EPDM, commonly used in the construction industry, is an abbreviation that stands for Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer. This versatile synthetic rubber material has gained popularity due to its exceptional resistance to weather elements, chemicals, and heat. EPDM is often used for roofing membranes, seals, gaskets, and various automotive applications. In this article, we will explore the properties and uses of EPDM, shedding light on why it has become such a prevalent choice in a range of industries. EPDM stands for Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer. This synthetic rubber material is commonly used in various industries due to its excellent properties and versatility. In this article, we will delve deeper into the meaning and characteristics of EPDM, its applications in different sectors, the manufacturing process, comparisons with other rubber compounds, installation and maintenance techniques, pricing factors, market trends, and the environmental impact of EPDM.


EPDM Definition and Characteristics
EPDM Meaning
EPDM refers to Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer, which is a type of synthetic rubber. It is composed of three key monomers, namely ethylene, propylene, and a diene monomer. This combination of monomers gives EPDM its unique properties, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
EPDM Properties
EPDM possesses several desirable properties that contribute to its widespread use. It has excellent weather, ozone, and UV resistance, which allows it to withstand harsh environmental conditions without deterioration. EPDM also exhibits superb heat resistance, making it suitable for both high and low-temperature applications. Additionally, EPDM has excellent electrical insulation properties and is resistant to water, chemicals, and steam. Its flexibility, durability, and good mechanical strength further enhance its usability.
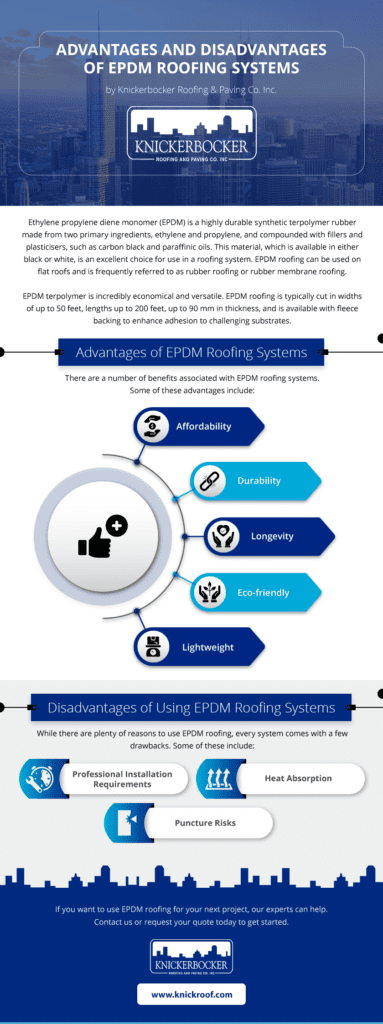
EPDM Advantages
EPDM’s numerous advantages make it a top choice for various industries. Its excellent weatherability and resistance to UV rays, ozone, and extreme temperatures make it highly durable and long-lasting. EPDM’s resistance to water, chemicals, and steam makes it suitable for use in applications where exposure to such substances is common. Furthermore, EPDM’s electrical insulation properties make it valuable in the electrical industry. Its flexibility, ease of installation, and low maintenance requirements add to its appeal.
Applications of EPDM
Automotive Industry
EPDM finds extensive use in the automotive sector due to its exceptional properties. It is commonly employed in the manufacturing of door seals, window seals, weatherstripping, and various under-the-hood components. EPDM’s resistance to weather, heat, and chemicals ensures longevity and performance in these demanding applications. Furthermore, EPDM’s flexibility allows for easy installation and reduces the risk of seal failure.
Construction Sector
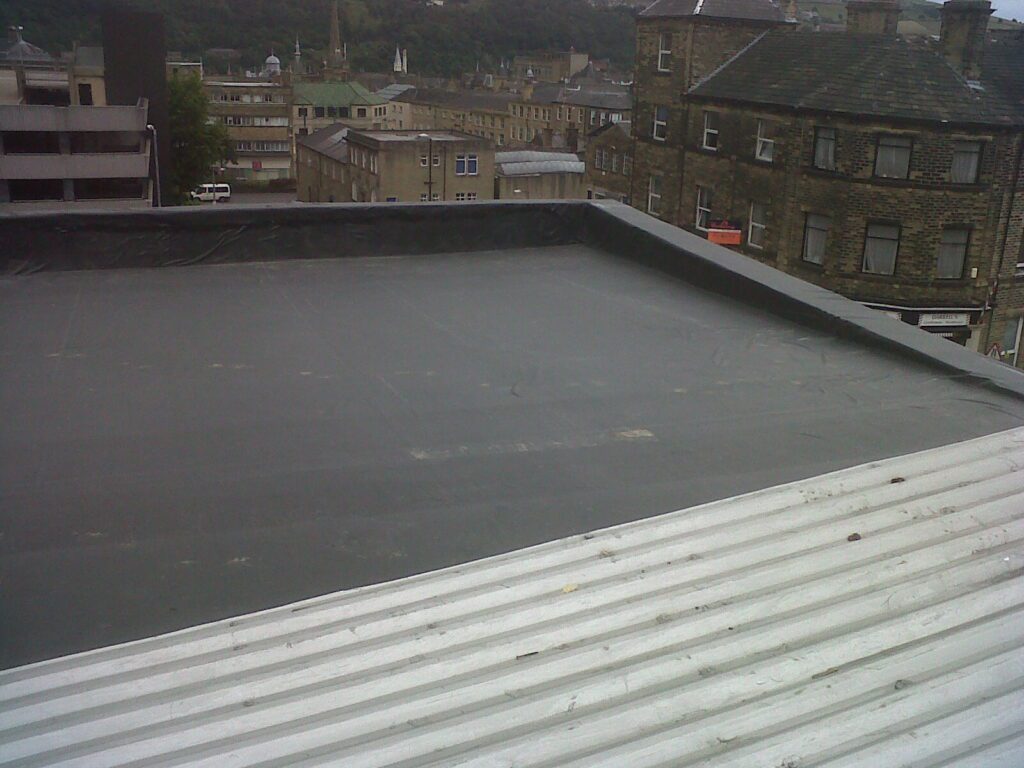
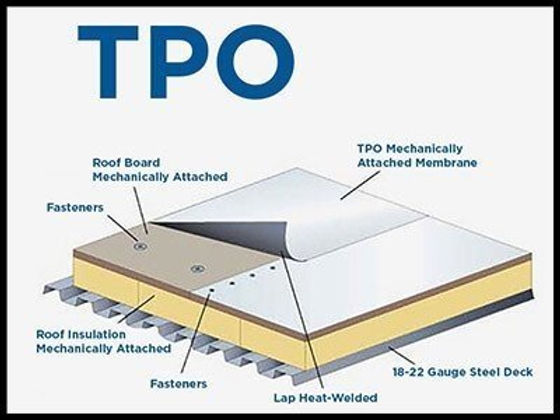
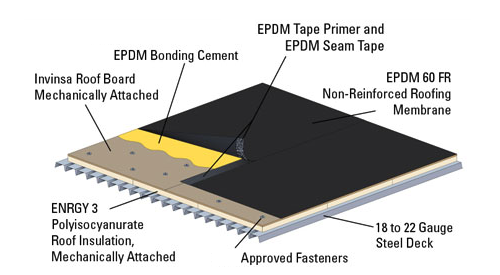
EPDM is widely utilized in the construction industry due to its suitability for waterproofing applications. It is commonly used as a roofing membrane to create watertight seals, preventing leaks and water damage. EPDM’s resistance to weather, UV rays, and chemicals make it ideal for protecting buildings from moisture ingress. Additionally, EPDM’s flexible nature allows it to conform to irregular surfaces, providing a seamless and reliable waterproofing solution.
Electrical Industry
EPDM’s exceptional electrical insulation properties make it highly valuable in the electrical industry. It is commonly used in cable insulation and connectors due to its ability to protect against electrical damage and ensure the safe transmission of electricity. EPDM’s resistance to heat and chemicals further enhances its usefulness in these applications.
Manufacturing Process of EPDM
Synthesis of EPDM
The manufacturing process of EPDM involves the synthesis of the ethylene, propylene, and diene monomers. The monomers are combined and polymerized through a process called copolymerization. This process creates long chains of EPDM molecules, resulting in the formation of a rubbery material. Various catalysts and initiators may be used to facilitate the polymerization process and control the properties of the resulting EPDM.
Vulcanization Process
After the synthesis of EPDM, the material undergoes a vulcanization process. Vulcanization involves treating the EPDM with sulfur or other vulcanizing agents, along with heat and pressure. This process cross-links the EPDM polymer chains, increasing its strength, durability, and resistance to deformation. Vulcanization also improves the temperature stability and chemical resistance of EPDM. The precise vulcanization conditions can be adjusted to achieve the desired properties for specific applications.
EPDM vs. Other Rubber Compounds
EPDM vs. Natural Rubber
EPDM exhibits several advantages over natural rubber. While natural rubber has good tear strength and resilience, EPDM surpasses it in terms of weather resistance, UV resistance, and chemical resistance. EPDM is also less susceptible to aging and degradation caused by ozone exposure. Additionally, EPDM has a wider range of temperature tolerance compared to natural rubber. These qualities make EPDM a preferred choice in applications where resistance to harsh environmental conditions is crucial.
EPDM vs. Silicon Rubber
EPDM and silicon rubber both have unique advantages that make them suitable for different applications. EPDM excels in weatherability, UV resistance, and resistance to chemicals and steam. Silicon rubber, on the other hand, has superior high-temperature resistance and excellent flexibility at low temperatures. While EPDM is more cost-effective, silicon rubber is often used in applications with extreme temperature variations or where food-grade compliance is necessary. The choice between EPDM and silicon rubber depends on the specific requirements of the application.

EPDM Installation and Maintenance
Installation Techniques
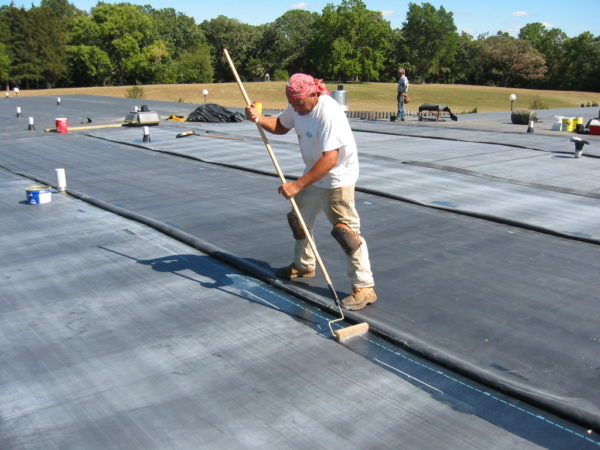
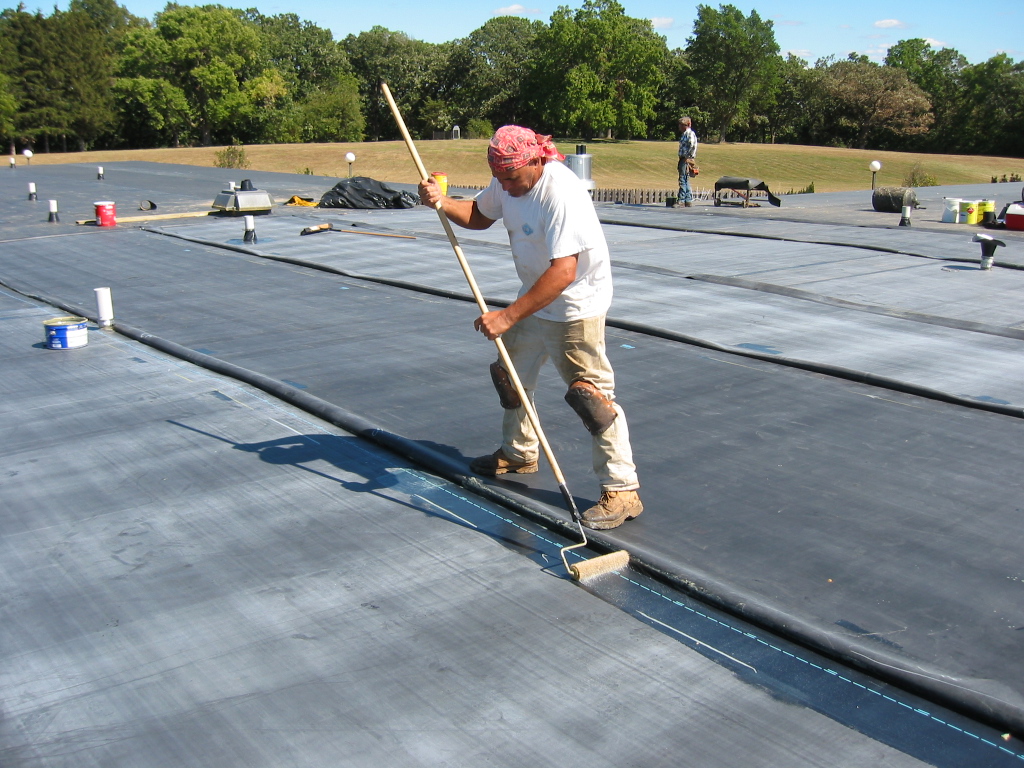
EPDM can be installed using several techniques, depending on the application and desired outcome. Some common installation methods include fully-adhered, mechanically attached, and ballasted systems. The fully-adhered technique involves bonding the EPDM membrane directly to the substrate using adhesive. The mechanically attached method secures the EPDM membrane with fasteners. In the ballasted system, EPDM is loose-laid and weighted down with ballast materials. Proper installation is crucial to ensuring a watertight seal and optimal performance.
Maintenance Tips
EPDM generally requires minimal maintenance, thanks to its durability and resistance to degradation. Regular visual inspections should be conducted to check for any signs of damage or wear and tear. It is advisable to remove any debris or pooling water on the EPDM surface to prevent potential issues. In case of damage, prompt repairs should be carried out using EPDM-compatible adhesives or patches. It is essential to follow manufacturer guidelines and consult professionals when dealing with EPDM installation or maintenance.
EPDM Pricing
Factors Affecting Price
Several factors influence the price of EPDM materials. The type and quality of EPDM, its thickness, and the quantity required for a particular project are significant considerations. Additional factors include the complexity of the installation, location, and market demand. EPDM accessories and associated installation materials may also contribute to the overall cost. It is advisable to gather multiple quotes and compare prices from different suppliers to ensure a fair price for the desired EPDM product.
Price Comparison
EPDM is a cost-effective solution for many applications, especially when compared to other materials with similar properties. While the initial cost of EPDM may be higher than some alternatives, its long lifespan, durability, and minimal maintenance requirements contribute to its overall cost-effectiveness. When comparing prices, it is crucial to consider the specific requirements of the application, as well as the performance, longevity, and other factors that EPDM offers.


EPDM Market and Trends
EPDM Market Overview
The EPDM market has experienced steady growth over the years, driven by its wide range of applications and favorable properties. The construction and automotive industries have emerged as significant consumers of EPDM products. Growing concerns regarding energy efficiency and sustainability in these sectors have further propelled the demand for EPDM. Additionally, the electrical industry continues to rely on EPDM for its excellent electrical insulation properties. The EPDM market is expected to witness continued growth in the coming years.
Recent Industry Trends
The EPDM industry is continuously evolving to meet the changing needs of various sectors. One of the notable trends is the increasing demand for EPDM with enhanced sustainability features. Manufacturers are striving to develop bio-based EPDM materials and incorporate recycled content into their products, reducing their environmental impact. Additionally, advancements in EPDM technology and formulations aim to further improve its properties and expand its applications. Such trends reflect the industry’s commitment to innovation and sustainability.
Environmental Impact of EPDM
Sustainability Measures
EPDM demonstrates several sustainability measures that contribute to its eco-friendliness. The production of EPDM requires lower energy consumption compared to some other rubber compounds. EPDM also offers long service life, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing waste generation. Furthermore, efforts are being made to incorporate bio-based materials and recycled content into EPDM manufacturing processes. These sustainability initiatives help reduce the overall environmental impact of EPDM and promote a more sustainable future.


Conclusion
EPDM, which stands for Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer, is a versatile synthetic rubber known for its exceptional properties. Its weather resistance, UV resistance, chemical resistance, and electrical insulation properties make it highly valuable across various industries. EPDM finds applications in the automotive, construction, and electrical sectors, among others. With its durability, flexibility, and ease of installation, EPDM offers a reliable solution for many critical applications. As sustainability becomes increasingly important, the EPDM industry is embracing eco-friendly measures and striving for innovation. The future looks promising for EPDM, and it will continue to serve as a reliable and environmentally friendly material for years to come.