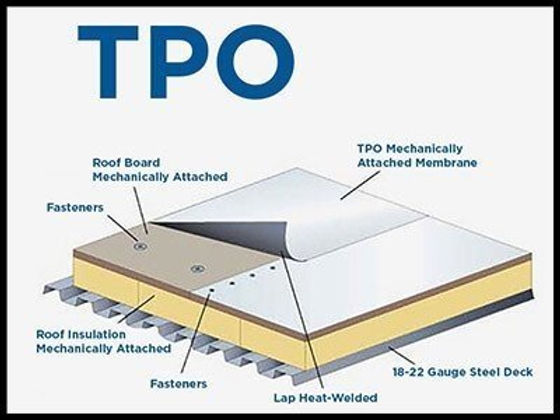
When it comes to roofing options, TPO has long been considered a popular choice. However, there might just be something even better out there. In this article, you will discover an alternative to TPO roofing that promises enhanced durability, energy efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. Say goodbye to your roofing woes as we unveil the next level in roofing technology. So, are you ready to elevate your roofing game? Let’s explore the exciting world beyond TPO!
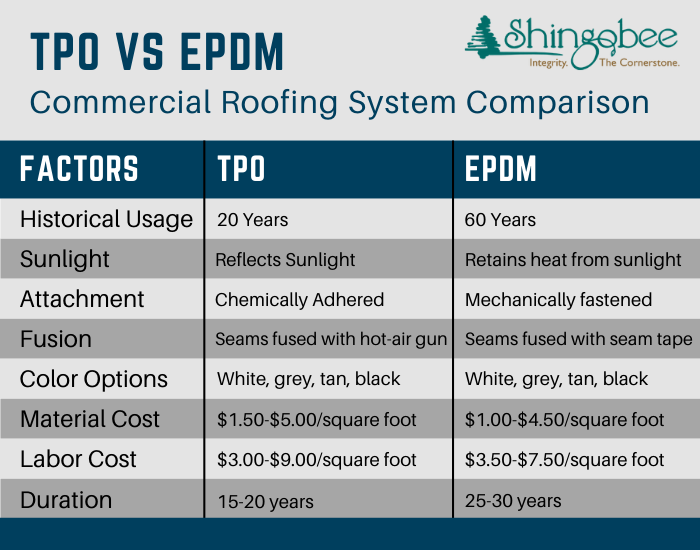

1. PVC Roofing
1.1 Overview of PVC Roofing
PVC roofing, also known as Polyvinyl Chloride roofing, is a highly durable and popular roofing material that is widely used in both residential and commercial applications. It is made from PVC membranes that are reinforced with polyester or fiberglass for added strength and stability. PVC roofing is known for its exceptional resistance to chemicals, moisture, fire, and UV radiation, making it a reliable choice for various roofing needs.
1.2 Advantages of PVC Roofing
There are several advantages associated with PVC roofing. Firstly, PVC membranes are extremely durable and have a long lifespan, often lasting up to 30 years or more with proper installation and maintenance. They are also resistant to punctures, tears, and weathering, making them an excellent choice for areas prone to extreme weather conditions.
PVC roofing is highly reflective, which means it can effectively reflect sunlight and reduce the heat absorbed by the building. This reflective property contributes to energy efficiency and can result in lower cooling costs, especially in hot climates. Additionally, PVC membranes are known for their excellent fire resistance, which adds an extra layer of safety to the building.
Another advantage of PVC roofing is its low maintenance requirements. The smooth surface of PVC membranes prevents the buildup of dirt, debris, and algae, reducing the need for frequent cleaning. PVC roofing is also easy to repair in case of damage, as individual membranes can be replaced without having to replace the entire roof.
1.3 Disadvantages of PVC Roofing
While PVC roofing has numerous advantages, it is essential to consider some potential disadvantages as well. One major concern is the environmental impact of PVC, as it is known to release toxic substances during its production and disposal. However, advancements in manufacturing techniques have greatly reduced the environmental impact of PVC roofing, with many manufacturers producing eco-friendly options.
Another disadvantage of PVC roofing is its initial cost compared to other roofing materials. PVC roofing tends to be more expensive upfront, but its long lifespan and low maintenance requirements often make it cost-effective in the long run. Additionally, PVC roofing may not be suitable for areas with extreme cold temperatures, as it can become brittle and prone to cracking.
2. EPDM Roofing
2.1 Overview of EPDM Roofing
EPDM roofing, short for Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer roofing, is a synthetic rubber roofing material widely used in both commercial and residential roofing applications. It is made from a single-ply membrane that is durable, flexible, and resistant to weathering. EPDM roofing is primarily available in black, but white options are also available to enhance energy efficiency.
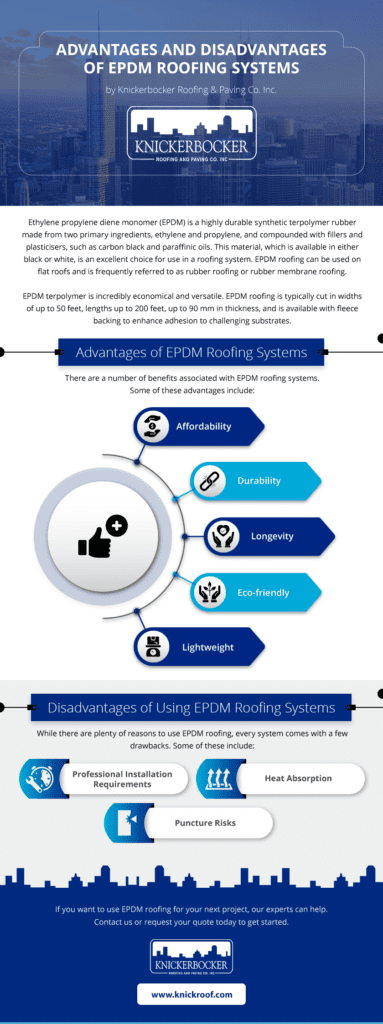
2.2 Advantages of EPDM Roofing
EPDM roofing offers several advantages that make it a popular choice among building owners and roofing professionals. Firstly, it is highly durable and can withstand prolonged exposure to UV radiation, heat, cold, and other weather elements. EPDM membranes are resistant to hail damage, punctures, and tears, ensuring a long lifespan and minimal maintenance requirements.
EPDM roofing is also known for its excellent flexibility, allowing it to accommodate building movements without cracking or splitting. This flexibility makes it suitable for a wide range of roof designs and shapes. Furthermore, EPDM roofing installations are relatively straightforward, which can potentially reduce labor costs and installation time.
Another significant advantage of EPDM roofing is its energy efficiency. The black EPDM membranes effectively absorb sunlight and can help reduce heating costs in colder climates. However, white EPDM membranes are available as well, which reflect sunlight and provide better energy efficiency in warmer climates.
2.3 Disadvantages of EPDM Roofing
Despite its numerous advantages, EPDM roofing has a few drawbacks that should be considered. One common concern is its aesthetic appeal, as the black EPDM membranes may not complement all architectural styles. However, the availability of white EPDM membranes offers more options in terms of appearance.
EPDM roofing can also be vulnerable to oil-based and petroleum-based products, which can cause the rubber to deteriorate over time. It is important to ensure that any potential contact with such substances is minimized to preserve the longevity of the EPDM roof. Additionally, EPDM roofing may require periodic cleaning to prevent the buildup of dirt, algae, and debris.
3. Metal Roofing
3.1 Overview of Metal Roofing
Metal roofing is a versatile and durable roofing option that has gained popularity in both residential and commercial applications. It is typically made from steel, aluminum, or copper and offers a range of design options, including standing seam, corrugated panels, and metal shingles. Metal roofing is known for its exceptional strength, longevity, and resistance to weathering.
3.2 Advantages of Metal Roofing
Metal roofing offers numerous advantages that make it a preferred choice for many building owners. Firstly, it has an exceptionally long lifespan, often lasting 50 years or more with proper installation and maintenance. Metal roofing is highly durable and can withstand severe weather conditions such as high winds, heavy snow, and hail.
One of the main advantages of metal roofing is its energy efficiency. Metal roofs reflect solar heat, reducing the amount of heat absorbed by the building and resulting in lower cooling costs. Additionally, metal roofing is typically made from recycled materials and is fully recyclable at the end of its life, making it an environmentally friendly choice.
Metal roofing is low maintenance and requires minimal repairs over its lifespan. It is resistant to cracking, shrinking, and warping, ensuring its structural integrity over time. Metal roofs are also fire-resistant, providing an extra layer of protection to the building and potentially reducing insurance costs.
3.3 Disadvantages of Metal Roofing
While metal roofing has many advantages, there are a few considerations to keep in mind. Metal roofs can be relatively expensive compared to other roofing materials, especially if premium materials such as copper are chosen. However, the long lifespan and low maintenance requirements often make metal roofing a cost-effective option in the long run.
Another potential disadvantage of metal roofing is the noise factor. During heavy rain or hailstorms, metal roofs can be noisy compared to other roofing materials. However, proper insulation and other soundproofing measures can be incorporated during installation to minimize noise levels.
Lastly, metal roofs can be prone to denting if struck by heavy objects such as falling branches. However, modern metal roofing systems are often designed to be resistant to dents and can withstand significant impact. Regular inspection and maintenance can help identify and address any potential issues before they become significant problems.
4. Built-up Roofing (BUR)
4.1 Overview of Built-up Roofing (BUR)
Built-up Roofing (BUR), also known as tar and gravel roofing, is a traditional roofing system that has been used for decades. It consists of multiple layers of roofing felt and asphalt or coal tar bitumen. The layers are applied in alternating patterns, creating a durable and waterproof roofing system.
4.2 Advantages of Built-up Roofing (BUR)
Built-up roofing offers several advantages that make it a popular choice for flat or low-slope roofs. Firstly, it provides excellent waterproofing capabilities due to its multiple layers. The alternating layers of roofing felt and asphalt or coal tar bitumen create an impermeable barrier that prevents water penetration.
BUR roofing is known for its long lifespan, often lasting 20 to 30 years or more with proper maintenance. It is resistant to UV radiation, extreme temperatures, and weathering, ensuring its durability over time. Additionally, BUR roofing has good fire resistance properties, which can contribute to the overall safety of the building.
Another advantage of BUR roofing is its versatility. It can be customized to match the specific needs and requirements of a building. The number and thickness of the layers can be adjusted to provide the desired level of insulation, strength, and protection. BUR roofing systems can also incorporate reflective coatings to enhance energy efficiency.
4.3 Disadvantages of Built-up Roofing (BUR)
While Built-up Roofing has numerous advantages, there are a few disadvantages to consider as well. BUR roofing systems tend to be heavier than other roofing materials, which may require additional structural support for the building. The installation process can also be labor-intensive, as each layer needs to be accurately applied and sealed.
Maintenance requirements for BUR roofing can be higher compared to some other roofing systems. Regular inspections and maintenance are necessary to ensure the integrity of the layers and to identify and repair any potential leaks or damages. Additionally, BUR roofing can be more prone to blistering and cracking over time, especially if not properly maintained.

5. Modified Bitumen Roofing
5.1 Overview of Modified Bitumen Roofing
Modified Bitumen roofing is a type of asphalt roofing system that has been modified with added polymers or rubber materials for enhanced performance. It combines the durability of asphalt with the flexibility and weather resistance of plastic or rubber. Modified Bitumen roofing is commonly used for flat or low-slope roofs and is available in various forms, including rolls and sheets.
5.2 Advantages of Modified Bitumen Roofing
Modified Bitumen roofing offers several advantages that make it a popular choice among building owners and roofing professionals. Firstly, it provides excellent waterproofing capabilities and is highly resistant to leaks and water damage. The added polymers or rubber materials enhance the flexibility and durability of the roofing system, allowing it to withstand the expansion and contraction that occurs due to temperature changes.
Modified Bitumen roofing is relatively easy to install and repair. The sheets or rolls can be applied using different methods, including torching, hot asphalt, or cold adhesives, depending on the specific product. This versatility in installation methods makes Modified Bitumen roofing suitable for a wide range of buildings and climates.
Another advantage of Modified Bitumen roofing is its energy efficiency. Light-colored or reflective coatings can be added to the surface, reducing the heat absorbed by the building and resulting in lower cooling costs. This can be particularly beneficial in warmer climates where reducing the cooling load is essential.
5.3 Disadvantages of Modified Bitumen Roofing
While Modified Bitumen roofing has many advantages, there are a few considerations to keep in mind. The installation process can be more complex compared to some other roofing systems, especially if torching or hot asphalt methods are used. This requires skilled professionals to ensure proper installation and minimize the risk of damage to the roofing system.
Modified Bitumen roofing may require regular inspections and maintenance to identify and address any potential issues. The roofing surface can be prone to cracking, blistering, or developing gaps over time, especially if the installation or repairs were not done correctly. Regular maintenance can help prolong the lifespan of the roofing system and prevent costly repairs.
6. Green Roofing
6.1 Overview of Green Roofing
Green roofing, also known as living roofing or vegetated roofing, is a unique and environmentally friendly roofing option that incorporates live vegetation and plants on the rooftop. It involves the installation of a specialized waterproofing system, insulation layers, and a growing medium where plants can thrive. Green roofing provides numerous environmental benefits while offering an aesthetically pleasing appearance.
6.2 Advantages of Green Roofing
Green roofing offers a range of advantages that make it an attractive choice for sustainable building designs. Firstly, it helps to improve air quality by reducing the amount of dust and pollutants in the surrounding environment. The plants and vegetation on the roof act as natural filters, absorbing carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen, thereby reducing the impact of air pollution.
One of the significant advantages of green roofing is its ability to provide thermal insulation. The layers of soil and plants create an additional barrier against heat transfer, reducing the need for excessive cooling during hot weather and lowering energy consumption. As a result, green roofs contribute to energy efficiency and can lead to cost savings on heating and cooling expenses.
Green roofing also plays a crucial role in stormwater management. The vegetation and growing medium absorb rainwater and reduce stormwater runoff, which can help prevent flooding and minimize pressure on municipal drainage systems. The plants also act as natural evaporative surfaces, releasing water vapor into the air and further reducing the risk of excess water accumulation.
6.3 Disadvantages of Green Roofing
Despite its numerous advantages, green roofing has a few considerations to keep in mind. The installation process can be more complex and requires specialized expertise and professional guidance. The additional weight of the growing medium and vegetation can also place a significant load on the structure, requiring careful planning and analysis of the building’s structural capacity.
Green roofing maintenance is also important to ensure the health and vitality of the plants. Regular watering, weeding, and fertilization may be required, depending on the specific vegetation chosen and the local climate. Additionally, green roofs may require periodic inspections to address any potential issues such as plant diseases, root penetration, or leaks in the waterproofing layer.


7. Asphalt Shingle Roofing
7.1 Overview of Asphalt Shingle Roofing
Asphalt shingle roofing is one of the most common and widely used roofing materials in North America. It is made from fiberglass or organic mats coated with asphalt and granules. Asphalt shingles are available in a range of colors, styles, and textures, making them suitable for various architectural styles and preferences.
7.2 Advantages of Asphalt Shingle Roofing
Asphalt shingle roofing offers several advantages that make it a popular choice among homeowners and contractors. Firstly, it is affordable and readily available, making it a cost-effective option for roofing projects with budget constraints. Asphalt shingles are manufactured in large quantities, resulting in lower production costs compared to some other roofing materials.
Another advantage of asphalt shingle roofing is its ease of installation. The shingles are lightweight, making them easier to handle and install compared to heavier roofing materials. This can potentially save on labor costs and reduce the overall installation time.
Asphalt shingles are known for their durability and weather resistance. They withstand a wide range of weather conditions, including high winds, rain, hail, and UV radiation. Additionally, asphalt shingles are available in impact-resistant options that provide added protection against hail or falling debris.
7.3 Disadvantages of Asphalt Shingle Roofing
While asphalt shingle roofing has many advantages, there are a few considerations to keep in mind. The lifespan of asphalt shingles can vary depending on the quality of the material and the specific environmental conditions. While some shingles can last up to 30 years or more, others may have a shorter lifespan, particularly in areas with extreme weather conditions.
Another potential disadvantage of asphalt shingle roofing is its environmental impact. The production and disposal of asphalt shingles can contribute to waste and pollution. However, many manufacturers now offer recycling programs for old asphalt shingles, which can help reduce environmental impact.
Asphalt shingles may also be susceptible to moss, algae, and mildew growth in areas with high humidity. Regular maintenance and cleaning can help prevent and address these issues. Additionally, asphalt shingles may not offer the same level of energy efficiency as some other roofing materials. However, reflective coatings and proper insulation can be added to improve energy efficiency.
8. Solar Roofing
8.1 Overview of Solar Roofing
Solar roofing, also known as photovoltaic (PV) roofing, is a sustainable and energy-efficient roofing option that incorporates solar panels or solar cells into the roof design. The solar panels convert sunlight into electricity, which can be used to power the building or sold back to the grid. Solar roofing combines the functions of a traditional roof with renewable energy generation.
8.2 Advantages of Solar Roofing
The adoption of solar roofing offers significant advantages both in terms of environmental sustainability and financial savings. Firstly, solar roofing allows buildings to generate their own clean and renewable energy. By harnessing the power of the sun, solar panels can produce electricity that can be used to power lighting, appliances, heating, and cooling systems, reducing dependence on traditional energy sources.
One of the main advantages of solar roofing is the potential for cost savings on energy bills. Solar panels generate electricity during daylight hours, allowing buildings to offset a portion of their energy usage. In some cases, excess energy can be sold back to the grid, potentially resulting in financial credits or reduced energy bills.
Solar roofing systems can also increase the overall value of a property. The addition of solar panels is often seen as a desirable feature among homebuyers, as it provides energy savings and reduces the carbon footprint. Investing in solar roofing can offer a return on investment in the form of increased property value and potential energy savings over time.
8.3 Disadvantages of Solar Roofing
While solar roofing offers numerous advantages, there are several considerations to keep in mind. The upfront cost of installing a solar roofing system can be significant, including the cost of the solar panels, installation, and any necessary modifications to the existing roof structure. However, it is important to consider the long-term financial benefits and potential energy savings when evaluating the overall cost.
The efficiency of solar panels can vary depending on factors such as the location, orientation, and shading. Some roofs may not receive optimal sunlight exposure due to surrounding buildings or trees, which can affect the energy generation potential. It is important to conduct a thorough assessment and analysis of the specific site conditions before investing in a solar roofing system.
Maintenance requirements for solar roofing systems are generally minimal. However, occasional cleaning and inspection may be necessary to ensure optimal performance. Dust, dirt, or debris on the surface of the solar panels can reduce their efficiency, and any issues or malfunctions should be addressed promptly by a qualified professional.


9. Clay Tile Roofing
9.1 Overview of Clay Tile Roofing
Clay tile roofing is a popular choice for homeowners who appreciate a classic and distinctive look. Clay tiles are made from natural clay that is fired in a kiln to achieve durability and weather resistance. Clay tile roofing offers a timeless aesthetic appeal and can be found in various styles, including traditional barrel tiles and flat interlocking tiles.
9.2 Advantages of Clay Tile Roofing
Clay tile roofing offers numerous advantages that make it a sought-after choice for homeowners. Firstly, it provides exceptional durability and longevity. Clay tiles are resistant to rot, insects, and fire, ensuring that the roof remains intact and structurally sound for many decades. With proper installation and maintenance, clay tile roofs can last up to 100 years.
Another advantage of clay tile roofing is its aesthetic appeal. The natural colors and textures of clay tiles create a visually appealing and distinctive look that complements various architectural styles. Clay tiles are available in a range of shapes, sizes, and finishes, providing homeowners with customizable options to suit their preferences.
Clay tile roofing is also known for its energy efficiency. The dense nature of clay tiles provides excellent insulation, reducing heat transfer and potentially lowering cooling costs. This can be particularly beneficial in warmer climates where minimizing the cooling load is essential.
9.3 Disadvantages of Clay Tile Roofing
While clay tile roofing has many advantages, there are a few considerations to keep in mind. One significant drawback is the weight of clay tiles. They are heavier compared to some other roofing materials, which may require additional structural support to ensure the roof’s stability and prevent potential damage.
The installation process for clay tile roofing can be complex and time-consuming. Each tile needs to be individually laid and secured, and the tiles should be properly overlapped and aligned to ensure proper waterproofing and structural integrity. This often requires skilled professionals with experience in working with clay tiles.
Clay tile roofs may require periodic maintenance to address any potential issues such as cracked or broken tiles. While clay tiles are durable, they can be vulnerable to impact damage, especially during severe weather events or if walked upon incorrectly. Regular inspections can help identify any damaged tiles and ensure timely replacements.
10. Synthetic Slate Roofing
10.1 Overview of Synthetic Slate Roofing
Synthetic slate roofing is an innovative roofing material that replicates the appearance and texture of natural slate while offering enhanced durability and ease of installation. It is typically made from a combination of recycled rubber or plastic, allowing for more cost-effective and environmentally friendly options. Synthetic slate roofing provides a visually appealing and long-lasting roofing solution.
10.2 Advantages of Synthetic Slate Roofing
Synthetic slate roofing offers several advantages that make it an attractive alternative to natural slate. Firstly, it provides the same classic and elegant appearance as natural slate, without the inherent drawbacks. Synthetic slate is available in a variety of colors and styles, allowing homeowners to achieve the desired aesthetic appeal for their roofs.
One of the significant advantages of synthetic slate roofing is its lightweight nature. It is significantly lighter than natural slate, which reduces the overall weight on the roof structure and makes installation easier and more cost-effective. The lightweight nature also minimizes the risk of damage to the building during transportation and installation.
Synthetic slate roofing offers exceptional durability and weather resistance. It is highly resistant to cracking, impact damage, and weathering, ensuring a long lifespan and minimal maintenance requirements. Synthetic slate is also resistant to mold, algae, and insects, providing added protection against common roofing issues.
10.3 Disadvantages of Synthetic Slate Roofing
While synthetic slate roofing has many advantages, there are a few considerations to keep in mind. One potential disadvantage is the initial cost compared to some other roofing materials. While synthetic slate is often more affordable than natural slate, it may still have a higher upfront cost compared to asphalt shingles or metal roofing. However, the long lifespan and low maintenance requirements often offset the initial investment.
Another consideration is the ongoing development and improvement of synthetic slate materials. As the technology and manufacturing processes continue to evolve, it is important to choose reputable manufacturers and suppliers that offer high-quality products. This ensures the durability and performance of the synthetic slate roofing system.
Lastly, color fading may be a concern with some synthetic slate materials, especially in areas with high UV radiation. Over time, exposure to sunlight and weathering can cause some synthetic slate tiles to fade or lose their vibrancy. It is essential to choose synthetic slate products that have been specifically designed to resist color fading and maintain their aesthetic appeal over time.
In conclusion, there are various roofing options available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. From PVC and EPDM to metal and clay tiles, understanding the characteristics and considerations of different roofing materials is crucial in making an informed decision. Whether prioritizing durability, energy efficiency, aesthetics, or budget, there is a roofing option that can meet your specific needs. Consulting with a roofing professional and considering factors such as climate, building structure, and maintenance requirements can help you choose the most suitable roofing material for your property.