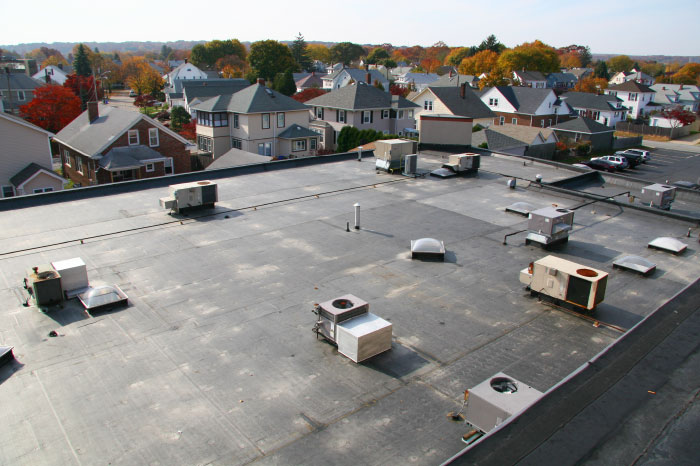
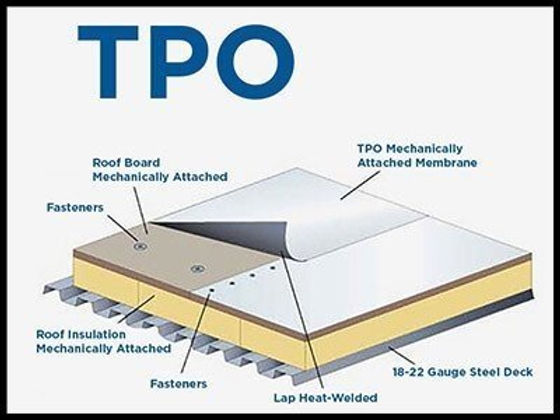
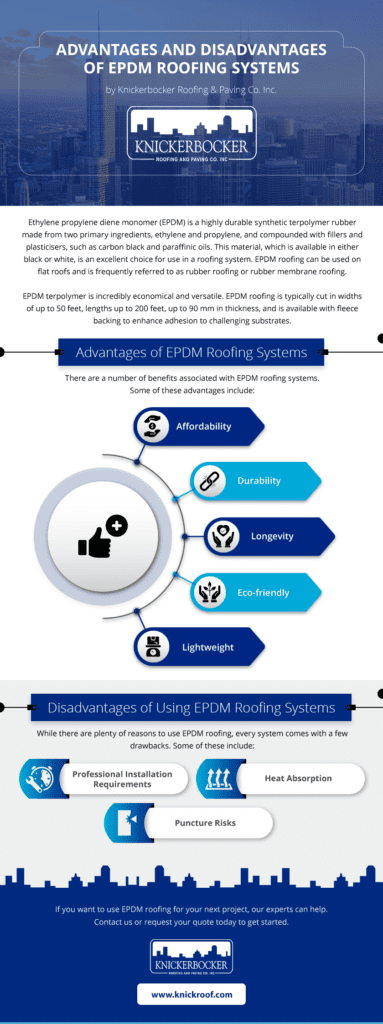
Have you ever considered the drawbacks of opting for a flat roof? While flat roofs might seem appealing with their clean lines and modern aesthetic, there is one major disadvantage that might make you think twice. In this article, we will explore the potential pitfalls of choosing a flat roof and how it can impact you in the long run. So, if you’re contemplating on whether a flat roof is the right choice for your home or building, keep on reading to make an informed decision.


Maintenance Challenges
Water Ponding
One of the major challenges associated with flat roofs is water ponding. Due to the lack of slope on a flat roof, water tends to accumulate and create pools on the surface. This can lead to various issues such as the deterioration of the roofing materials, weakening of the structure, and potential leakage problems. Water sitting on a flat roof for extended periods can cause the formation of algae, moss, and fungi, which not only look unsightly but also contribute to the degradation of the roof.
Debris Accumulation
Another maintenance challenge with flat roofs is the accumulation of debris. Due to their horizontal surface, flat roofs are more prone to collect leaves, branches, dust, and other debris. If left unattended, this debris can clog the drainage system and hinder proper water flow. Moreover, the presence of debris can cause additional weight and put stress on the roof structure, potentially leading to structural issues and even collapse in severe cases.
Leakage Issues
Flat roofs are notorious for their vulnerability to leakage problems. With their lack of pitch, water often struggles to drain properly, leading to stagnant water and moisture seeping into the roofing materials over time. This continuous exposure to moisture increases the likelihood of leaks, which can result in damage to the interior of the building, mold growth, and compromised structural integrity. Regular inspections and proactive maintenance measures are crucial to prevent and address leakage issues on flat roofs.
Limited Lifespan
Compared to other types of roofs, flat roofs generally have a shorter lifespan. The constant exposure to harsh weather conditions, pooling water, and other maintenance challenges can accelerate the wear and tear of the roofing materials. Additionally, the lack of proper insulation and ventilation on flat roofs can contribute to the deterioration of the roofing system. As a result, flat roofs may require more frequent replacements or repairs, which can be costly and inconvenient for property owners.
Drainage Problems
Inadequate Slope
One of the primary drainage problems that flat roofs face is the inadequate slope. Without an adequate slope to facilitate the natural flow of water, flat roofs can struggle with drainage. Water may accumulate in certain areas, leading to ponding and potential leakage issues. To overcome this challenge, it is essential to ensure that the flat roof has proper drainage systems in place, such as gutters, scuppers, or drains, that can effectively channel water away from the roof’s surface.
Clogging of Drains
Flat roofs are also prone to the clogging of drains, which can adversely affect the drainage system. Debris, leaves, and other foreign objects can accumulate in the drains over time, obstructing the flow of water. This can result in water pooling on the roof, increasing the risk of leaks and structural damage. Regularly inspecting and cleaning the drains is crucial to prevent clogging and maintain the effective functioning of the roof’s drainage system.
Water Pooling
Water pooling is a common drainage problem associated with flat roofs. If the roofing materials are not properly installed or if the roof structure has settled over time, low areas can form on the roof’s surface, allowing water to pool. Prolonged water pooling can lead to the deterioration of the roof materials, increased weight on the structure, and potential leakage issues. Regular roof inspections and addressing any low spots promptly can help minimize the risk of water pooling on flat roofs.
Extreme Weather Vulnerability
Heavy Snow Load
Flat roofs are particularly vulnerable to heavy snow loads. Unlike sloped roofs, where snow can easily slide off, flat roofs have a greater surface area for snow accumulation. The weight of the snow can exert significant pressure on the roof structure, potentially causing it to collapse or suffer structural damage. Proper snow removal techniques, such as using snow rakes or hiring professionals, are crucial to prevent excessive snow buildup and protect the integrity of flat roofs during snowy seasons.
Pooling of Water during Rainstorms
During heavy rainstorms, flat roofs face the challenge of water pooling due to their lack of slope. The accumulation of water on the roof can lead to added weight, increased pressure on the roofing materials, and heightened risk of leaks. Regular maintenance, including prompt removal of any standing water and ensuring the proper functioning of the drainage system, is essential to mitigate the potential damage caused by water pooling during rainstorms.
Wind Uplift
Flat roofs are more prone to wind uplift compared to sloped roofs. The horizontal surface of flat roofs creates a larger target for the wind to exert pressure on. This can result in the lifting of the roofing materials, weakening of the roof’s structure, and increased risk of damage during strong winds or storms. Reinforcing the roof with appropriate fasteners, proper installation techniques, and ensuring a secure perimeter are essential measures to enhance the wind resistance of flat roofs.
Limited Insulation
Insufficient Energy Efficiency
Flat roofs often lack proper insulation, resulting in insufficient energy efficiency. The absence of insulation or insufficient insulation thickness can lead to increased heat transfer, especially during hot summer months and cold winter seasons. This can result in higher cooling and heating costs as the building’s HVAC system needs to work harder to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature. Proper insulation installation and regular inspections are crucial to improve energy efficiency and reduce energy consumption.
Heat Loss and Gain
The limited insulation of flat roofs contributes to significant heat loss and gain. Without adequate insulation, the building’s interior is more susceptible to temperature fluctuations caused by external weather conditions. Flat roofs, due to their direct exposure to the elements, can absorb heat during sunny days and radiate it into the building, causing discomfort and increased energy usage for cooling. Conversely, during colder months, heat from the interior can escape more easily through the poorly insulated roof, resulting in higher heating costs. Adding insulation and improving the thermal resistance of flat roofs can help address these heat-related challenges.
Condensation Issues
Insufficient insulation on flat roofs can also lead to condensation problems. When warm, moist air comes into contact with a cold roof surface, condensation can occur. This can result in the formation of water droplets, which can cause mold growth, damage the roofing materials, and compromise the indoor air quality. Proper insulation materials and techniques that prevent the formation of condensation are essential for maintaining a healthy and efficient flat roof system.


Structural Issues
Weight Bearing Capacity
Flat roofs face unique challenges in terms of weight bearing capacity. Unlike sloped roofs, which naturally shed water and snow, flat roofs often have to bear the weight of these elements. Additionally, rooftop equipment, like HVAC systems or solar panels, can further increase the load on the roof. Ensuring that the roof structure is designed to handle the anticipated weight and conducting regular inspections to identify any signs of structural stress or weaknesses are crucial to prevent collapse or damage.
Additional Supports and Reinforcements
In some cases, flat roofs may require additional support or reinforcements to address structural weaknesses. Roof overhangs, parapet walls, or additional beams can be incorporated to enhance the strength and stability of the roof. However, these modifications may incur additional costs and may require obtaining proper permits and approvals. Evaluating the structural integrity of flat roofs and consulting professionals for necessary reinforcements can help mitigate potential structural issues.
Risk of Collapse
Due to their flat nature, incorrect design or inadequate structural support can increase the risk of collapse for flat roofs. The weight of accumulated snow, water pooling, or excessive loads from equipment can all contribute to excessive stress on the roof structure. Regular inspections, proper design considerations, reinforcing weak areas, and ensuring adherence to building codes and regulations are essential to minimize the risk of roof collapse and ensure the safety of the occupants.
Material Limitations
Lack of Aesthetics
Flat roofs are often perceived as less aesthetically pleasing compared to sloped roofs. Their simple, flat design may not offer the same visual appeal or architectural variety that pitched roofs can provide. This limitation can be a concern for those who value the overall aesthetics of their property and seek to create a visually appealing exterior. However, with proper architectural design and the use of visually appealing roofing materials, flat roofs can still achieve a modern and attractive look.
Susceptibility to UV Damage
Flat roofs are also more susceptible to UV damage compared to sloped roofs. The direct exposure to sunlight can cause the roofing materials to degrade, leading to deterioration, discoloration, and potential leaking. UV radiation can accelerate the aging process of certain roofing materials, such as asphalt or single-ply membranes, reducing their lifespan and requiring more frequent replacements or repairs. Proper selection of UV-resistant roofing materials and regular maintenance can help minimize the impact of UV damage on flat roofs.
Higher Chance of Cracking
Flat roofs are more prone to cracking due to their horizontal design and exposure to constant temperature fluctuations. These cracks can allow water to penetrate the roofing system, leading to leaks and damage to the underlying structure. Factors such as poor installation, insufficient insulation, or inadequate maintenance can further increase the chances of cracks on flat roofs. Regular inspections, addressing any cracks promptly, and using appropriate sealants or coatings are essential to prevent water infiltration and extend the lifespan of flat roofs.


Difficulty of Installation and Repairs
Complex Installations
Compared to sloped roofs, the installation process for flat roofs can be more complex. Proper slope design, adequate sealing and flashing techniques, and precise membrane installation are essential to ensure a watertight and durable roof. The installation of flat roofs requires a high level of skill and expertise, making it essential to hire experienced roofing professionals or contractors who specialize in flat roofs. Any errors or improper installation can result in costly repairs, compromised performance, and potential leakage issues.
Accessibility Challenges
Flat roofs can present accessibility challenges during installation, repairs, and maintenance. Unlike sloped roofs, which have easily accessible surfaces, flat roofs often require the use of ladders, scaffolding, or special safety equipment to access the roof. This can add complexity, time, and sometimes additional costs to any required maintenance or repair work. Ensuring that proper safety measures are in place, such as using fall protection systems, can help address the accessibility challenges associated with flat roofs.
Costly Repairs
Repairs for flat roofs can be more costly compared to sloped roofs. The complexity of the installation process, coupled with the limited access, can make repairs more challenging and time-consuming. Additionally, the cost of materials specifically designed for flat roofs, such as specialized membranes or coatings, can be higher compared to materials used for sloped roofs. Regular maintenance and addressing any issues promptly can help prevent major repair expenses and extend the lifespan of flat roofs.
Lack of Usable Space
Reduced Interior Headroom
Flat roofs can result in reduced interior headroom compared to sloped roofs. The horizontal design of flat roofs decreases the available space between the ceiling and the roof surface. This limitation can be a disadvantage for buildings where interior space is a priority, such as residential properties or commercial buildings that require higher ceilings. Proper planning and architectural design considerations can help mitigate the impact of reduced interior headroom on flat roofs.
Limited Rooftop Usability
Unlike sloped roofs that can provide additional usable space, flat roofs often have limited rooftop usability. The lack of a pitched surface can make it challenging to utilize the roof area effectively. However, with proper planning and design, flat roofs can still offer some level of usability. Rooftop gardens, recreational areas, or storage spaces can be incorporated with the right engineering and architectural considerations. Ensuring proper waterproofing and load-bearing capacities are crucial for creating functional and safe rooftop spaces on flat roofs.
Challenges for Solar Panel Installations
Flat roofs can create challenges for the installation of solar panels. Without the natural pitch to optimize sun exposure, flat roofs may require additional support structures or racks to properly angle the panels for maximum sunlight absorption. The installation process may also involve drilling into the roof, which can increase the risk of leaks if not done correctly. Adequate planning, consultation with solar professionals, and ensuring proper waterproofing measures are in place can help overcome these challenges and maximize the potential for solar panel installations on flat roofs.


Building Regulations and Insurance
Restrictions from Local Regulations
Flat roofs may face restrictions or specific requirements imposed by local building regulations or homeowner associations. These regulations can dictate aspects such as the pitch of the roof, the materials used, or the color choices, which can limit the design freedom for property owners. It is crucial to be aware of any relevant regulations and obtain necessary approvals or permits to ensure compliance and avoid potential penalties or delays during construction or renovation projects involving flat roofs.
Higher Insurance Premiums
Insurance companies often consider flat roofs to be higher risk compared to sloped roofs. The increased risk of leakage, potential for structural issues, and susceptibility to extreme weather events can result in higher insurance premiums for properties with flat roofs. Property owners may need to allocate additional budget for insurance coverage, especially if their flat roofs have existing maintenance issues or are made of materials that are deemed riskier by insurance providers. It is advisable to consult with insurance experts to understand the potential impact on insurance premiums when considering flat roofs.
Fire Hazards
Flat roofs can pose potential fire hazards. As flat roofs are often used to house HVAC systems, vents, or other mechanical equipment, the risk of fire can be higher in case of equipment malfunctions or electrical issues. Fire can spread more quickly on flat roofs due to the lack of a pitch that could otherwise help limit its spread. Proper fire safety measures, regular equipment inspections, and compliance with fire codes and regulations are crucial to minimize the fire hazards associated with flat roofs.
Lesser Resale Value
Potential Buyer Disinterest
The use of flat roofs can sometimes result in potential buyer disinterest. Some buyers may have a preference for sloped roofs due to their traditional appearance or perceived advantages, such as better drainage or more attic space. This buyer bias can limit the market appeal for properties with flat roofs, potentially resulting in longer selling times or lower demand. However, with proper marketing and highlighting the advantages of flat roofs, such as energy efficiency or potential rooftop utilization, sellers can still attract interested buyers.
Impact on Property Valuation
Flat roofs can influence the valuation of a property. Appraisers may assign a lower value to properties with flat roofs due to their perceived disadvantages, maintenance challenges, or potential shorter lifespan. It is important to ensure that the appraiser is aware of the specific qualities and advantages of the flat roof, such as energy efficiency or durability, to attain a fair and accurate valuation. Consulting with real estate professionals or appraisers who have expertise in assessing flat roofs can help ensure a more accurate property valuation.
Lower Market Demand
The limited market demand for properties with flat roofs can impact their resale value. As flat roofs are not as widely desired as sloped roofs, properties with flat roofs may take longer to sell. The smaller pool of potential buyers can result in lower demand, potentially affecting the selling price and negotiation power of the property owner. While market trends and buyer preferences can vary, effectively marketing the unique features and benefits of flat roofs can help attract potential buyers who appreciate the advantages offered by this roofing style.
In conclusion, while flat roofs offer certain advantages such as easier accessibility and potential for rooftop utilization, they also come with their fair share of challenges. Maintenance issues, drainage problems, vulnerability to extreme weather, limited insulation, potential structural concerns, material limitations, installation difficulties, lack of usable space, building regulations and insurance considerations, and lower resale value are among the major disadvantages associated with using a flat roof. By understanding these challenges and taking proactive measures to address them, property owners can ensure the longevity, functionality, and aesthetics of their flat roofs. Regular inspections, prompt repairs, proper insulation, effective drainage systems, and adherence to building codes are key to overcoming the disadvantages and maximizing the benefits of flat roofs.