety, shedding light on the intersection between our environment and our mental well-being. So, take a deep breath, and let’s explore this fascinating topic together.
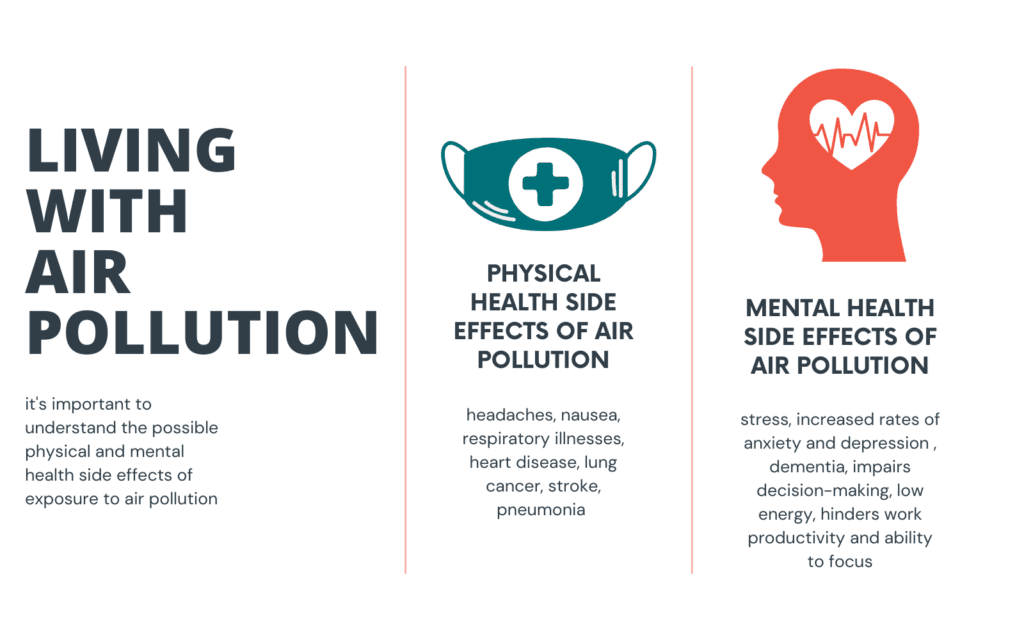

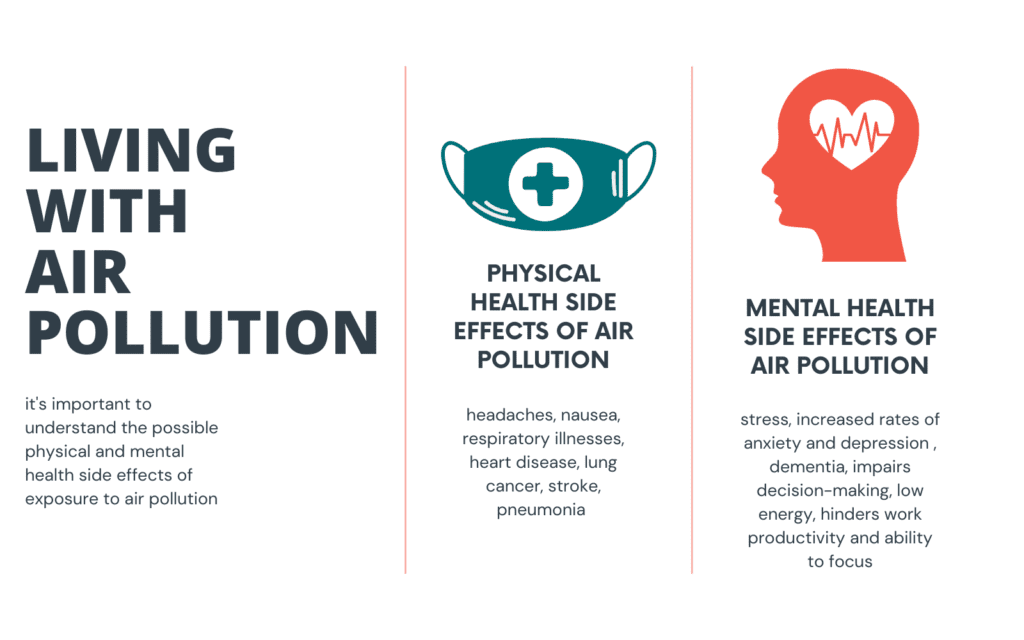
Effects of Bad Air Quality on Physical Health
Respiratory Issues
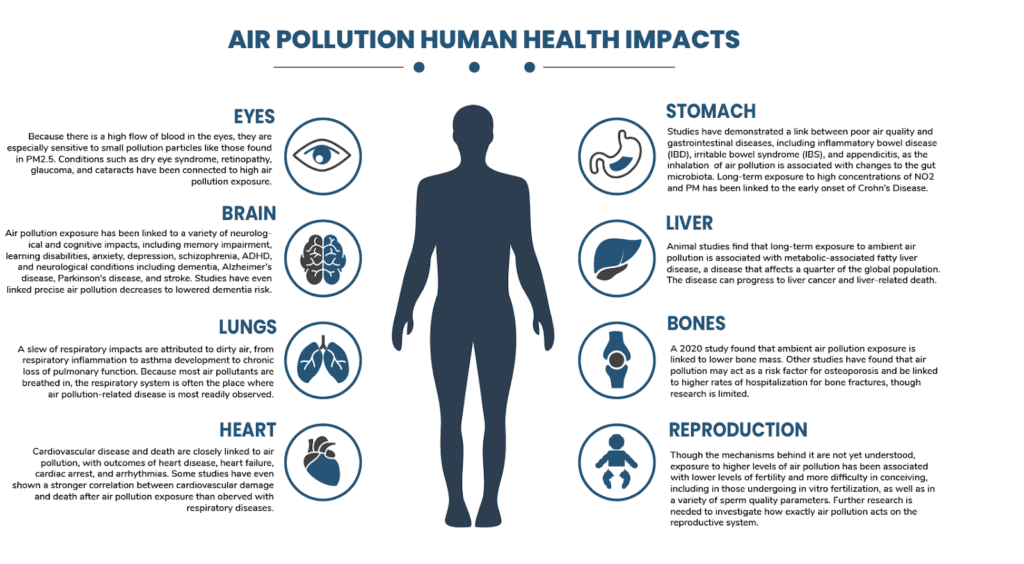
Poor air quality can have detrimental effects on your respiratory system. When you breathe in polluted air, it can irritate your airways and lead to symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath. Long-term exposure to bad air quality can also increase the risk of developing chronic respiratory conditions like bronchitis and asthma. These respiratory issues can significantly impact your physical health, making it difficult to perform everyday activities and decreasing your overall quality of life.
Cardiovascular Problems
In addition to respiratory issues, bad air quality can also pose a threat to your cardiovascular health. Studies have shown that exposure to air pollution can increase the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular diseases. When you breathe in polluted air, harmful particles can enter your bloodstream and trigger inflammation in your blood vessels. This inflammation can lead to the formation of plaques, narrowing your arteries and increasing your risk of heart-related problems. Furthermore, long-term exposure to air pollution has been linked to the development of high blood pressure, which further contributes to cardiovascular issues.
Allergies and Asthma
If you suffer from allergies or asthma, bad air quality can exacerbate your symptoms and make your condition worse. Pollutants in the air, such as pollen, mold spores, and dust mites, can trigger allergic reactions and asthma attacks. These allergens can irritate your airways and cause inflammation, leading to symptoms like sneezing, itching, congestion, and difficulty breathing. For individuals with pre-existing allergies or asthma, it is crucial to be aware of the air quality and take necessary precautions to reduce exposure to pollutants.
Effects of Bad Air Quality on Mental Health
Anxiety and Stress
While bad air quality primarily affects physical health, it is also closely linked to mental health issues. One of the most common mental health problems associated with poor air quality is anxiety. Breathing in polluted air can contribute to feelings of unease, restlessness, and nervousness. Studies have found that individuals living in areas with high levels of air pollution are more likely to experience symptoms of anxiety and chronic stress. The constant worry about the impact of air pollution on health can weigh heavily on your mind and significantly affect your overall well-being.
Depression
In addition to anxiety, bad air quality has also been associated with an increased risk of depression. Living in areas with high pollution levels can negatively impact your mood and lead to feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and despair. The exact mechanisms behind this connection are still being studied, but it is believed that the inflammatory response triggered by pollutants in the air may play a role in the development of depressive symptoms. Moreover, the reduced ability to engage in outdoor activities and connect with nature due to poor air quality can contribute to the onset or worsening of depression.
Sleep Disturbances
Poor air quality can disrupt your sleep and leave you feeling tired and groggy during the day. When you are exposed to polluted air, your body may experience increased levels of inflammation, which can interfere with your sleep patterns. Additionally, irritants in the air, such as allergens and particulate matter, can cause nasal congestion, coughing, and wheezing, making it difficult to fall asleep and stay asleep throughout the night. Lack of quality sleep can have a significant impact on your mental health, leading to increased irritability, difficulty concentrating, and decreased overall productivity.


Understanding Anxiety
Definition and Symptoms
Anxiety is a mental health disorder characterized by excessive worry, fear, and apprehension. It is a normal and adaptive response to stressful situations, but when it becomes chronic and interferes with daily life, it can be classified as an anxiety disorder. Common symptoms of anxiety include persistent worrying, restlessness, irritability, difficulty concentrating, muscle tension, and sleep disturbances.
Causes of Anxiety
Anxiety can have various causes, including genetic factors, traumatic experiences, and imbalances in brain chemistry. Additionally, certain lifestyle choices, such as excessive caffeine or alcohol consumption, can contribute to anxiety symptoms. It is important to understand that anxiety disorders are complex and can be influenced by a combination of factors, including environmental conditions like air quality.
Environmental Factors and Anxiety
Environmental factors, such as bad air quality, can contribute to the development and exacerbation of anxiety symptoms. The constant exposure to pollutants in the air can create a sense of unease and increase feelings of anxiety and stress. Breathing in polluted air may also trigger physical symptoms, such as shortness of breath or chest tightness, which can further intensify anxiety. The link between air quality and anxiety is complex and requires further research, but it is clear that the environment we live in plays a role in our mental well-being.
Link Between Air Quality and Anxiety
Research on Air Pollution and Anxiety
Numerous studies have explored the relationship between air pollution and anxiety. Research has consistently shown that individuals living in areas with high levels of air pollution are more likely to experience symptoms of anxiety. One study conducted in China found that higher exposure to fine particulate matter (PM2.5) was associated with increased anxiety levels among residents. Similar results have been found in studies conducted in other countries, highlighting the global impact of air pollution on mental health.
Chemicals in Polluted Air and Their Impact on Mental Health
Bad air quality contains a multitude of harmful chemicals, including volatile organic compounds (VOCs), carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, and ozone. These pollutants can affect the central nervous system and have various neurotoxic effects, potentially contributing to the development of anxiety disorders. For example, exposure to VOCs has been linked to increased anxiety levels and cognitive impairments. The specific mechanisms through which these chemicals impact mental health are still being explored, but it is clear that they can have profound effects on the brain and contribute to the development of anxiety.
Effects of Long-Term Exposure to Bad Air Quality on Anxiety Levels
Long-term exposure to bad air quality can have cumulative effects on mental health, including anxiety. Living in areas with consistently poor air quality can lead to chronic stress and increase the risk of developing anxiety disorders. Prolonged exposure to pollutants can disrupt the body’s stress response system, leading to an imbalance of stress hormones and triggering anxiety symptoms. Furthermore, the constant worry and concern about the impact of air pollution on health can contribute to feelings of anxiety and uncertainty.


Individual Vulnerability to Air Pollution-Induced Anxiety
Pre-existing Mental Health Conditions
Individuals with pre-existing mental health conditions, such as anxiety disorders or depression, may be more vulnerable to the effects of air pollution on their mental well-being. These individuals already have a heightened sensitivity to stress and may be more likely to experience exacerbated symptoms when exposed to bad air quality. Managing and treating pre-existing mental health conditions is essential to mitigate the impact of air pollution on anxiety levels.
Genetic Factors
Genetic factors can also influence an individual’s vulnerability to air pollution-induced anxiety. Certain genetic variations may make some individuals more susceptible to the mental health effects of air pollution. Understanding the interplay between genetics and environmental factors can help identify those at greater risk and develop targeted interventions.
Socioeconomic Factors
Socioeconomic factors, such as income and access to healthcare, can contribute to an individual’s vulnerability to air pollution-induced anxiety. Lower-income communities often face higher levels of air pollution due to proximity to industrial areas or lack of environmental regulations. Moreover, limited access to healthcare resources can make it challenging for individuals in these communities to seek and receive proper treatment for mental health issues caused or exacerbated by bad air quality.
The Role of Inflammation in Air Pollution-Related Anxiety
Inflammatory Response and Mental Health
Inflammation is the body’s natural response to harmful stimuli, including exposure to air pollutants. However, when inflammation becomes chronic, it can have detrimental effects on mental health. Inflammatory markers in the body, such as C-reactive protein (CRP), have been found to be elevated in individuals with anxiety disorders. The inflammatory response triggered by air pollution can contribute to the development and progression of anxiety symptoms.
Association Between Air Pollution, Inflammation, and Anxiety
There is growing evidence suggesting a link between air pollution, inflammation, and anxiety. Studies have found that exposure to air pollution can lead to increased levels of inflammatory markers in the body, which, in turn, can contribute to the development of anxiety symptoms. The constant exposure to pollutants in the air can create a state of chronic inflammation, disrupting the balance of neurotransmitters in the brain and contributing to anxiety. Further research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms underlying this association and develop targeted interventions.

Coping Strategies for Air Pollution-Induced Anxiety
Indoor Air Quality Improvement
Improving indoor air quality can help reduce exposure to pollutants and alleviate anxiety symptoms. Simple steps like keeping windows closed during times of high outdoor pollution, using air purifiers with HEPA filters, and properly ventilating your home can significantly improve the air you breathe indoors. Additionally, avoiding activities that can introduce pollutants into your home, such as smoking and using harsh cleaning products, can further enhance indoor air quality.
Use of Air Purifiers
Air purifiers can be an effective tool in filtering out pollutants and improving air quality. Look for air purifiers with HEPA filters, as these can capture and remove fine particles, allergens, and other harmful substances from the air. Placing air purifiers in areas where you spend the most time, such as your bedroom or office, can help create a cleaner and healthier environment for you to relax and focus in.
Limiting Exposure to Polluted Areas
When air pollution levels are high, it is important to limit your exposure to polluted areas as much as possible. Pay attention to air quality reports and avoid spending extended periods of time outdoors when pollution levels are at their peak. If you need to be outside, consider wearing a mask designed to filter out particles and pollutants. Planning outdoor activities during times of lower pollution levels can minimize your exposure and reduce the risk of worsening anxiety symptoms.
Policy and Advocacy for Clean Air
Environmental Regulations and Their Impact on Air Quality
Environmental regulations play a crucial role in improving air quality and protecting public health. Stricter regulations on industrial emissions, vehicle emissions, and other sources of pollution can significantly reduce the levels of pollutants in the air. Advocating for strong environmental policies and supporting initiatives aimed at reducing air pollution can have a substantial impact on improving air quality and mitigating the mental health effects associated with bad air.
Community Initiatives for Clean Air
Communities can come together to implement initiatives that promote clean air and enhance mental well-being. Raising awareness about the importance of air quality, organizing community clean-up events, and supporting local environmental organizations can contribute to creating a cleaner and healthier living environment for everyone. Engaging in these initiatives not only benefits the community’s physical health but also fosters a sense of collective responsibility and resilience.
Health Impact Assessments
Conducting health impact assessments can evaluate the potential effects of proposed projects or policies on air quality and mental health. By considering the health implications of decisions related to transportation, urban planning, and industrial development, policymakers can make more informed choices to protect public health. Integrating mental health considerations into these assessments is crucial to address the social and psychological impacts of air pollution.


Conclusion
The effects of bad air quality extend beyond physical health and can significantly impact mental well-being. Anxiety, depression, and sleep disturbances are among the mental health issues associated with poor air quality. Understanding the links between air pollution and mental health is crucial in developing effective strategies to mitigate the impact on individuals and communities. By implementing clean air policies, engaging in community initiatives, and adopting coping strategies to reduce exposure, we can create healthier environments for ourselves and future generations.