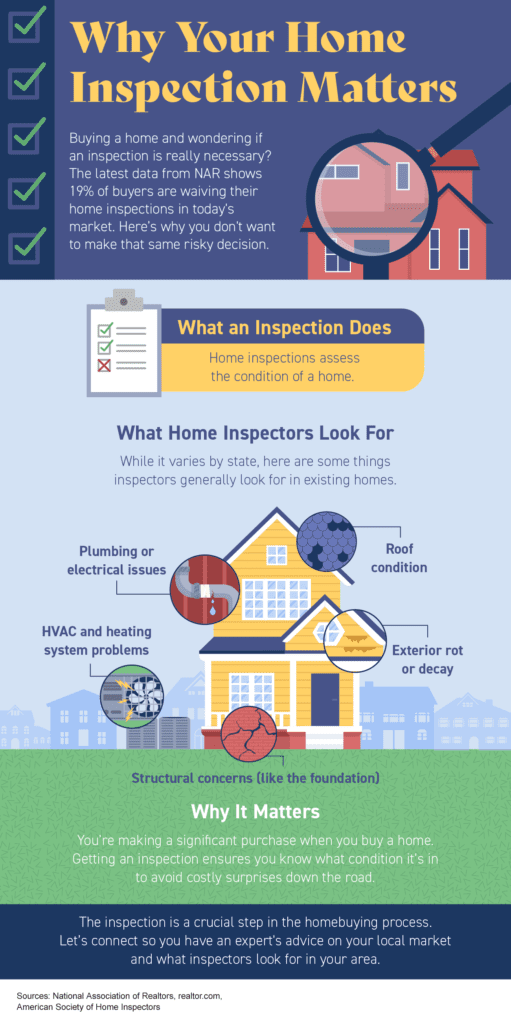
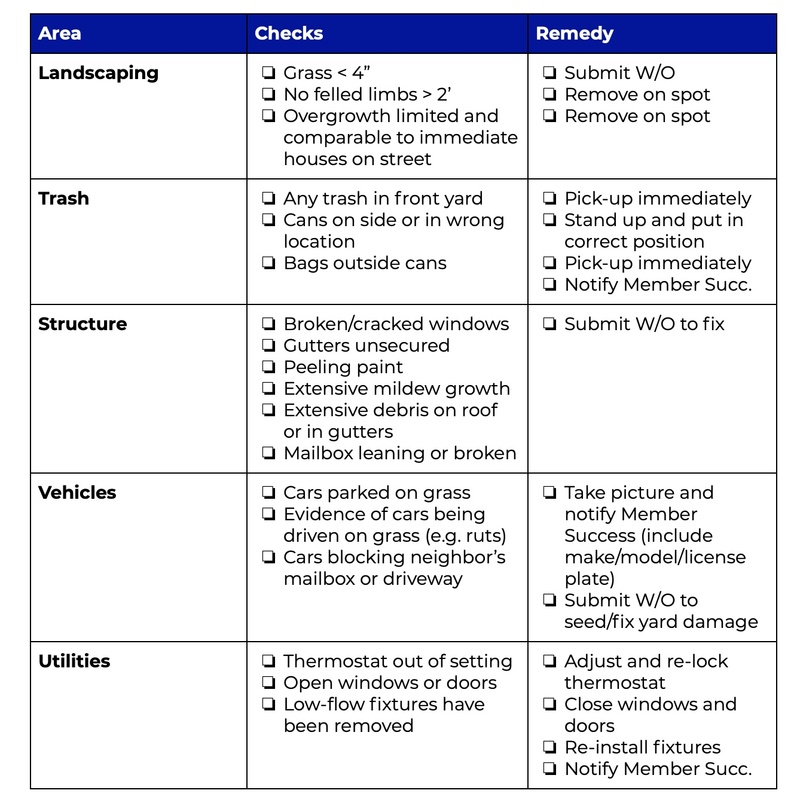
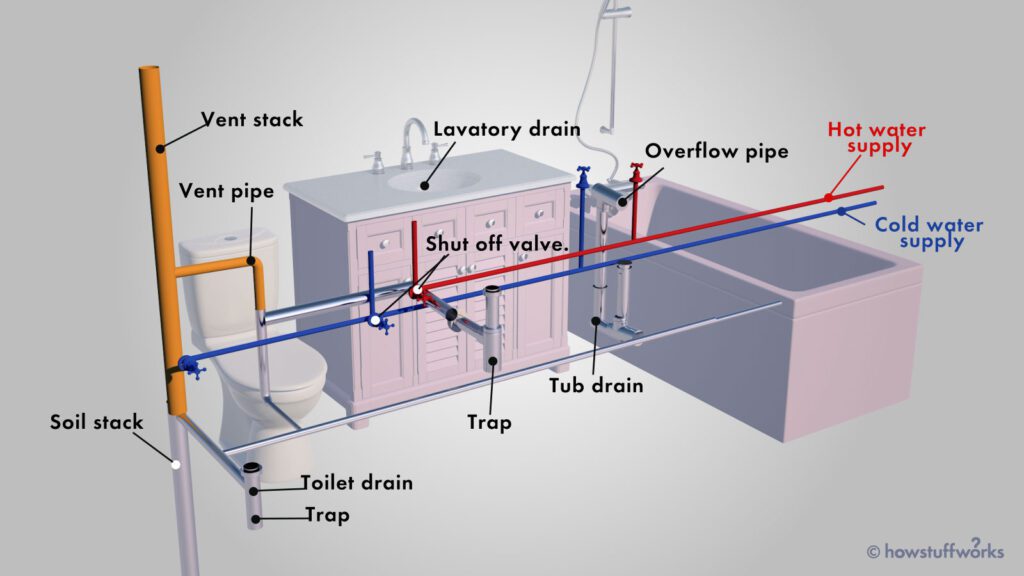
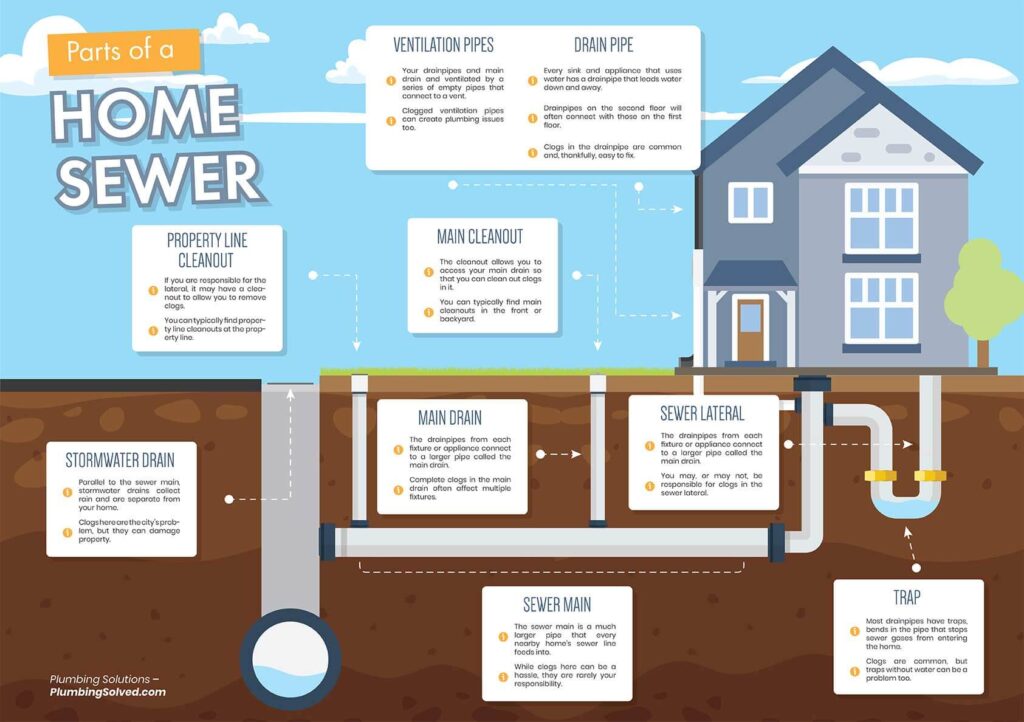
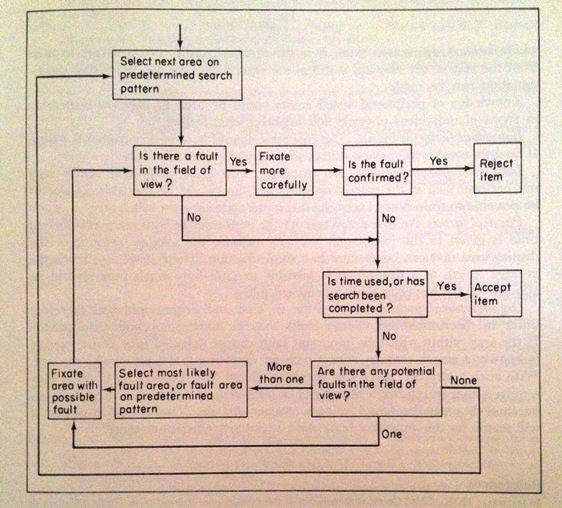
In the world of quality control and safety measures, inspection plays a crucial role. It focuses on scrutinizing products, processes, and facilities to ensure that they meet the desired standards and regulations. Inspection aims to identify any defects, faults, or deviations that may arise during the manufacturing or production process. By conducting thorough examinations and assessments, inspection helps businesses maintain high-quality standards, comply with industry regulations, and ultimately provide safe and reliable products to consumers. Inspection is a process that involves examining, evaluating, and assessing various aspects of a particular object, system, or environment. It is concerned with ensuring compliance with legal and regulatory requirements, controlling and assuring product quality, maintaining health and safety standards, monitoring building and construction projects, assessing transportation infrastructure, evaluating environmental impact, ensuring food safety, conducting pharmaceutical and medical inspections, and performing insurance and risk assessments.
Definition of Inspection
Inspection refers to the activity of carefully examining or scrutinizing something to determine its condition, quality, or compliance with specified requirements. It is a systematic process that involves observation, measurement, testing, and documentation. Whether it’s a product, process, facility, or area of operation, inspections play a crucial role in ensuring standards and regulations are met, identifying potential risks or defects, and maintaining the overall quality and safety.
Meaning of Inspection
Inspection entails the thorough examination of various aspects to ensure that they meet predetermined criteria. This can involve visual inspections, tests, audits, or any other form of assessment that helps to provide confidence in the reliability, safety, and compliance of the subject under inspection. The purpose of inspection is to identify any deviations from established standards, detect potential hazards or risks, and maintain the quality, integrity, and safety of the inspected object.
Purpose of Inspection
The primary purpose of inspection is to uphold standards, regulations, and policies. It ensures that the inspected entities or processes are compliant with legal and regulatory requirements, guaranteeing public safety, product quality, and environmental preservation. Inspection serves as a means of verifying and ensuring the reliability, performance, and safety of various objects, systems, or environments. It helps to identify and rectify any non-compliance, deviations, defects, or risks, and promotes continuous improvement in various industries and sectors.
Types of Inspection
Inspections can take various forms depending on the sector, industry, and specific requirements. Here are some common types of inspection:
- Visual Inspection: This involves a detailed visual examination of the object or system to detect any visible defects, damages, or abnormalities. It is often the first step in the inspection process and can be performed manually or with the aid of technology.
- Functional Inspection: This type of inspection focuses on assessing the performance and functionality of the object or system under inspection. It involves conducting tests, measurements, or simulations to ensure that the item or process works as intended.
- Documentary Inspection: This inspection involves verifying the accuracy, completeness, and compliance of documents, records, or certificates related to the inspected entity. It ensures that the necessary paperwork is in order and that the relevant standards and regulations are being followed.
- Sampling Inspection: In this type of inspection, a representative sample is selected from a larger population and thoroughly examined to make inferences or judgments about the entire lot or batch. It is commonly used in quality control processes to assess the overall quality of a production run.
- Periodic Inspection: This refers to regular inspections conducted at predetermined intervals to ensure continuous compliance with regulations, standards, or maintenance requirements. It helps to identify any gradual deterioration, wear and tear, or changes that may occur over time.
- Ad Hoc Inspection: Ad hoc inspections are unplanned, often triggered by specific events or circumstances. They are conducted in response to complaints, accidents, incidents, or suspected non-compliance to investigate and address immediate concerns.

Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Compliance with legal and regulatory requirements is of paramount importance in various industries and sectors. Inspection plays a vital role in ensuring that businesses, products, and services adhere to the necessary standards and regulations.
Importance of Compliance
Compliance with laws and regulations ensures the protection of consumers, employees, and the environment. It helps to prevent fraud, ensure fair competition, maintain product safety, and promote ethical practices. Inspection plays a crucial role in ensuring that businesses operate within the legal framework, comply with industry-specific regulations, and maintain the integrity and safety of their operations.
Inspection of Businesses
Inspections of businesses focus on assessing compliance with legal, regulatory, and industry-specific requirements. These inspections can cover various aspects, such as occupational health and safety, employee working conditions, financial reporting, environmental impact, and adherence to specific business licensing requirements.
Inspectors may visit businesses on a regular basis or conduct surprise inspections to verify compliance with relevant laws and regulations. They assess records, conduct interviews, review procedures, and inspect facilities to ensure that businesses are operating legally and following appropriate standards.
Inspection of Products and Services
Inspection of products and services is essential to protect consumers and ensure quality and safety. Regulatory bodies may conduct inspections on goods such as food items, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and consumer products to verify compliance with labeling requirements, quality standards, and safety regulations.
Service-related inspections focus on sectors such as healthcare, hospitality, transportation, and professional services. Inspectors assess the quality, safety, and adherence to service standards to safeguard consumers’ interests and regulate industry practices.
Quality Control and Assurance
Product quality is paramount for businesses to maintain customer satisfaction and ensure the success of their operations. Inspection is a vital element in quality control and assurance processes.
Ensuring Product Quality
Inspection plays a crucial role in ensuring that products meet predefined quality standards and specifications. It helps to identify any defects or deviations from the desired attributes. Through visual inspection, functional testing, and rigorous quality control checks, businesses can assess the quality of raw materials, intermediate products, and finished goods.
By implementing robust inspection processes, businesses can prevent the delivery of defective products, reduce customer complaints, and maintain a strong reputation for delivering high-quality goods.
Inspection in Manufacturing Processes
Inspection is integrated into various stages of the manufacturing process to monitor and verify quality. It can include incoming inspection of raw materials, in-process inspection during production, and final inspection before product release.
By conducting inspections at every stage, businesses can identify potential issues or defects early, allowing for timely corrective actions. This proactive approach helps to minimize waste, improve production efficiency, and ensure consistent product quality.
Quality Inspection Techniques
To ensure reliable and accurate inspection results, various techniques and methods are employed. These include visual inspection, measurement and testing, sampling, statistical process control, and non-destructive testing.
Visual inspection involves the use of visual cues to identify defects or abnormalities. It can be aided by magnification tools or imaging technologies to enhance inspection accuracy.
Measurement and testing techniques involve assessing critical product dimensions, characteristics, or performance attributes. This can include the use of precision instruments, testing equipment, or automated systems to measure physical properties, assess functionality, or verify compliance with specific standards.
Sampling techniques are utilized when inspecting large quantities of products or materials. By selecting representative samples and subjecting them to inspection, businesses can make inferences about the quality of the entire lot.
Statistical process control techniques enable the monitoring and control of manufacturing processes to ensure consistent quality. By analyzing data collected during inspections and production, businesses can identify trends, deviations, or process variations that may impact product quality.
Non-destructive testing methods are used to assess the integrity of materials or structures without causing any damage. These techniques can include ultrasound, X-ray scanning, or thermal imaging, providing valuable insights into the quality or structural integrity of inspected items.
By employing a combination of these techniques, businesses can establish robust quality control and assurance processes, ensuring the delivery of high-quality products to their customers.


Health and Safety
The health and safety of individuals within workplaces and public environments are of utmost importance. Inspection plays a key role in maintaining safe conditions and complying with applicable regulations.
Inspection of Workplace Environment
Workplace inspections focus on assessing the overall safety and health conditions within a workplace. These inspections aim to identify potential hazards, promote safe working practices, and ensure compliance with occupational health and safety regulations.
During workplace inspections, trained inspectors assess different aspects such as ergonomics, fire safety, electrical safety, use of personal protective equipment (PPE), proper handling of hazardous substances, and adherence to ventilation and hygiene standards.
Inspectors typically conduct interviews, review accident logs, check safety equipment, and inspect the premises to ensure safe working conditions for employees.
Safety Inspection Procedures
Safety inspections involve meticulous examination and evaluation of safety systems, equipment, and protocols to ensure that they meet applicable safety regulations. These inspections focus on identifying any potential risks, hazards, or deficiencies that could pose a threat to the safety of individuals or the environment.
Safety inspection procedures can include assessing:
- Compliance with fire safety regulations, including the presence and functionality of fire alarms, extinguishers, emergency exits, and evacuation plans.
- Compliance with electrical safety regulations, such as proper grounding, appropriate wiring, and regular maintenance of electrical systems.
- Safety standards in the handling and storage of potentially hazardous materials, including checking for proper labeling, storage conditions, and control measures.
- Adequate training and implementation of safe working practices, including the use of personal protective equipment, adherence to ergonomic guidelines, and proper manual handling techniques.
- Safety protocols and procedures in high-risk environments such as construction sites, factories, or laboratories.
By conducting regular safety inspections, businesses and organizations can prevent accidents, injuries, and health hazards, ensuring the well-being of their employees and visitors.
Occupational Health and Safety Regulations
Occupational health and safety regulations are specific requirements set by governing bodies to protect workers and the general public from workplace-related hazards. These regulations outline the responsibilities of employers, employees, and regulatory authorities in ensuring a safe and healthy working environment.
Inspections play a crucial role in enforcing occupational health and safety regulations. Regulatory authorities may conduct inspections to verify compliance, address complaints, conduct incident investigations, and promote continuous improvement in safety practices.
By inspecting workplaces and enforcing health and safety standards, regulatory bodies contribute to the prevention of occupational injuries, illnesses, and fatalities, as well as the overall well-being of the working population.
Building and Construction
The construction industry involves complex processes that require adherence to strict regulations, quality standards, and safety practices. Inspection plays a vital role in ensuring that building and construction projects meet the necessary requirements.
Construction Site Inspections
Construction site inspections are vital to monitor project progress, compliance with regulations, and adherence to safety protocols. Inspectors assess various aspects of a construction site, including safety practices, regulatory compliance, structural integrity, and adherence to approved plans.
Construction site inspections typically cover:
- Health and safety practices, including the presence of safety barriers, proper scaffolding, fall protection systems, and adherence to safe working at heights protocols.
- Compliance with building codes and regulations, including proper foundation and structural elements, fire safety measures, electrical installations, and plumbing systems.
- Construction project documentation, including permits, plans, and certifications for specialized activities such as excavation, welding, or crane operation.
- Environmental impact assessment to ensure that construction activities do not cause undue harm to the surroundings or violate environmental regulations.
- Inspection of material quality, including checking the specifications, storage conditions, and usage of approved materials.
By conducting regular construction site inspections, regulatory authorities, project owners, and contractors can ensure compliance with regulations, identify potential risks or issues, and promote safe and environmentally conscious construction practices.
Electrical and Plumbing Inspections
Inspections of electrical and plumbing systems are critical to ensuring safety, functionality, and compliance with relevant codes and standards. Electrical inspections involve assessing the integrity, safety, and compliance of electrical installations, wiring, and appliances.
Plumbing inspections evaluate the installation, maintenance, and performance of plumbing systems, including fixtures, pipes, drainage systems, and wastewater treatment facilities.
These inspections typically involve checking for:
- Compliance with electrical and plumbing codes and regulations.
- Adherence to safety standards, such as grounding and proper insulation in electrical systems, or prevention of cross-contamination in plumbing systems.
- Functional performance of electrical devices, such as switches, outlets, circuit breakers, and lighting fixtures.
- Plumbing system integrity, including proper drainage, sewage disposal, water supply, and backflow prevention mechanisms.
- Compliance with energy efficiency and conservation requirements, with a focus on electrical lighting, appliances, or water conservation measures.
Electrical and plumbing inspections are vital to ensuring the safety of building occupants, efficient energy utilization, and compliance with regulatory standards.
Inspection of Completed Structures
Inspection of completed structures plays a crucial role in approving buildings for occupancy and ensuring compliance with applicable codes and regulations. These inspections assess the overall structural integrity, safety features, and functionality of a building or structure.
Inspectors typically examine various elements of the completed structure, including:
- Structural components, such as beams, columns, foundations, and load-bearing walls, to ensure compliance with engineering design and safety requirements.
- Building envelope, including walls, roofs, and windows, to assess insulation, weatherproofing, and energy efficiency.
- Fire safety measures, evaluating the presence and functionality of fire alarms, sprinkler systems, emergency exits, and fire-resistant materials.
- Accessibility features, such as ramps, elevators, and disabled access points, to ensure compliance with disability accessibility standards.
- Compliance with zoning regulations, setback requirements, and adherence to approved building plans and permits.
By inspecting completed structures, regulatory authorities can ensure that buildings are safe for occupancy and do not pose any risks to inhabitants or surrounding areas. This inspection process provides assurance to owners, occupants, and the public that the structures meet the necessary standards as defined by the applicable building codes and regulations.

Transportation and Infrastructure
Inspection plays a pivotal role in maintaining the integrity, safety, and functionality of transportation and infrastructure systems. Whether it relates to vehicles, bridges, highways, airports, or railways, inspections are crucial for ensuring compliance with regulations and identifying potential risks or deficiencies.
Vehicle Inspections
Vehicle inspections are conducted to assess the safety, emissions compliance, and overall operational condition of automobiles, trucks, buses, and other motorized vehicles. These inspections aim to identify defects, maintenance requirements, or modifications that may affect the vehicle’s performance, safety, or compliance with regulatory standards.
Common types of vehicle inspections include:
- Preventive Maintenance Inspections: These inspections focus on regular maintenance activities to ensure vehicles are in safe operating condition, including checking fluid levels, tire conditions, brakes, lights, and other critical components.
- Safety Inspections: Safety inspections verify compliance with safety standards and regulations. They may include checking the integrity of the vehicle’s structure, inspection of safety systems (such as seat belts and airbags), and measures to prevent emissions and noise pollution.
- Periodic Inspections: Periodic inspections assess the overall condition of a vehicle and its compliance with regulations or standards. They often include emissions testing, mechanical checks, and verification of the vehicle’s documentation (such as registration, insurance, and appropriate licensing).
By conducting vehicle inspections, regulatory bodies, law enforcement agencies, and transportation authorities can ensure that vehicles on the road are safe, compliant, and pose minimal risks to drivers, passengers, and pedestrians.
Bridge and Highway Inspections
Inspections of bridges and highways are crucial for ensuring their structural integrity, identifying maintenance needs, and addressing potential risks or hazards. These inspections aim to assess the condition of bridges, roadways, pavements, and related structures.
Bridge and highway inspections typically focus on:
- Structural components, evaluating the condition of beams, piers, abutments, and foundations to identify any signs of deterioration, corrosion, or structural vulnerabilities.
- Signs of wear and tear, including cracks, potholes, or other damages that may impact the safety and functionality of roadways.
- Traffic control devices, evaluating signage, lighting, road markings, and traffic signals to ensure clear communication and safe navigation for drivers.
- Drainage systems, assessing the effectiveness of drainage channels, culverts, and stormwater management measures to prevent flooding or erosion.
- Compliance with design codes, standards, and regulations, including load capacity requirements, highway geometrics, and accessibility features.
By conducting regular bridge and highway inspections, transportation authorities can ensure the safety and reliability of road networks, detect potential risks or hazards, and plan for necessary maintenance or improvement projects.
Airport and Railway Inspections
Airports and railway systems are complex infrastructures that require thorough inspections to ensure safety, efficiency, and regulatory compliance.
Airport inspections cover various aspects, including:
- Runway and taxiway conditions, ensuring functionality, proper lighting, and compliance with applicable regulations.
- Terminal facilities, assessing the safety, cleanliness, and accessibility for passengers, including fire safety measures, security systems, or baggage handling.
- Airfield lighting systems, verifying the proper functioning of runway lights, approach lights, and navigational aids to support safe aircraft operations.
- Compliance with aviation regulations, including air traffic control procedures, security protocols, and adherence to international standards.
Railway inspections typically focus on:
- Track condition, evaluating the operational safety and integrity of railway tracks, switches, and crossings.
- Rolling stock inspections, assessing the condition and compliance of locomotives, passenger cars, freight wagons, and related equipment.
- Station facilities, ensuring the safety, cleanliness, accessibility, and passenger amenities at railway stations.
- Compliance with railway safety regulations, including signaling systems, level crossings, train control systems, and emergency response preparedness.
By conducting regular inspections of airports and railways, regulatory bodies and transportation authorities can maintain high safety standards, ensure compliance with regulations, and provide the general public with reliable and efficient transportation services.
Environmental Impact
Inspections related to environmental impact aim to assess and manage the ecological and environmental sustainability of various activities, operations, or facilities. These inspections contribute to the preservation of natural resources, prevention of pollution, and compliance with environmental regulations.
Environmental Inspection Standards
Environmental inspection standards are designed to ensure that activities, processes, or facilities are conducted in a manner that minimizes environmental impact. These standards focus on various areas, including air quality, water management, waste management, and land conservation.
Environmental inspections typically cover:
- Compliance with emission regulations, ensuring that industries or facilities do not release pollutants beyond acceptable limits, causing air pollution or contributing to climate change.
- Water pollution control, verifying compliance with regulations related to wastewater treatment, stormwater management, water quality monitoring, or prevention of coastal or marine pollution.
- Waste management practices, assessing the proper handling, storage, treatment, and disposal of hazardous waste, solid waste, or other forms of waste generated from industrial, commercial, or residential activities.
- Preservation of natural resources and sensitive ecosystems, ensuring that activities or developments do not harm protected areas, endangered species, or critical habitats.
- Environmental impact assessments and monitoring, evaluating the potential or actual ecological impacts of projects, activities, or facilities and recommending mitigation measures to minimize adverse effects.
By conducting environmental inspections and enforcing environmental standards, regulatory bodies contribute to sustainable development, environmental protection, and the preservation of natural resources for future generations.
Inspection of Waste Management Practices
Inspections related to waste management focus on verifying compliance with regulations, ensuring proper waste segregation, treatment, storage, transportation, and disposal. These inspections aim to prevent environmental contamination, reduce the generation of waste, and promote recycling and reuse practices.
Inspections of waste management typically assess:
- Compliance with waste management regulations, including permits, licenses, and reporting requirements for waste generators, transporters, and disposal facilities.
- Adequacy of waste storage and handling facilities, assessing the condition of containers, storage areas, and potential risks of leakage, spillage, or accidents.
- Compliance with proper waste segregation and labeling practices, including the separation of hazardous waste, biohazardous waste, recyclables, or organic waste.
- Verification of waste transportation practices, ensuring that waste is transported by licensed carriers and that regulatory requirements on labeling, manifesting, and secure containment are met.
- Evaluation of treatment, recycling, or disposal facilities, assessing compliance with applicable environmental standards and verifying proper handling of different types of waste.
By conducting inspections of waste management practices, regulatory bodies can ensure the safe handling and disposal of waste, minimize environmental contamination, and promote sustainable waste management practices.
Pollution Control Inspections
Pollution control inspections aim to assess and control various sources of pollution, including air pollution, water pollution, soil contamination, or noise pollution. These inspections focus on identifying potential pollutants, monitoring compliance with regulations, and enforcing pollution control standards.
Pollution control inspections typically include:
- Air quality assessments, measuring pollutant levels, monitoring compliance with emissions limits, and evaluating the effectiveness of air pollution control technologies.
- Water pollution monitoring, assessing the quality of surface water or groundwater sources, identifying potential pollution sources, and enforcing regulations on discharges into water bodies.
- Soil contamination assessments, evaluating the presence and impact of hazardous substances in soil, assessing risks to human health and the environment, and enforcing remediation requirements.
- Noise pollution control, evaluating noise levels in different environments, assessing compliance with noise regulations, and implementing measures to mitigate excessive noise emissions.
By conducting pollution control inspections, regulatory bodies help to protect public health, minimize adverse ecological impacts, and ensure compliance with pollution control regulations in various industries and areas.


Food Safety
Food safety inspections are critical to ensuring that the handling, processing, and distribution of food and beverages meet specified quality and safety standards. These inspections aim to protect consumers from contamination, improper handling, or misleading labeling.
Inspection of Food Handling and Processing Facilities
Food handling and processing facilities, such as restaurants, grocery stores, factories, or warehouses, are subject to inspections to verify compliance with food safety regulations. These inspections focus on the cleanliness, hygiene practices, and proper control of food storage, preparation, and handling.
Inspections of food handling and processing facilities include:
- Verification of compliance with hygiene standards, including cleanliness of premises, control of pests, sanitation practices, and the presence of handwashing facilities.
- Inspection of food storage areas, verifying proper temperature control, separation of raw and cooked foods, storage conditions, and adherence to expiration dates.
- Assessment of food preparation practices, ensuring proper cooking temperatures, prevention of cross-contamination, safe thawing and reheating methods, and compliance with allergen control requirements.
- Verification of proper labeling practices, including accurate product labeling, ingredient lists, nutritional information, and allergen warnings.
- Documentation reviews, including record-keeping of temperature logs, supplier certifications, lot tracing, and appropriate training records for food handlers.
By conducting inspections of food handling and processing facilities, regulatory bodies ensure the safety and quality of food products, reduce the risk of foodborne illnesses, and protect the interests of consumers.
Food Hygiene Inspections
Food hygiene inspections focus on assessing the personal hygiene practices of food handlers, ensuring that they adhere to proper hygiene standards and prevent contamination during food preparation and handling.
Common areas inspected during food hygiene inspections include:
- Personal cleanliness, ensuring that food handlers maintain good personal hygiene, including regular handwashing, use of appropriate protective clothing, and absence of contagious illnesses.
- Training and knowledge of food safety practices, verifying that food handlers are familiar with proper food handling techniques, temperature control, allergen management, and cleaning procedures.
- Proper storage of food products, ensuring that perishable items are stored at appropriate temperatures, food is protected from contamination, and the use of expired or spoiled ingredients is prevented.
- Prevention of cross-contamination, assessing practices to avoid the transfer of harmful bacteria, allergens, or contaminants between different food items or preparation areas.
- Cleaning and sanitation practices, verifying the cleanliness of food preparation surfaces, equipment, utensils, and the presence of appropriate cleaning and sanitizing agents.
Food hygiene inspections play a critical role in preventing foodborne illnesses, ensuring proper food handling practices, and maintaining high standards of food safety across various establishments.
Food Labeling and Packaging Inspections
Food labeling and packaging inspections aim to verify the accuracy, completeness, and compliance of labeling information, including ingredients, nutritional claims, health claims, and allergy warnings.
Inspections of food labeling and packaging typically include:
- Verification of ingredient lists, ensuring that all ingredients are properly listed, allergens are clearly identified, and no misleading information is present.
- Assessment of nutritional information, ensuring accurate reporting of calories, fat content, sugar content, and other relevant nutritional data.
- Compliance with specific labeling requirements, such as country of origin labeling, organic certification, halal or kosher labeling, or product-specific regulations.
- Examination of health claims and nutritional claims, ensuring that claims made on packaging or in advertising are supported by scientific evidence and comply with applicable regulations.
- Presentation and packaging standards, assessing the clarity, legibility, and appropriate language used on food labels, as well as the presence of necessary warnings or cautionary statements.
By conducting inspections of food labeling and packaging, regulatory bodies ensure that consumers receive accurate information about the products they purchase, allowing them to make informed choices and reducing the risk of misrepresentation or fraud.
Pharmaceutical and Medical Inspections
Inspections related to pharmaceutical and medical industries focus on ensuring that drugs, medical devices, clinical trials, and research activities adhere to regulatory requirements, safety standards, and ethical guidelines.
Drug Manufacturing Inspections
Drug manufacturing inspections aim to verify compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to ensure the safety, efficacy, and quality of pharmaceutical products. These inspections are essential for establishing robust quality assurance systems and maintaining the integrity of drug manufacturing processes.
Key areas covered in drug manufacturing inspections include:
- Facility inspection, assessing the suitability, cleanliness, and integrity of manufacturing areas, storage facilities, equipment, and documentation systems.
- Process controls, verifying that appropriate measures are in place to control critical manufacturing processes, ensure consistent quality of pharmaceutical products, and prevent contamination or cross-contamination.
- Quality control, evaluating the implementation and effectiveness of quality control procedures, including testing methods, sampling protocols, and laboratory practices.
- Documentation and record-keeping, ensuring the proper documentation of manufacturing processes, batch records, materials used, deviations, and any changes made during production.
- Compliance with regulatory requirements, manufacturing regulations, and standards, including adherence to licensing requirements, facility certifications, and obligations for reporting safety-related information.
By conducting drug manufacturing inspections, regulatory bodies play a crucial role in ensuring the availability of safe and effective pharmaceutical products and maintaining public trust in the healthcare industry.
Medical Equipment Inspections
Inspections of medical equipment verify compliance with regulatory requirements and safety standards to ensure the reliability and performance of medical devices. These inspections aim to prevent the use of faulty or substandard equipment that may pose risks to patient safety or compromise the effectiveness of medical procedures.
Inspections of medical equipment typically focus on:
- Compliance with manufacturing and quality standards, assessing the design, production, and quality assurance processes associated with medical devices.
- Verification of calibration and maintenance practices, ensuring that equipment is regularly maintained, calibrated, and functional for accurate diagnosis, treatment, or monitoring.
- Safety features and labeling, evaluating the presence and functionality of safety mechanisms, clear labeling, and appropriate instructions for use of medical devices.
- Appropriate documentation and traceability, including the availability of manuals, device history records, labeling records, and corrective or preventive actions taken to address any safety concerns or defects.
By conducting inspections of medical equipment, regulatory bodies and healthcare institutions ensure the safety and reliability of medical devices, promote patient safety, and minimize potential risks during medical procedures.
Clinical Trials and Research Inspections
Inspections related to clinical trials and research aim to ensure compliance with ethical guidelines, regulatory requirements, and scientific integrity. These inspections play a crucial role in protecting human subjects involved in clinical trials, safeguarding data integrity, and verifying the adherence to approved protocols.
Inspections of clinical trials and research activities typically include:
- Compliance with ethical guidelines, verifying that clinical trials are conducted in accordance with relevant ethical standards, informed consent procedures, and protection of vulnerable populations.
- Adherence to applicable regulatory requirements, ensuring compliance with regulations related to investigational new drugs, data privacy, adverse event reporting, and protocol deviations.
- Scientific integrity and data quality, ensuring the accuracy, completeness, and reliability of data generated during the clinical trial or research study.
- Proper documentation and record-keeping, including the availability of study protocols, case report forms, investigational product accountability records, and other essential documentation.
- Site inspection and monitoring, evaluating the suitability of research facilities, the experience and qualifications of investigators, the availability of necessary equipment, and the provision of adequate informed consent procedures for study participants.
By conducting inspections of clinical trials and research activities, regulatory bodies, ethics committees, and sponsors ensure the ethical conduct of research studies, protect study participants, and maintain the validity and reliability of scientific results.
Insurance and Risk Assessment
Inspections form an integral part of insurance and risk assessment processes. These inspections assist insurers and risk assessors in evaluating potential risks, assessing the quality and condition of insured objects, and estimating insurance premiums.
Inspection for Insurance Purposes
Inspections for insurance purposes involve the assessment of risks associated with insurable objects, such as properties, vehicles, or other valuable assets. These inspections help insurers determine the appropriate coverage, conditions, and pricing for insurance policies.
Insurance inspections generally focus on:
- Property conditions and hazards, evaluating the structural integrity, fire safety measures, proximity to potential risks (such as flood zones or earthquake fault lines), and any previous claims history.
- Vehicle inspection, verifying the overall condition, maintenance practices, and any potential risks associated with the insured vehicle, such as modifications, past accidents, or use in high-risk locations.
- Compliance with safety standards and regulations, ensuring that insured objects meet appropriate safety requirements and adhere to building codes, zoning regulations, or traffic regulations.
By conducting inspections for insurance purposes, insurance companies enhance their ability to accurately assess risks, estimate potential losses, and provide appropriate coverage to policyholders.
Risk Assessment Inspections
Risk assessment inspections focus on identifying potential hazards, vulnerabilities, or risks associated with specific activities, environments, or operations. These inspections help assess the likelihood and impact of potential risks and develop risk management strategies to mitigate them effectively.
Risk assessment inspections typically involve:
- Hazard identification, identifying potential risks or hazards that may arise from specific activities, materials, or environments.
- Exposure assessment, evaluating the likelihood and extent of exposure to identified risks or hazards, considering factors such as frequency, duration, and intensity.
- Risk analysis, estimating the probability of an event or incident occurring and analyzing potential consequences or impacts on people, assets, or the environment.
- Risk evaluation, assessing the acceptability of identified risks based on predetermined criteria, including legal requirements, societal expectations, or economic considerations.
- Risk mitigation strategies, proposing corrective actions, control measures, or risk transfer mechanisms to reduce or manage the identified risks effectively.
By conducting risk assessment inspections, organizations can proactively identify risks, implement appropriate control measures, and develop comprehensive risk management strategies to protect their assets, employees, and stakeholders.
Inspection in Claims Evaluation
Inspections play a significant role in evaluating insurance claims and assessing the extent of loss or damages. These inspections focus on verifying the authenticity of claims, estimating the value of losses, and ensuring compliance with policy terms and conditions.
Inspections in claims evaluation often involve:
- Physical inspection of damaged property or assets, assessing the extent and nature of damages, and estimating repair or replacement costs.
- Verification of claimed losses, evaluating the authenticity and accuracy of loss-related documentation, such as invoices, receipts, or medical reports.
- Investigation of potential fraud or misrepresentation, conducting background checks, assessing claim history, and analyzing patterns or suspicious circumstances.
- Compliance with policy terms and conditions, ensuring that the claimed losses fall within the coverage specified in the insurance policy and assessing any limitations, exclusions, or deductible amounts.
- Coordination with specialists, such as engineers, adjusters, or medical professionals, to gather expert opinions or conduct detailed assessments of specialized claims.
By conducting inspections in claims evaluation, insurers ensure the fair settlement of claims, prevent fraudulent activities, and maintain the integrity and sustainability of the insurance industry.