Have you ever wondered if breathing in toxic fumes can make you sick? In this article, we explore the potential health hazards of inhaling harmful fumes and the serious consequences it can have on your well-being. From the dangers of chemical exposure to the long-term effects on your respiratory system, we delve into the science behind toxic fumes and the precautions you can take to protect yourself. So, if you want to stay informed and safeguard your health, keep reading to find out more about this pressing issue.


Definition of Toxic Fumes
Understanding Toxic Fumes
Toxic fumes are substances that, when released into the air, can be harmful and pose a significant risk to human health. These fumes are composed of various chemicals and gases that can cause immediate or long-term health effects upon exposure. Understanding the nature of toxic fumes is crucial to effectively prevent and manage the associated dangers.
Sources of Toxic Fumes
Toxic fumes can originate from a wide range of sources, both natural and man-made. Some common sources of toxic fumes include industrial processes, vehicle exhaust, chemical spills, burning of fossil fuels, and certain household products. It is important to be aware of the potential sources of toxic fumes in order to minimize exposure and protect your health.
Common Chemicals in Toxic Fumes
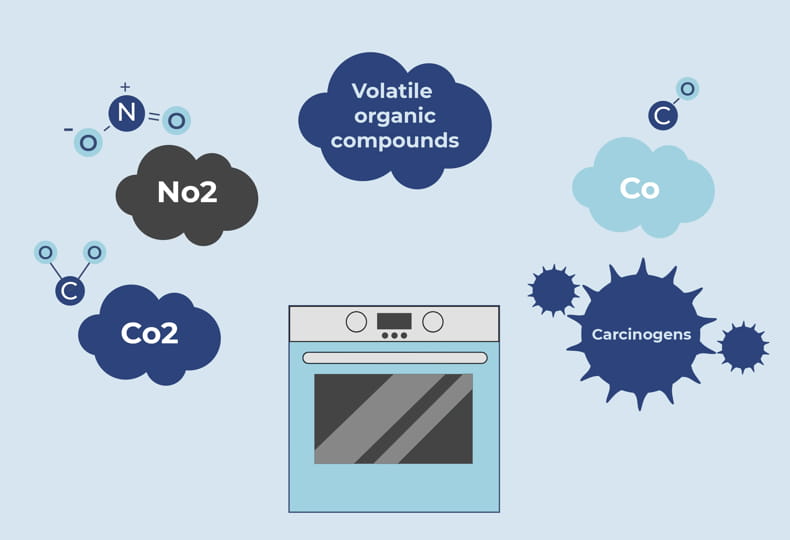
Toxic fumes can contain a variety of chemicals, many of which are hazardous to human health. Some common chemicals found in toxic fumes include volatile organic compounds (VOCs), carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, formaldehyde, benzene, and ammonia. These chemicals can have damaging effects on various systems of the body and can lead to serious health issues if inhaled.
Health Effects of Toxic Fumes
Immediate Health Effects
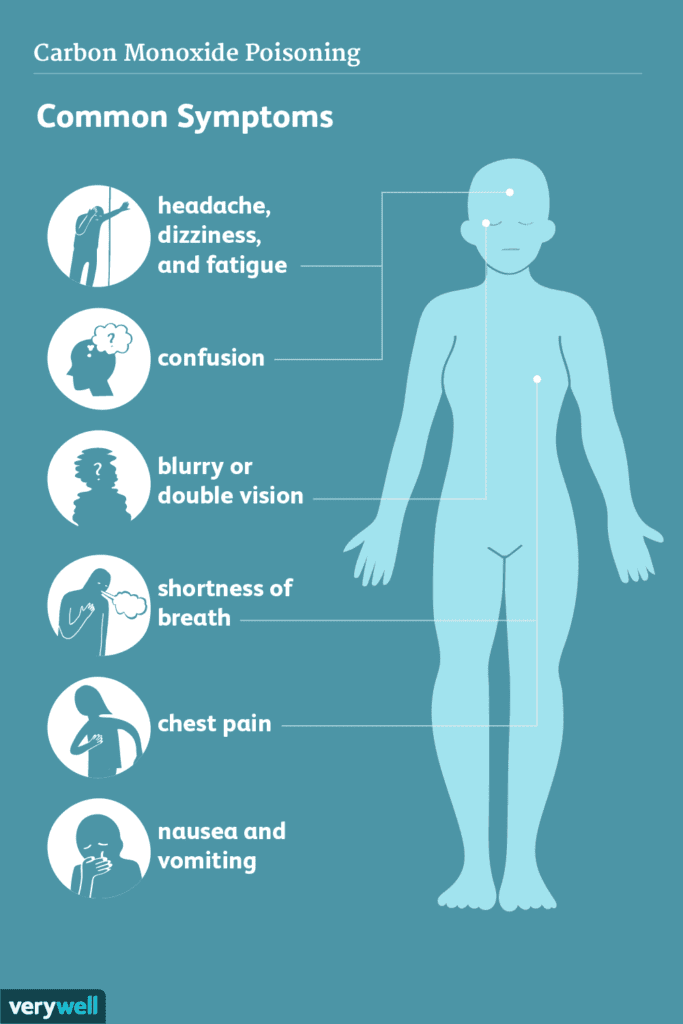
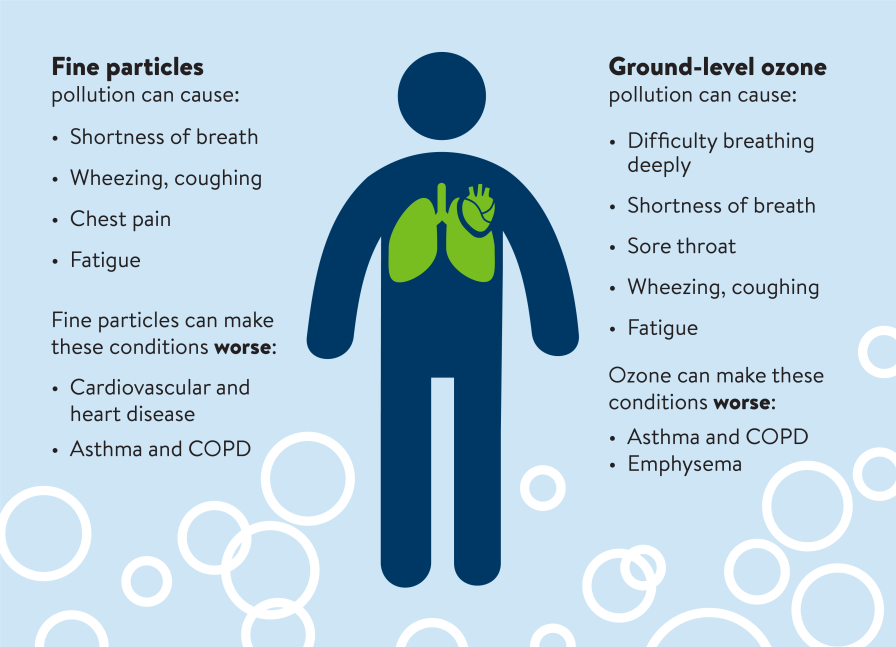
Exposure to toxic fumes can result in immediate health effects. These effects may include irritation of the respiratory system, such as coughing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness. Additionally, exposure to toxic fumes can cause eye and skin irritation, headaches, dizziness, nausea, and even chemical burns. It is important to seek immediate medical attention if you experience any of these symptoms after exposure to toxic fumes.
Long-Term Health Effects
Prolonged or repeated exposure to toxic fumes can lead to long-term health effects. These effects may include respiratory diseases, such as chronic bronchitis and asthma, as well as cardiovascular problems and an increased risk of cancer. It is important to understand that the severity of these long-term effects can vary depending on the specific chemicals involved and the duration and concentration of exposure.
Specific Organs Affected by Toxic Fumes
Toxic fumes can affect specific organs in the body. The respiratory system is particularly vulnerable, as toxic fumes can damage the lungs and lead to respiratory conditions such as pneumonitis and pulmonary edema. Additionally, toxic fumes can also impact the liver, kidneys, and nervous system. Understanding the potential harm that toxic fumes can cause to specific organs is crucial to prevent and manage the associated health risks.

Symptoms of Exposure to Toxic Fumes
Respiratory Symptoms
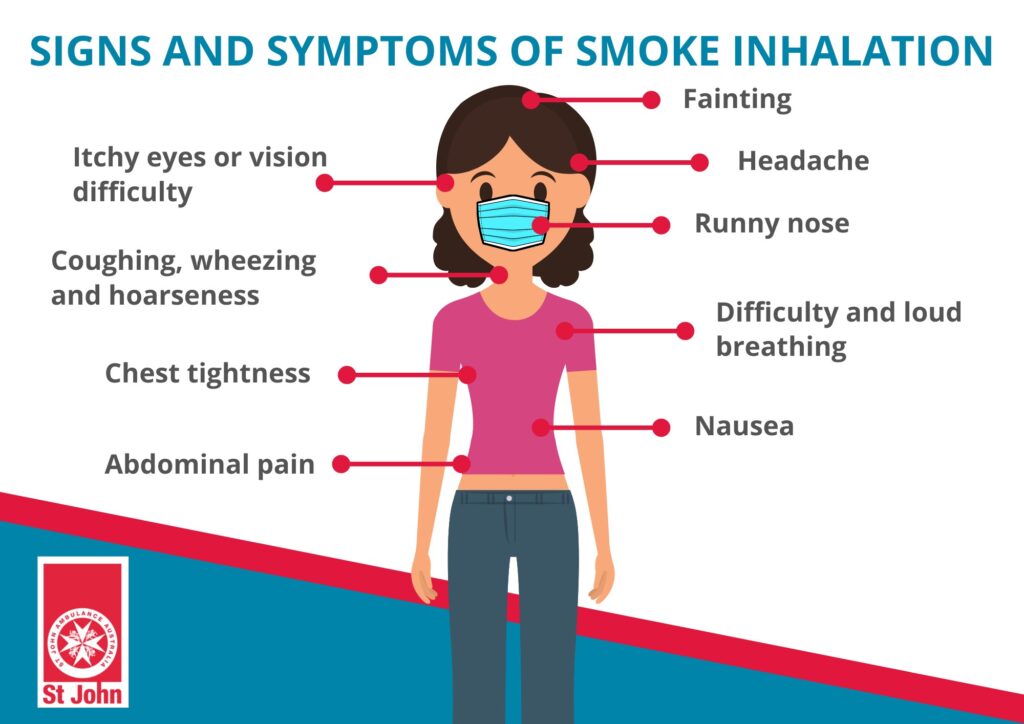
Exposure to toxic fumes can result in a range of respiratory symptoms. These may include coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, and difficulty breathing. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention, as they may indicate damage to the respiratory system.
Skin and Eye Irritation
Toxic fumes can cause skin and eye irritation upon contact. This can manifest as redness, itching, rash, or chemical burns on the skin, as well as redness, watering, and blurred vision in the eyes. It is important to wash any affected areas thoroughly with water and seek medical attention if the irritation persists or worsens.
Neurological Symptoms
Exposure to certain toxic fumes can affect the nervous system and result in neurological symptoms. These symptoms may include headaches, dizziness, confusion, memory problems, and even seizures. If you experience any of these symptoms after exposure to toxic fumes, it is important to seek immediate medical attention.
Digestive Symptoms
Ingesting or inhaling certain toxic fumes can also cause digestive symptoms. These symptoms may include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. If you experience these symptoms after exposure to toxic fumes, it is important to seek medical attention and take appropriate measures to prevent further exposure.
Factors Influencing Susceptibility to Toxic Fumes
Individual Sensitivity
Individual sensitivity to toxic fumes can vary significantly. Some individuals may be more susceptible to the effects of toxic fumes due to genetic factors, pre-existing health conditions, or lifestyle choices. It is important to understand your individual sensitivity to toxic fumes and take appropriate precautions to minimize exposure.
Duration and Concentration of Exposure
The duration and concentration of exposure to toxic fumes play a significant role in determining the severity of health effects. Prolonged or high-level exposure to toxic fumes is more likely to result in severe symptoms and long-term health complications. Minimizing exposure time and ensuring proper ventilation in potentially hazardous environments can help mitigate the risks associated with toxic fume exposure.
Pre-existing Health Conditions
Individuals with pre-existing health conditions, such as respiratory diseases or compromised immune systems, may be more vulnerable to the effects of toxic fumes. It is important for individuals with these conditions to take extra precautions and consult with healthcare professionals to effectively manage and minimize the risks associated with toxic fume exposure.
Age and Vulnerability
Certain age groups, such as infants, children, and the elderly, may be more vulnerable to the effects of toxic fumes. Their developing or weakened immune systems and bodies can make them more susceptible to the health risks associated with toxic fume exposure. Extra caution should be taken to protect these vulnerable populations from exposure to toxic fumes.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors, such as temperature, humidity, and air quality, can influence the behavior and impact of toxic fumes. Poor ventilation, for example, can increase the concentration of toxic fumes in an enclosed space and subsequently increase the risk of adverse health effects. It is important to consider and address these environmental factors to minimize the risk of toxic fume exposure.

Common Workplace Hazards
Solvents and Cleaning Agents
Many workplaces utilize solvents and cleaning agents that can release toxic fumes. These substances, often found in industries such as manufacturing, printing, and janitorial services, can contain volatile organic compounds and other harmful chemicals. Proper ventilation and the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) are essential in minimizing exposure to toxic fumes in these work environments.
Industrial Chemicals
Workers in industries such as chemical manufacturing, construction, and oil refining may be exposed to toxic fumes from various industrial chemicals. These chemicals can include asbestos, lead, mercury, and many others, which can have severe health effects if inhaled. Implementing rigorous safety protocols and providing workers with adequate protective gear are crucial in preventing toxic fume exposure in these industries.
Paints and Varnishes
Paints and varnishes often contain volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that can release toxic fumes during and after application. Workers in the painting and construction industries are particularly at risk of inhaling these fumes. Proper ventilation, respiratory protection, and adherence to safety guidelines can help minimize the health risks associated with exposure to toxic fumes from paints and varnishes.
Pesticides and Herbicides
Agricultural workers, gardeners, and pest control professionals may encounter toxic fumes from pesticides and herbicides. These chemicals are designed to be toxic to pests and can pose risks to human health as well. Following proper handling procedures, using appropriate protective equipment, and minimizing direct exposure are essential in preventing the adverse effects of toxic fumes from pesticides and herbicides.
Automotive Exhaust
Automotive exhaust can release toxic fumes, such as carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides, into the air. Workers in the automotive industry, especially those involved in repair and maintenance, may be exposed to these fumes. Proper ventilation systems and the use of protective equipment can help reduce the risk of toxic fume exposure in automotive workplaces.
Formaldehyde and VOCs (Volatile Organic Compounds)
Formaldehyde and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are commonly found in various products, including building materials, furniture, and cleaning supplies. Workers in construction, manufacturing, and janitorial services may come into contact with toxic fumes from these substances. Ensuring good ventilation, using appropriate personal protective equipment, and substituting toxic materials with safer alternatives are key measures in preventing toxic fume exposure in these industries.
Treatment and Prevention
First Aid Measures
If exposed to toxic fumes, it is important to take immediate first aid measures. These may include moving to a well-ventilated area, removing contaminated clothing, and rinsing affected areas with plenty of water. In case of ingestion or significant exposure, it is crucial to seek medical attention promptly.
Medical Treatments
Medical treatments for toxic fume exposure depend on the specific chemicals involved and the severity of symptoms. They may include supportive care, such as oxygen therapy for respiratory distress, the administration of antidotes for specific chemicals, and monitoring for long-term health effects. Prompt medical evaluation and treatment are vital in minimizing the potential complications of toxic fume exposure.
Preventing Exposure to Toxic Fumes
Preventing exposure to toxic fumes is crucial in protecting your health and well-being. This can be achieved by implementing effective safety measures and practices, such as proper ventilation, minimizing the use of harmful chemicals, and using personal protective equipment (PPE) when necessary. Additionally, following appropriate handling and storage guidelines for toxic substances can help reduce the risk of exposure.
Safety Measures in Workplaces
Workplaces should implement comprehensive safety measures to minimize the risk of toxic fume exposure. These measures may include proper training and education for employees, regular monitoring of air quality, strict adherence to safety protocols, and providing adequate ventilation systems and personal protective equipment (PPE). Regular inspections and assessments should also be conducted to identify and mitigate potential hazards.
Proper Ventilation and Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Proper ventilation is essential in preventing the accumulation of toxic fumes in enclosed spaces. This can be achieved through the installation and maintenance of effective ventilation systems, such as exhaust fans, air filters, and proper air exchange rates. Additionally, the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) such as respiratory masks, gloves, and eye protection can provide an added layer of defense against toxic fumes.


Legal and Regulatory Framework
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) Standards
In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets and enforces standards to ensure safe and healthy workplaces. These standards include regulations and guidelines related to hazardous substances, ventilation systems, personal protective equipment, and employee training. Employers are legally required to comply with OSHA standards to protect workers from the risks associated with toxic fume exposure.
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Regulations
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States is responsible for regulating and enforcing environmental laws. The EPA sets standards to control and reduce air pollution, including toxic fumes emitted by industries and vehicles. These regulations aim to protect both human health and the environment by minimizing the release of harmful chemicals into the air.
Worker’s Compensation Laws
Worker’s compensation laws vary by country and provide benefits to employees who suffer work-related illnesses or injuries. These laws can cover medical expenses, lost wages, and rehabilitation costs resulting from toxic fume exposure. Understanding and complying with worker’s compensation laws is crucial for employers to ensure the well-being and safety of their employees.
International Standards and Guidelines
Various international organizations, such as the International Labour Organization (ILO) and the World Health Organization (WHO), develop standards and guidelines to address occupational health and safety issues globally. These standards and guidelines provide valuable resources for governments, employers, and workers to prevent and manage the risks associated with toxic fumes and ensure the protection of human health worldwide.
Examples of Major Toxic Gas Incidents
Bhopal Gas Tragedy
The Bhopal gas tragedy, which occurred in December 1984 in India, is one of the most devastating industrial disasters in history. A pesticide plant leaked toxic methyl isocyanate gas, exposing thousands of people and causing immediate deaths and long-term health effects. The tragedy highlighted the importance of strict safety regulations and the need for effective emergency response plans to prevent and mitigate the impact of toxic gas incidents.
Chernobyl Disaster
The Chernobyl disaster, which occurred in April 1986 in Ukraine, involved a catastrophic nuclear accident. The explosion and subsequent fire released large amounts of radioactive materials into the air, causing immediate deaths and long-term health effects for workers and nearby residents. This incident reinforced the importance of adhering to stringent safety protocols in industries involving hazardous materials and the need for international cooperation in nuclear safety.
World Trade Center Dust and Toxins
The collapse of the World Trade Center towers on September 11, 2001, released a vast amount of toxic dust and fumes into the surrounding area. Rescue workers, firefighters, and nearby residents were exposed to harmful substances, including asbestos, lead, and other hazardous chemicals. The health effects of this exposure continue to impact individuals years after the incident, underscoring the importance of proper respiratory protection and decontamination procedures in emergency response situations.
Seveso Disaster
The Seveso disaster, which occurred in Italy in July 1976, involved a chemical explosion at a pesticide manufacturing plant. The explosion released a toxic cloud containing dioxin, a highly hazardous substance. The incident resulted in immediate deaths and a significant number of long-term health effects, emphasizing the need for strict monitoring, adherence to safety regulations, and effective emergency response plans.
Texas City Disaster
The Texas City disaster, which occurred in April 1947 in the United States, involved a massive explosion on a freighter carrying ammonium nitrate fertilizer. The explosion released toxic fumes, causing widespread destruction and multiple fatalities. This disaster led to increased awareness of the hazards associated with the transportation and handling of hazardous materials, prompting the development of safety regulations and guidelines that are still in place today.

Case Studies
Health Impacts of Industrial Pollution in a Local Community
A case study examining the health impacts of industrial pollution on a local community can shed light on the specific risks and consequences of toxic fume exposure. This study may involve assessing the prevalence of respiratory diseases, evaluating the levels of toxic chemicals in the air and water, and analyzing health records and medical data. Such case studies can help identify the underlying causes and effects of toxic fume exposure, and inform the development of strategies to protect the community’s health.
Occupational Exposure in a Chemical Plant
Conducting a case study on occupational exposure in a chemical plant can provide insights into the risks faced by workers in this environment. This study may involve monitoring air quality, assessing employee health through medical examinations, and conducting interviews or surveys with workers. Understanding the specific hazards and health effects associated with working in a chemical plant can contribute to the development of occupational safety measures and guidelines to protect workers’ health.
Effects of Indoor Air Pollution on Human Health
A case study investigating the effects of indoor air pollution, including toxic fumes, on human health can highlight the potential risks within households and workplaces. This study may involve monitoring air quality in different indoor environments, assessing the prevalence of respiratory symptoms in occupants, and evaluating the sources of indoor air pollution. By understanding the impact of indoor air pollution on human health, effective strategies can be developed to improve indoor air quality and minimize toxic fume exposure.
Environmental and Health Consequences of Emissions from Coal Power Plants
A case study focusing on the environmental and health consequences of emissions from coal power plants can provide valuable insights into the risks associated with this industry. This study may involve analyzing air and water quality data, assessing the prevalence of respiratory diseases and other health conditions in nearby communities, and evaluating the effectiveness of emission control measures. By understanding the impacts of coal power plant emissions, appropriate measures can be taken to reduce toxic fume exposure and protect the environment and public health.
Conclusion
Breathing in toxic fumes can indeed make you sick, as exposure to these harmful substances can result in a wide range of immediate and long-term health effects. Understanding the sources, chemicals, symptoms, and factors influencing susceptibility to toxic fumes is crucial to protect your health. Additionally, implementing safety measures, such as proper ventilation and the use of personal protective equipment, can help prevent exposure to toxic fumes in workplaces. By following regulations and guidelines, raising awareness, and conducting rigorous case studies, we can foster a safer environment and minimize the risks associated with toxic fume exposure. Prioritizing the health and well-being of individuals and communities is essential in ensuring a sustainable and safe future for all.