If you’ve ever wondered why your indoor air quality seems to be less than ideal, you’re not alone. The air we breathe indoors can often be filled with various contaminants and pollutants that can negatively impact our health and well-being. From dust and allergens to volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and mold, there are several factors that contribute to poor indoor air quality. In this article, we’ll explore some of the common reasons why your indoor air quality may be less than satisfactory and provide you with practical solutions to improve the air you breathe in your home.

Common Indoor Air Pollutants
Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
Volatile Organic Compounds, also known as VOCs, are gases emitted from certain household products and materials. These can include cleaning chemicals, paints, adhesives, and even furniture. When VOCs are released into the air, they can contribute to poor indoor air quality. Breathing in high levels of VOCs can lead to irritation of the eyes, nose, and throat, as well as respiratory issues and headaches. To reduce VOC levels in your home, opt for low-VOC or VOC-free products whenever possible, increase ventilation, and maintain a clean living environment.
Mold and Mildew
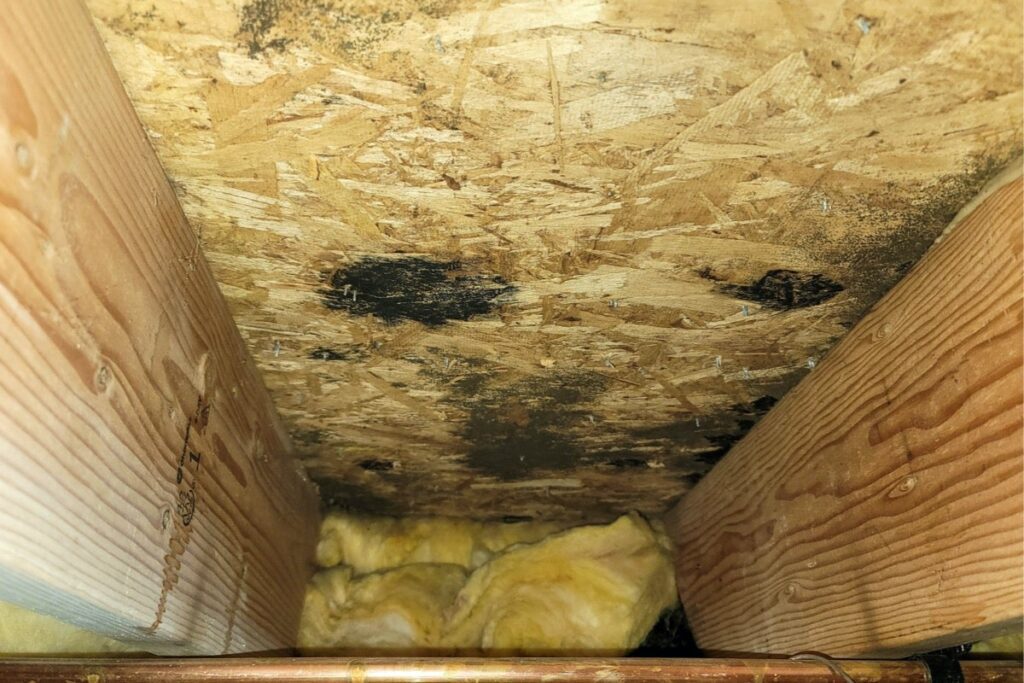
Mold and mildew are common indoor air pollutants that thrive in damp and poorly ventilated areas of the home. These fungi release spores into the air, which can cause a range of health issues when inhaled. Exposure to mold and mildew can lead to respiratory problems, allergies, and asthmatic symptoms. To prevent the growth of mold and mildew, it is important to keep your home dry and well-ventilated, promptly repair any water leaks or intrusion, and address any visible signs of mold growth.
Dust and Dust Mites
Dust and dust mites are another common cause of poor indoor air quality. Dust consists of various particles, including pollen, pet dander, and even tiny insect remains. Dust mites, which are microscopic organisms that thrive in dust, can also contribute to respiratory problems and allergies. Regular dusting, vacuuming, and washing of bedding can help minimize dust and dust mite activity, thus improving indoor air quality. It is also beneficial to use allergen-proof covers on mattresses and pillows.
Pet Dander and Allergens
If you have pets, their dander can contribute to poor indoor air quality. Pet dander is made up of tiny particles shed from the skin, fur, or feathers of animals. These particles can become airborne and trigger allergic reactions, especially in individuals with pet allergies. Regular grooming, vacuuming, and washing of pet bedding can help reduce the amount of pet dander in the home. It is also important to designate pet-free areas to minimize exposure to allergens.
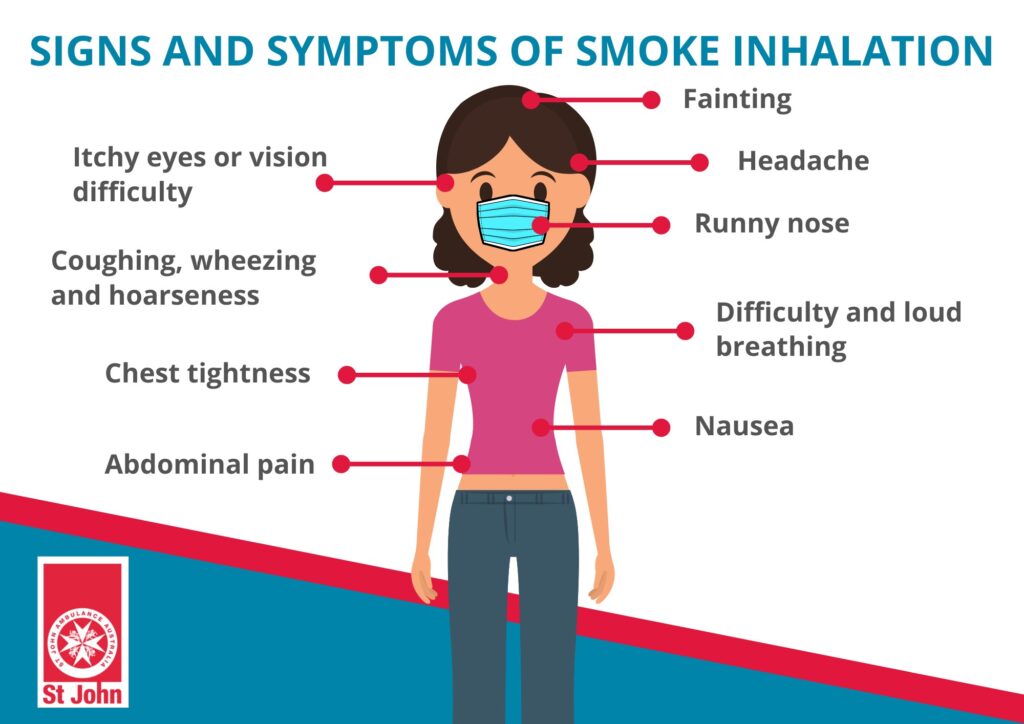
Cigarette Smoke
Cigarette smoke contains a wide range of harmful chemicals and toxins, including nicotine, formaldehyde, and benzene. Breathing in secondhand smoke can have serious health consequences, including respiratory issues, increased risk of lung cancer, and exacerbation of existing health conditions such as asthma. To improve indoor air quality, it is crucial to enforce a smoke-free environment and avoid smoking indoors.
Chemical Cleaning Products
Many conventional cleaning products contain harsh chemicals that can release fumes and contribute to poor indoor air quality. Ingredients such as ammonia, bleach, and volatile organic compounds found in these cleaners can cause respiratory irritation and other health problems. Opting for natural, eco-friendly cleaning alternatives or DIY cleaning solutions can significantly reduce the amount of pollutants released into the air during cleaning activities.
Pollen and Outdoor Allergens
While indoor air pollutants are a major concern, it’s important to remember that outdoor allergens can also impact indoor air quality. Pollen, grass, and other outdoor allergens can easily find their way indoors through open windows, doors, and on clothing. These allergens can cause allergic reactions and worsen symptoms for individuals with allergies. Regularly cleaning and maintaining your home and using air purifiers can help minimize the presence of these allergens indoors.
Radon Gas
Radon is a colorless and odorless gas that is produced naturally from the decay of uranium in soil, rock, and water. It can enter homes through cracks in the foundation, gaps around pipes, and other entry points. Long-term exposure to high levels of radon can increase the risk of developing lung cancer. It is important to have your home tested for radon and take appropriate measures to mitigate its levels if necessary. Professional radon mitigation systems can effectively reduce radon gas in your home.
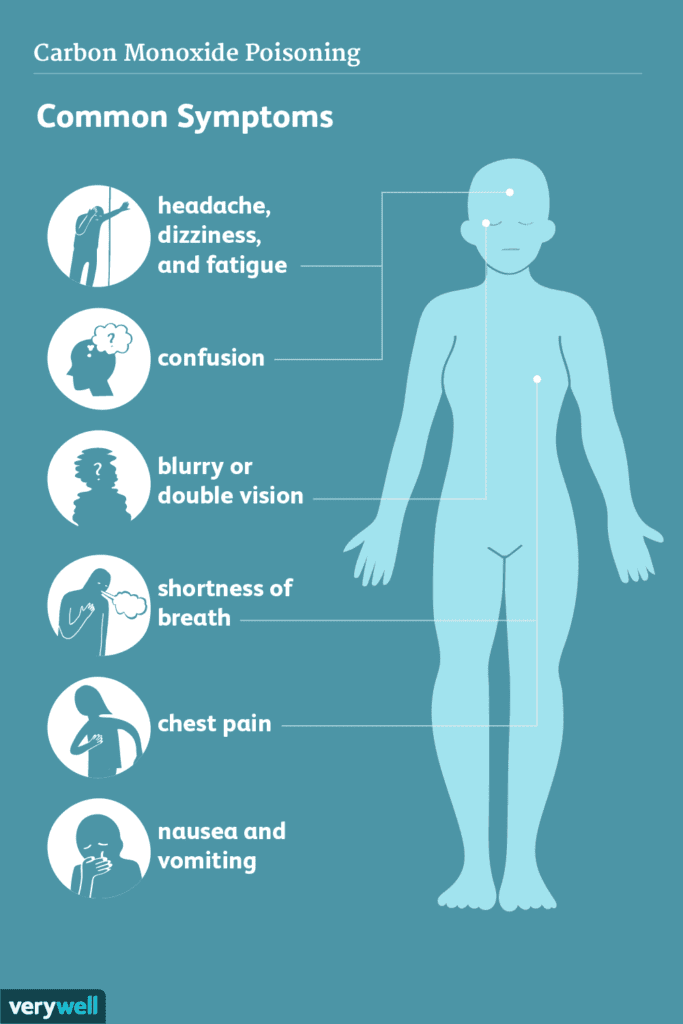
Carbon Monoxide
Carbon monoxide is a toxic gas that is produced by the incomplete combustion of fossil fuels, such as gas, oil, or coal. It is especially dangerous because it is odorless and colorless, making it difficult to detect without a carbon monoxide detector. Inhaling high levels of carbon monoxide can be life-threatening, causing symptoms such as dizziness, nausea, and headaches. Proper ventilation and regular maintenance of fuel-burning appliances, as well as the installation of carbon monoxide detectors, are crucial for preventing carbon monoxide poisoning.
Excess Humidity
High levels of humidity can create a breeding ground for mold, mildew, and dust mites, leading to various health issues. Excess moisture in the air can also cause discomfort, making it difficult to breathe and affecting overall indoor air quality. Proper ventilation, use of dehumidifiers, and fixing any moisture-related problems like leaks or condensation can help maintain optimal humidity levels and improve indoor air quality.
Health Effects of Poor Indoor Air Quality
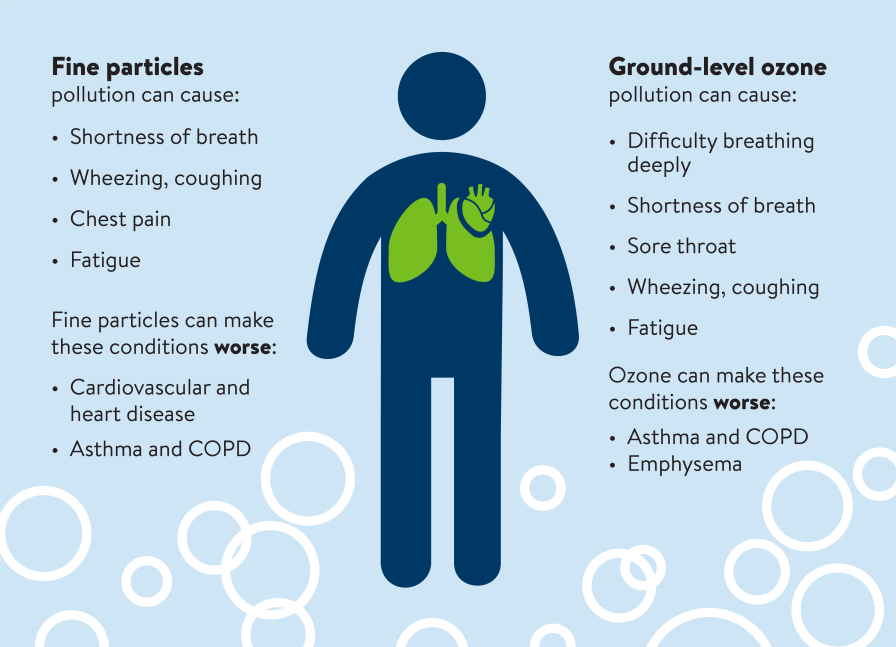
Respiratory Issues
One of the most common health effects of poor indoor air quality is respiratory issues. Breathing in pollutants, such as VOCs, mold spores, and dust particles, can irritate the respiratory system and lead to symptoms like coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath. Individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions, such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), may experience worsening of their symptoms.
Allergies and Asthma
Poor indoor air quality can trigger allergies and worsen asthma symptoms. Allergens like pet dander, pollen, and dust mites can cause allergic reactions, characterized by symptoms such as sneezing, runny nose, itchy eyes, and skin rashes. Asthma, a chronic inflammatory respiratory condition, can be exacerbated by inhaling pollutants, leading to increased coughing, wheezing, and difficulty breathing.
Headaches and Fatigue
Exposure to certain indoor air pollutants, such as VOCs and carbon monoxide, can cause headaches and fatigue. These symptoms can occur due to the irritation of the respiratory system, reduced oxygen levels, or the direct toxic effects of the pollutants on the central nervous system. Improving indoor air quality can help alleviate these symptoms and promote a healthier living environment.
Dizziness and Nausea
Inhaling high levels of certain indoor air pollutants, such as carbon monoxide or some VOCs, can lead to dizziness and nausea. Carbon monoxide poisoning, in particular, can be life-threatening if not detected and addressed promptly. If you experience persistent dizziness or nausea, it is important to seek fresh air and medical attention immediately.
Irritated Eyes, Nose, and Throat
Irritation of the eyes, nose, and throat is a common complaint associated with poor indoor air quality. Dust, allergens, and chemicals in the air can cause redness, itching, stinging, nasal congestion, and a sore throat. Minimizing exposure to these irritants through proper ventilation, regular cleaning, and reducing the use of harsh chemicals can help alleviate these symptoms.
Worsening of Existing Health Conditions
Individuals with pre-existing health conditions, such as allergies, asthma, or respiratory diseases, may experience a worsening of their symptoms in environments with poor indoor air quality. The presence of indoor pollutants can trigger inflammation, respiratory distress, and increased sensitivity to allergens. Maintaining a clean and healthy indoor environment is crucial for managing these conditions and reducing symptom severity.


Insufficient Ventilation
Limited Fresh Air Exchange
Insufficient ventilation can result in limited fresh air exchange between the indoors and outdoors. This can lead to a buildup of indoor pollutants, such as VOCs, mold spores, and dust, as well as an increase in humidity levels. Without adequate ventilation, these pollutants can accumulate, contributing to poor indoor air quality and potential health problems.
Buildup of Indoor Pollutants
When there is insufficient ventilation, indoor pollutants become trapped in the living space. This includes pollutants emitted from cleaning products, furniture, and other household items. The stagnant air allows these pollutants to linger, increasing the chances of inhaling them and experiencing adverse health effects. Proper ventilation, such as opening windows, using exhaust fans, or installing a whole-house ventilation system, can help remove pollutants and improve indoor air quality.
Increased Humidity Levels
Insufficient ventilation can also lead to increased humidity levels indoors. Without adequate airflow and fresh air exchange, moisture from activities like cooking, cleaning, and bathing may remain trapped, creating an environment conducive to mold and mildew growth. High humidity can contribute to respiratory issues, worsen allergies, and create an uncomfortable living space. Proper ventilation, along with the use of dehumidifiers, can help control humidity levels and prevent mold-related problems.
Inadequate Removal of Contaminants
A lack of ventilation can hinder the removal of contaminants from the indoor air. Without proper airflow and fresh air exchange, pollutants such as dust, pet dander, and VOCs can accumulate and persist in the living environment. Regularly opening windows, using exhaust fans, and ensuring proper ventilation systems are in place can help remove these contaminants and maintain a healthier indoor environment.
Inadequate Filtration and Air Circulation
Inefficient HVAC Filters
Inadequate filtration can result from using inefficient HVAC filters. HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) filters are designed to trap airborne particles and improve indoor air quality. However, using filters with low efficiency or not using filters at all allows pollutants to circulate through the system and back into the living space. Upgrading to high-quality filters with a higher MERV (Minimum Efficiency Reporting Value) rating can enhance filtration capabilities and effectively capture pollutants.
Filters Not Being Changed Regularly
Even with efficient HVAC filters, poor indoor air quality can still result if the filters are not changed regularly. Over time, filters become clogged with accumulated dust, pet dander, and other particles, reducing their effectiveness. This can lead to decreased air circulation, increased strain on the HVAC system, and the release of pollutants back into the air. It is crucial to follow manufacturer recommendations and replace filters regularly to ensure optimal performance and maintain good indoor air quality.
Poor Air Circulation
Inadequate air circulation can contribute to the buildup of indoor pollutants. When air cannot freely circulate throughout the living space, pollutants become stagnant and settle on surfaces, leading to a higher concentration of contaminants. This can be particularly problematic in rooms with limited airflow or those that are not frequently used. Opening windows, using fans, and periodically rearranging furniture to facilitate airflow can help improve indoor air circulation and reduce the buildup of pollutants.
Closed-off or Blocked Vents
Closed-off or blocked vents can impede the proper distribution of heated or cooled air throughout the home. This can result in uneven temperatures, reduced air circulation, and an increase in pollutants. Vents should be kept open and unobstructed to promote the efficient flow of air from the HVAC system. Regularly checking and cleaning vents, as well as ensuring furniture or other items are not blocking them, can help maintain good air circulation and prevent indoor air quality issues.


Presence of Moisture and Dampness
Water Leaks or Intrusion
Water leaks or intrusion can introduce excess moisture and dampness into the home, creating an environment conducive to mold and mildew growth. Roof leaks, plumbing issues, or even high humidity levels can lead to water damage and moisture-related problems. Promptly addressing any water leaks or intrusion, repairing damaged areas, and ensuring proper ventilation and humidity control are essential for preventing the growth of mold and improving indoor air quality.
High Humidity Levels
High humidity levels can be a result of inadequate ventilation, excessive moisture generation, or a combination of both. Moisture from activities like cooking, bathing, and drying clothes can become trapped indoors without proper airflow. High humidity can fuel the growth of mold and dust mites, leading to respiratory issues and allergies. Using dehumidifiers, properly venting humid areas, and managing moisture sources can help control humidity levels and alleviate associated problems.
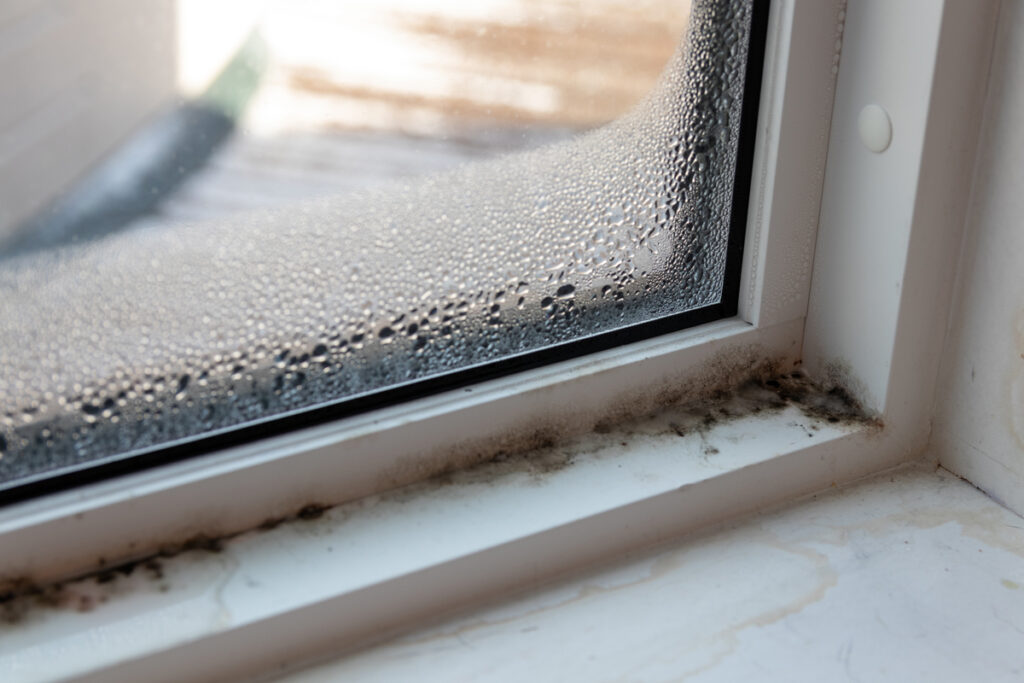
Condensation on Windows or Walls
Condensation on windows or walls is a common sign of excess moisture in the home. When warm, moist air comes into contact with cooler surfaces, condensation forms. Prolonged exposure to condensation can result in mold growth, water damage, and deterioration of building materials. Increasing ventilation, using exhaust fans, and improving insulation and weatherproofing can help reduce condensation and maintain good indoor air quality.
Leaking or Inefficient HVAC System
An HVAC system that is leaking or inefficient can contribute to moisture-related issues and poor indoor air quality. Leaks in the HVAC system can introduce excess moisture into the air, promoting the growth of mold and mildew. Additionally, an inefficient HVAC system may not effectively remove moisture from the air, leading to high humidity levels and potential mold growth. Regular maintenance and inspections of the HVAC system are crucial for identifying and rectifying any moisture-related problems.
Indoor Activities and Habits
Cooking and Food Preparation
Cooking and food preparation can release moisture, smoke, and cooking byproducts into the air, affecting indoor air quality. High heat cooking methods, like frying, can generate grease particles that become suspended in the air and contribute to poor air quality. Adequate ventilation, such as using range hoods or opening windows, can help remove cooking-related pollutants. Using lids on pots and pans, keeping burners clean, and regularly cleaning kitchen surfaces can also minimize the release of pollutants during cooking.
Cleaning and Chemical Use
Cleaning activities, particularly when using harsh chemical cleaners, can release fumes and VOCs into the indoor environment. These fumes can irritate the respiratory system and contribute to poor indoor air quality. Choosing natural, non-toxic cleaning products or making homemade cleaners using vinegar, baking soda, or lemon juice can reduce exposure to harmful chemicals. Additionally, ensuring proper ventilation during cleaning activities, such as opening windows or using exhaust fans, can help remove pollutants from the air.
Smoking
Smoking indoors significantly impacts indoor air quality and poses health risks to both smokers and non-smokers. Secondhand smoke contains numerous harmful chemicals and toxins that can linger in the air for long periods. Breathing in secondhand smoke can lead to respiratory issues, increased risk of lung cancer, and worsened symptoms for individuals with asthma. It is important to implement a strict no-smoking policy indoors to protect the health of everyone in the living environment.
Burning Candles and Incense
Burning candles and incense can release soot, particles, and VOCs into the air, contributing to poor indoor air quality. Soot particles can accumulate on surfaces and in the lungs, causing respiratory irritation and allergies. Opting for beeswax or soy-based candles, which produce fewer pollutants, and using natural incense can help minimize the release of harmful substances. It is also important to burn candles and incense in well-ventilated areas and avoid leaving them unattended.
Using Aerosol Sprays and Air Fresheners
Aerosol sprays and air fresheners, while they may temporarily mask odors, can introduce pollutants into the air. Many of these products contain VOCs, which can contribute to respiratory issues and other health problems. Using natural air fresheners, such as essential oil diffusers or potpourri, can provide a safer alternative. It is also important to ensure proper ventilation when using any aerosol products to minimize exposure to harmful pollutants.


Off-Gassing from Building Materials and Furniture
Paints, Stains, and Varnishes
Paints, stains, and varnishes can release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into the air during the drying and curing process. These VOCs can contribute to poor indoor air quality and cause respiratory irritation. Opting for low-VOC or VOC-free paint and finishes can help reduce exposure to harmful chemicals. Proper ventilation during painting projects and allowing sufficient drying time can also help minimize the release of VOCs into the indoor environment.
Carpets and Upholstery
New carpets and upholstery can release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other chemicals into the air. These chemicals are often used in the manufacturing process to treat the materials and provide stain resistance. The off-gassing of these chemicals can contribute to poor indoor air quality and cause respiratory issues. When purchasing carpets and upholstery, choose low-VOC or natural materials. It is also beneficial to allow for proper ventilation and airing out of new furnishings to minimize the release of harmful chemicals.
Particleboard and Plywood
Particleboard and plywood, commonly used in furniture and cabinetry, can release formaldehyde, a known carcinogen, into the air. This off-gassing can contribute to poor indoor air quality and pose health risks. Opting for furniture made from solid wood or choosing furniture with low-formaldehyde or formaldehyde-free materials can help reduce exposure to this harmful compound. Proper ventilation and allowing new furniture to off-gas in a well-ventilated area can also minimize indoor air quality issues.
Foam Insulation
Certain types of foam insulation, such as spray polyurethane foam, can release VOCs and other chemicals into the air when installed. These chemicals can contribute to poor indoor air quality and cause respiratory irritation. When selecting insulation materials, consider low-emission or formaldehyde-free options. Proper ventilation during and after installation can help remove potential pollutants from the indoor environment.
Glues and Adhesives
Glues and adhesives used in construction, furniture, and household repairs can release VOCs into the air. This off-gassing can contribute to poor indoor air quality and cause respiratory issues. Choosing low-VOC or low-emission adhesives can help reduce exposure to harmful chemicals. When using adhesives indoors, ensure proper ventilation, and allow sufficient drying or curing time to minimize the release of VOCs into the indoor environment.
Lack of Regular Cleaning and Maintenance
Dust and Dirt Accumulation
Lack of regular cleaning can lead to the accumulation of dust and dirt, contributing to poor indoor air quality. Dust particles can contain allergens, pet dander, pollen, and even harmful substances like lead or pesticides. Regular dusting, vacuuming, and floor cleaning can help minimize the amount of dust in the living environment. It is also important to clean or replace air filters regularly to prevent the recirculation of dust particles.
Poorly Maintained HVAC System
A poorly maintained HVAC system can become a source of indoor air pollutants. Dust, debris, and biological contaminants can accumulate within the system if not properly cleaned and maintained. When the system is turned on, these pollutants can be circulated throughout the home, leading to poor indoor air quality. Regular maintenance, including professional inspections and cleanings, is essential for ensuring the HVAC system operates efficiently and delivers clean air.
Neglected Indoor Plants
Indoor plants can contribute to better air quality by naturally removing certain pollutants. However, if not properly cared for, they can become a source of mold, mildew, and pests. Overwatering, lack of proper drainage, or neglecting plant health can lead to the growth of mold or attract insects, diminishing the benefits they provide. Regularly inspecting plants for signs of mold or pests, proper watering and drainage, and maintaining good plant health practices can ensure they continue to improve indoor air quality.
Dirty or Clogged Air Ducts
Dirty or clogged air ducts can negatively impact indoor air quality. Over time, dust, pet dander, and other particles can accumulate within the ductwork. When the HVAC system is in use, these pollutants can be blown into the living space, reducing air quality. Professional duct cleaning can help remove contaminants from the ductwork and improve indoor air quality. Routine inspections and filter changes can also help prevent excessive buildup.
Inadequate Cleaning of Ventilation System
The ventilation system, including exhaust fans and range hoods, requires regular cleaning to effectively remove pollutants from the air. Accumulation of grease, dust, and other contaminants can hinder the system’s ability to perform optimally and maintain good indoor air quality. Cleaning these ventilation systems as recommended by the manufacturer or a professional can help ensure proper functioning and improved indoor air quality.


Ineffective or Absent Radon Mitigation
Radon Entry Points
Radon can seep into a home through cracks in the foundation, gaps around pipes, or other entry points. Without proper mitigation measures, radon gas levels can become dangerously high and pose health risks. Identifying potential radon entry points, sealing cracks, and using techniques like soil suction or ventilation systems can effectively reduce radon levels and protect the indoor environment.
Lack of Radon Testing
Lack of testing for radon gas prevents homeowners from knowing if their indoor air quality is affected. Radon is invisible and odorless, making it impossible to detect without proper testing. Conducting radon tests regularly, especially in areas with higher radon potential, can provide valuable information regarding the need for radon mitigation measures. Radon test kits and professional testing services are available to assess radon levels in your home.
Inefficient Radon Remediation Methods
In cases where high levels of radon are detected, choosing inadequate or ineffective radon remediation methods can result in continued poor indoor air quality. Depending on the specific radon levels and home construction, different mitigation techniques may be required. Seeking professional guidance and consulting with certified radon mitigation specialists can ensure appropriate measures are taken to reduce radon levels and improve indoor air quality.
Foundation Cracks or Openings
Cracks and openings in the foundation provide potential entry points for radon gas. These openings can occur due to settling of the building, natural wear and tear, or even poor construction practices. Identifying and repairing foundation cracks and openings is essential for preventing radon gas from entering the home. Professional inspection and repair of foundation issues can help mitigate radon risks and improve indoor air quality.
Improper Use of Heating and Cooling Systems
Overheating or Overcooling
Improper use of heating and cooling systems can compromise indoor air quality and energy efficiency. Overheating or overcooling a home beyond recommended temperature ranges can lead to excessive energy consumption and increased strain on the HVAC system. This can result in poor air circulation, uneven temperatures, and higher levels of indoor pollutants. Setting temperatures within appropriate ranges and using programmable thermostats can help maintain comfort while minimizing energy waste and indoor air quality issues.
Improperly Sized HVAC System
An HVAC system that is improperly sized for the home can impact indoor air quality and energy efficiency. An undersized HVAC system may struggle to maintain desired temperatures, leading to increased humidity levels and poor air circulation. Conversely, an oversized system may cycle on and off frequently, resulting in inefficient operation and less effective removal of contaminants. Consulting with HVAC professionals and ensuring the proper sizing and installation of the system can optimize indoor comfort and air quality.
Blocked or Dirty Air Filters
Blocked or dirty air filters can hinder the proper functioning of the HVAC system and negatively impact indoor air quality. Over time, air filters collect dust, pollen, pet dander, and other particles, reducing their efficiency and restricting airflow. This can lead to decreased performance and increased recirculation of indoor pollutants. Regularly changing air filters according to manufacturer recommendations is essential for maintaining good indoor air quality and prolonging the lifespan of the HVAC system.
Ignoring Proper Temperature Settings
Ignoring proper temperature settings, such as setting the thermostat too high or too low, can affect indoor air quality and energy consumption. Extreme temperatures can lead to discomfort, encourage the growth of mold and mildew, and contribute to poor air circulation. Adhering to recommended temperature ranges and adjusting the thermostat to suit occupancy patterns can help create a comfortable and healthy indoor environment while promoting energy efficiency.
In conclusion, understanding the various factors that contribute to poor indoor air quality is essential for maintaining a healthy living environment. From common indoor pollutants such as volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and mold to insufficient ventilation and improper use of heating and cooling systems, numerous elements can impact the air you breathe indoors. By addressing these factors through proper ventilation, regular cleaning and maintenance, and mindful indoor activities, you can significantly improve indoor air quality and promote the well-being of yourself and those around you. Remember, maintaining good indoor air quality is a continuous effort that requires attention to detail and a commitment to creating a healthy living space.