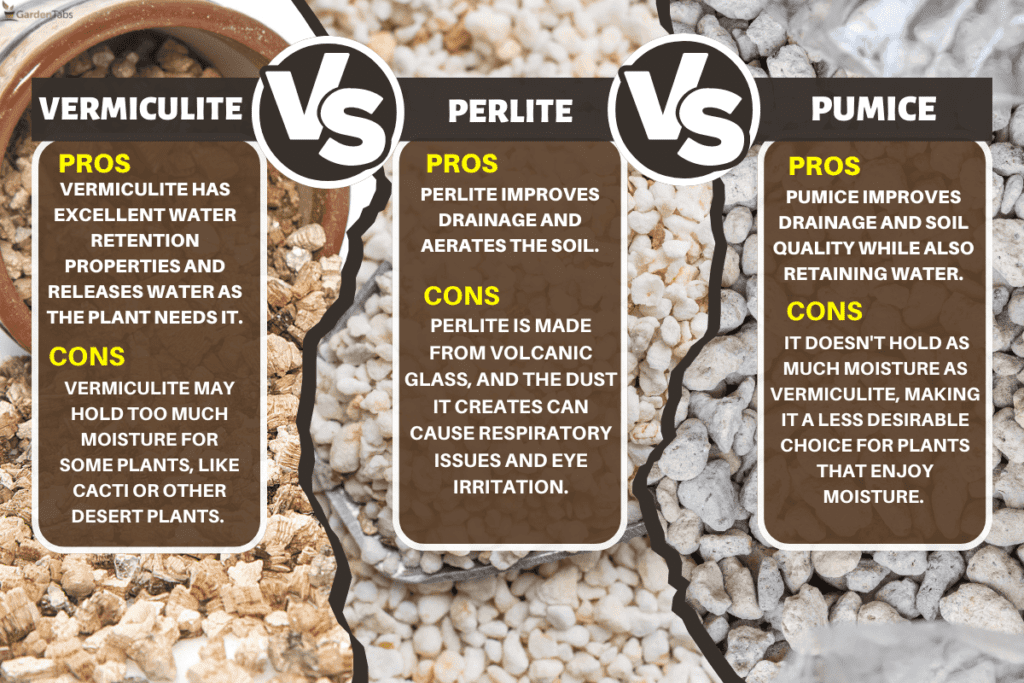
Vermiculite, a popular gardening material, has its fair share of drawbacks that shouldn’t be overlooked. While it possesses beneficial properties like moisture retention and insulation capabilities, there are concerns to be aware of. From its potential to contain asbestos-like fibers, to its limited ability to provide long-term nutrients for plants, it’s important to consider the disadvantages before incorporating vermiculite into your gardening routine.

Introduction
Overview of Vermiculite
Vermiculite is a natural mineral that is widely used in various industries due to its lightweight and insulating properties. It is commonly found in mines and undergoes a heating process to expand its volume. This expansion creates pockets of air within the mineral, making it an excellent insulator for both heat and sound. Vermiculite is commonly used in construction, gardening, and horticulture applications. However, despite its many advantages, there are several potential disadvantages associated with the use of vermiculite.
Potential for Disadvantages
While vermiculite has gained popularity for its versatility and insulation properties, it also poses potential risks and concerns. Some of these disadvantages include health risks, environmental concerns, limited insulation properties, moisture retention issues, limited use in high-temperature applications, poor drainage, weight and handling challenges, maintenance difficulties, and limited availability. It is crucial to be aware of these drawbacks to make informed decisions when considering the use of vermiculite.
1. Health Risks
Asbestos Contamination
One significant concern associated with vermiculite is the potential presence of asbestos. Asbestos is a naturally occurring mineral that has been linked to serious health conditions, including lung cancer and mesothelioma. Many vermiculite deposits are often found to contain asbestos fibers due to their geological formation. Therefore, it is essential to ensure that the vermiculite used does not contain any asbestos, as exposure to these fibers can have severe health consequences.
Respiratory Issues
Another health risk associated with vermiculite is the potential for respiratory issues. Fine particles of vermiculite dust can become airborne during handling or installation, leading to the inhalation of these particles. Breathing in vermiculite dust over an extended period can potentially cause respiratory problems such as coughing, wheezing, and difficulty breathing. This risk is particularly significant for individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions or those who are highly sensitive to airborne particles.
Skin Irritation
Direct contact with vermiculite can also lead to skin irritation for some individuals. The sharp edges of vermiculite particles may cause mild to moderate skin irritation, including redness, itching, and rashes. It is crucial to handle vermiculite with caution and wear appropriate protective clothing, such as gloves and long sleeves, to minimize the risk of skin irritation.
2. Environmental Concerns
Mining Impact
The mining process of vermiculite can have adverse environmental effects. Mining operations can disrupt ecosystems, lead to habitat destruction, and contribute to soil erosion. Large-scale mining activities may also lead to the displacement of wildlife and impact local biodiversity. It is important to consider sustainable mining practices and minimize the environmental impact associated with vermiculite mining.
Soil Contamination
Vermiculite contains naturally occurring minerals and trace elements, some of which may leach into the soil over time. While this can provide additional nutrients to plants, it also has the potential to contaminate the soil. Excessive use of vermiculite in gardening or horticulture applications may result in an imbalance of soil pH or the accumulation of certain minerals, which can affect plant growth. Proper testing and monitoring of soil conditions are essential to avoid any adverse effects on the environment.
3. Limited Insulation Properties
Low R-Value
Although vermiculite is known for its insulation properties, it has a relatively low R-value compared to other insulating materials. R-value is a measure of thermal resistance, indicating how effective a material is at preventing heat transfer. While vermiculite can provide some level of insulation, it may not be as efficient as other insulation materials with higher R-values. This limitation may result in higher heating or cooling costs in buildings or structures where vermiculite is used as insulation.
Degradation over Time
Over time, vermiculite may undergo degradation or compression, leading to a decrease in its insulating capabilities. The lightweight nature of vermiculite can make it susceptible to compaction, especially in areas with heavy foot traffic or frequent handling. This gradual degradation may reduce the overall effectiveness of vermiculite insulation and require periodic maintenance or replacement to maintain its optimum insulation properties.


4. Moisture Retention
Potential for Mold Growth
Vermiculite’s ability to retain moisture can be both advantageous and disadvantageous. While it can help in retaining moisture for plants in gardening applications, it also creates a favorable environment for mold growth. Mold thrives in damp conditions, and the moisture-retention properties of vermiculite can contribute to the growth of mold, especially in humid or poorly ventilated areas. This can pose health risks and cause damage to surrounding materials if left unaddressed.
Increased Risk of Rot
Excessive moisture retention in vermiculite can also increase the risk of rot in plants and organic materials. Poor drainage may result in waterlogged soil, preventing proper aeration and root oxygenation. This stagnant environment can lead to root rot and the decline of plant health. It is crucial to ensure proper drainage and avoid overwatering when using vermiculite in gardening or horticulture to mitigate the risk of rot and promote healthy plant growth.
5. Limited Use in High-Temperature Applications
Failure under Extreme Heat
Vermiculite has a limited tolerance for high temperatures. When exposed to extreme heat, vermiculite can break down and lose its structural integrity. This can be a potential issue in applications where high temperatures are present, such as in fire-resistant materials or thermal insulation for industrial purposes. It is essential to consider the specific heat resistance requirements of a project and explore alternative materials that can withstand higher temperatures if needed.
Fire Hazards
In addition to its vulnerability to heat, vermiculite itself can pose a fire hazard. The lightweight nature of vermiculite makes it highly combustible, and in the event of a fire, it can easily ignite and contribute to the spread of flames. This characteristic limits its suitability for use in fire-resistant applications and highlights the importance of careful consideration when choosing materials for fire safety purposes.


6. Poor Drainage
Compaction and Waterlogging
Vermiculite’s lightweight and porous nature can lead to poor drainage when used in gardening or horticulture applications. Over time, the particles may become compacted, reducing the pore space and hindering proper water movement. This can result in waterlogging, which can suffocate plant roots and lead to poor plant growth or even death. Adequate drainage measures, such as adding additional materials to improve soil structure, should be taken to mitigate these issues.
Root Rot in Plants
Coupled with poor drainage, vermiculite’s moisture-retention properties can contribute to the development of root rot in plants. Excessive moisture trapped around the roots can create a breeding ground for pathogens that cause root diseases. This can weaken plant health and potentially lead to plant mortality. It is crucial to establish a balance between moisture retention and drainage to prevent the onset of root rot in plants.
7. Weight and Handling
Limited Load Bearing Capacity
Vermiculite’s lightweight nature may limit its load-bearing capacity in certain applications. When used as a structural material, vermiculite may not be able to support heavy loads or withstand significant pressure. This limitation can affect the structural integrity of buildings or structures where vermiculite is utilized. It is important to assess the load requirements of a project and consider alternative materials with higher load-bearing capabilities when necessary.
Difficult to Transport and Install
Due to its lightweight and granular nature, vermiculite can be challenging to transport and install effectively. Its small particle size can result in particles becoming airborne during handling, causing potential health hazards. The powdery nature of vermiculite may also lead to difficulties in achieving uniform coverage or consistent application. Proper safety measures and techniques should be followed when handling and installing vermiculite to minimize any potential issues.


8. Maintenance Challenges
Difficulty in Removing or Replacing
Vermiculite’s lightweight and loose properties can make it challenging to remove or replace once it has been installed. Whether it is insulation in walls or in gardening applications, removing vermiculite can be a labor-intensive and time-consuming task. This can pose challenges for renovation or remodeling projects that require vermiculite removal or replacement. Planning ahead and considering the long-term implications of using vermiculite can help mitigate potential maintenance challenges.
Compaction and Settling
Over time, vermiculite can gradually become compacted or settle, especially in areas with frequent use or physical activity. This compaction may reduce its insulating or moisture-retention properties, as well as contribute to poor drainage. Regular maintenance and monitoring are necessary to address any settling issues promptly and restore vermiculite to its optimal performance.
10. Limited Availability
Difficulty in Sourcing
Despite its widespread use, sourcing vermiculite can sometimes be challenging. Not all regions may have readily available sources of vermiculite, making it difficult to obtain for specific projects or applications. This limited availability can increase costs or lead to delays in projects that rely on the use of vermiculite. Conducting thorough research and exploring alternative materials may be necessary to overcome these challenges.
Reduced Distribution Channels
Furthermore, the distribution of vermiculite may be limited in some areas, particularly in rural or remote locations. Fewer suppliers or distributors may carry vermiculite, making it less accessible to individuals or businesses in these areas. This reduced availability can restrict the options for those seeking to use vermiculite, requiring them to explore alternative materials or incur additional costs to have vermiculite shipped to their location.
In conclusion, while vermiculite offers several advantages in insulation, gardening, and horticulture applications, it is important to consider the potential disadvantages associated with its use. These disadvantages include health risks such as asbestos contamination, respiratory issues, and skin irritation, as well as environmental concerns such as mining impact and soil contamination. Other drawbacks include limited insulation properties, moisture retention issues leading to mold growth and increased risk of rot, limited use in high-temperature applications, poor drainage, weight and handling challenges, maintenance difficulties, and limited availability. Being aware of these disadvantages allows individuals and businesses to make informed decisions and select the most suitable materials for their specific needs and circumstances.







