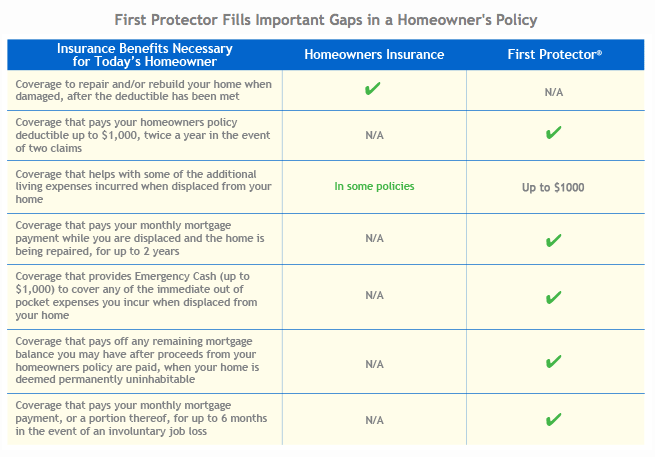
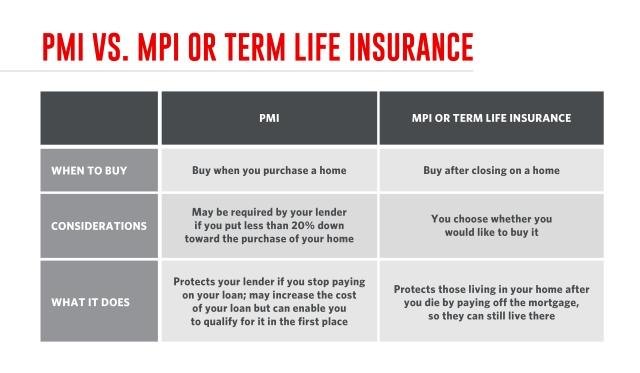
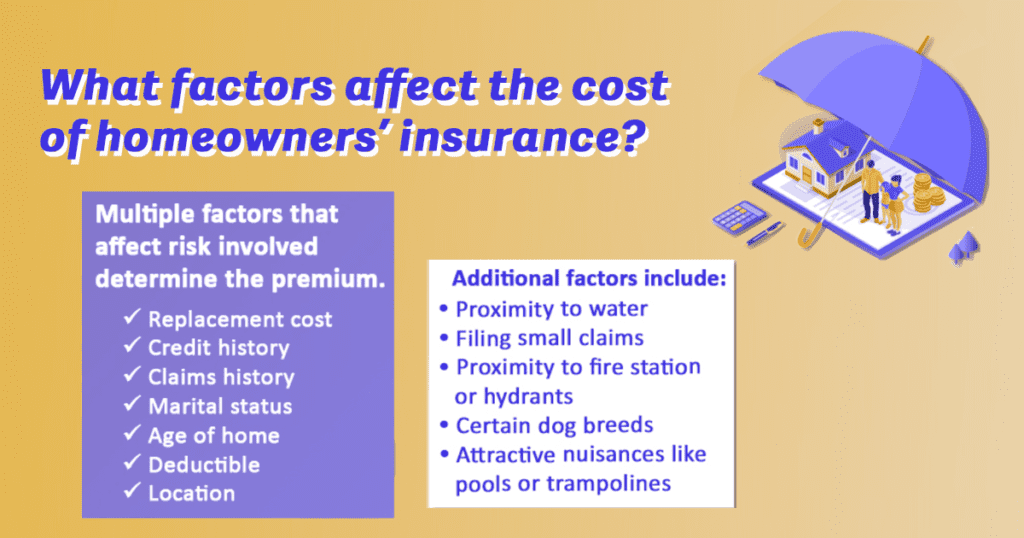
So you’ve finally paid off your mortgage, congratulations! Now that you’ve reached this financial milestone, you may be wondering if your homeowners insurance premiums will go down. After all, with no outstanding balance to protect, it only seems logical that your insurance costs would decrease, right? In this article, we’ll explore this commonly asked question and shed some light on whether or not paying off your mortgage affects your homeowners insurance.


Factors Affecting Homeowners Insurance Premiums
Property Value
The value of your property is one of the main factors that influence your homeowners insurance premiums. Insurance companies take into account the cost of rebuilding or repairing your home in the event of damage or destruction. If your property has a higher value, it may translate into higher insurance premiums since the insurance company would need to pay more in the case of a claim.
Location
The location of your home plays a crucial role in determining your homeowners insurance premiums. Insurance providers consider the risk associated with the area where your property is located. Factors such as crime rates, proximity to a fire station or hydrant, and the likelihood of natural disasters can impact your premiums. Homes located in high-risk areas, such as flood-prone regions or areas prone to forest fires, may have higher insurance premiums to account for the increased risk.
Age and Condition of the Home
The age and condition of your home are also taken into consideration by insurance companies. Older homes might have outdated electrical systems, plumbing, or other infrastructure that can pose higher risks of accidents or damage. Consequently, these homes might have higher insurance premiums than newer homes with updated systems and structures.
Safety Features
The presence of safety features in your home can help reduce your homeowners insurance premiums. Insurance companies appreciate proactive measures taken by homeowners to mitigate risks. Safety features such as security systems, smoke detectors, fire alarms, and sprinkler systems can lower the chance of accidents or damage, thus resulting in potential premium discounts.
Claims History
Your claims history can affect your homeowners insurance premiums. If you have a history of filing claims, especially for significant or frequent damages, it can indicate a higher risk for the insurance company. As a result, your premiums might increase to reflect the likelihood of future claims. Conversely, a clean claims history can lead to more favorable rates, as it suggests a lower risk of future financial burden on the insurance provider.
The Relationship Between Homeownership and Insurance
Importance of Homeowners Insurance
As a homeowner, having homeowners insurance is crucial for protecting your investment and providing financial security. Insurance coverage can help you rebuild or repair your home in the event of a disaster or unforeseen circumstances. It also offers liability coverage, protecting you if someone gets injured on your property and decides to sue. Homeowners insurance provides peace of mind and ensures that you can recover financially from unexpected events that could otherwise cause significant financial hardship.
Lenders and Homeowners Insurance
If you have a mortgage on your home, your lender will likely require you to have homeowners insurance. Lenders want to protect their investment, and homeowners insurance ensures that in the event of damage or destruction, the necessary funds will be available to repair or rebuild the property. Lenders may also require you to have a specific level of coverage to meet their loan requirements.
Insurance Coverage Requirements
Insurance coverage requirements vary depending on the lender and the type of mortgage you have. However, most lenders will require you to have coverage for the full replacement value of your home. This means that the insurance coverage should be enough to rebuild your property if it is completely destroyed. It’s important to understand your coverage requirements and work with your insurance provider to ensure that your policy meets the necessary criteria.

The Impact of Mortgage Payment on Insurance Premiums
Cost Breakdown of Homeowners Insurance
Homeowners insurance premiums are influenced by various factors, and the cost breakdown can help you understand how your payments are allocated. Typically, the majority of the premium goes towards property coverage, which protects the physical structure of your home. Other components may include liability coverage, which protects against lawsuits, and personal property coverage, which covers the contents of your home. Understanding the cost breakdown can help you evaluate your coverage options and make informed decisions.
Escrow Accounts and Mortgage Payments
Many homeowners pay their insurance premiums through an escrow account, which is managed by their mortgage lender. In this setup, a portion of your monthly mortgage payment is allocated towards your insurance premium. The lender then pays the insurance provider on your behalf. When your mortgage is paid off, you might have the choice to manage your insurance payments directly. However, it’s important to remember that homeowners insurance is still essential, even without a mortgage.
Insurance Premiums After Paying Off the Mortgage
Paying off your mortgage does not necessarily lead to a significant decrease in your homeowners insurance premiums. While it’s true that your lender’s requirements may no longer apply, the factors that determine your premiums remain unchanged. Your property value, location, the age and condition of your home, and other relevant factors still influence the cost of insurance coverage. It’s essential to review your policy periodically and update it as needed to ensure you have adequate coverage at a fair price.

Other Factors to Consider
Changes in Property Value
Changes in property value can impact your homeowners insurance premiums. If the value of your property increases significantly, such as through renovations or appreciation, you may need to adjust your coverage to reflect the updated value. Similarly, if the value decreases, adjusting your coverage accordingly can help avoid overpaying for insurance.
Policy Coverage and Deductibles
The coverage options and deductibles you choose can also affect your premiums. Higher coverage limits or lower deductibles typically result in higher premiums, as they provide more extensive coverage and potential financial liability for the insurance provider. It’s essential to review your policy and consider your individual needs to strike a balance between coverage and cost.
Renewal Periods and Premium Adjustments
Insurance policies typically have renewal periods, during which the insurance company reassesses the coverage and adjusts the premiums if necessary. Changes in your property’s value or the introduction of new safety features can be factors that lead to premium adjustments. It’s wise to review your policy at each renewal period to ensure you have appropriate coverage and take advantage of any available discounts.
Discounts and Bundling
Many insurance companies offer discounts for various reasons. Installing safety features, such as burglar alarms or deadbolts, might result in lower premiums. Additionally, bundling your homeowners insurance with other policies like auto insurance can lead to discounted rates. It’s worth exploring these options and discussing discount opportunities with your insurance provider to optimize your coverage and potentially reduce costs.
In conclusion, homeowners insurance premiums are influenced by various factors such as property value, location, age and condition of the home, safety features, and claims history. While paying off your mortgage may not directly decrease your premiums, it removes the lender’s requirements and gives you more flexibility in managing your insurance payments. However, it’s important to regularly review and update your policy to ensure adequate coverage and take advantage of any available discounts. Homeowners insurance is an essential investment that protects your home and provides financial security, making it crucial for all homeowners, regardless of their mortgage status.