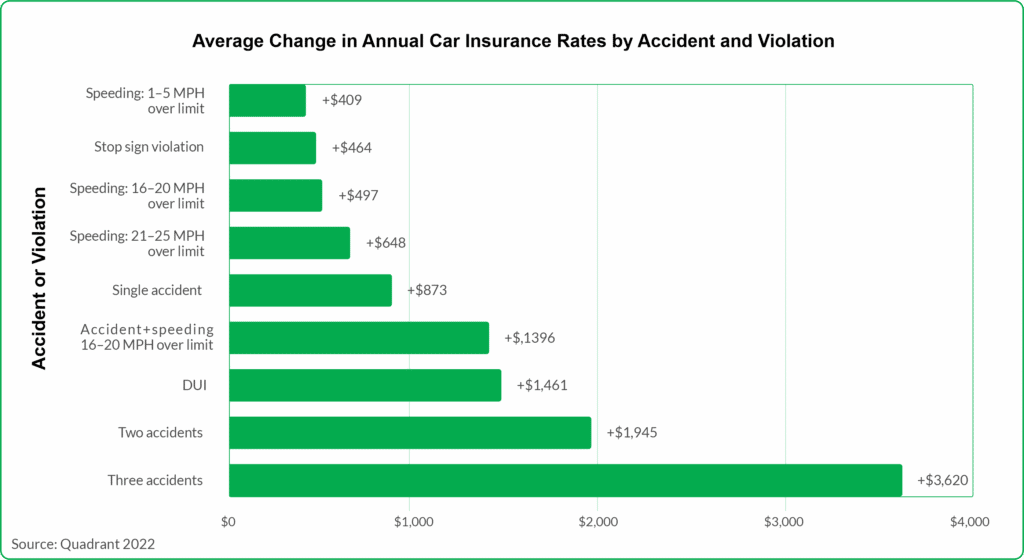
Curious to understand what has led to the skyrocketing costs of insurance premiums? If you’ve ever wondered why your monthly payments seem to be reaching new heights, this article aims to shed light on the factors that have contributed to this financial burden. Unravel the intricate web of circumstances that have led to these exorbitant prices and gain a comprehensive understanding of the current insurance landscape.
Increase in Healthcare Costs
Rising cost of medical treatments
One of the main factors contributing to the increase in insurance premiums is the rising cost of medical treatments. As medical technologies and procedures become more advanced, the costs associated with them also increase. New medications and treatment options that offer improved outcomes often come with a hefty price tag. This means that insurance companies have to pay higher amounts for medical services, which in turn leads to higher premiums for policyholders.
Expensive prescription drugs
Prescription drugs are another major contributor to the rising healthcare costs. The prices of many life-saving medications have skyrocketed in recent years, leaving insurance companies with no choice but to increase premiums to cover these costs. Specialty drugs, which are used to treat complex conditions such as cancer and autoimmune disorders, can be particularly expensive. As these drugs become more prevalent, insurance companies are left with no option but to pass on the costs to their customers.
Advanced medical technologies and procedures
The advancements in medical technologies and procedures have undeniably improved patient outcomes, but they have also significantly increased healthcare costs. Cutting-edge technologies such as robotic surgeries and advanced imaging devices require substantial investment, which is ultimately reflected in the insurance premiums. While these innovations have undoubtedly revolutionized healthcare, their high cost comes at a price for policyholders.
Increased Frequency and Severity of Claims
More people seeking medical care
An increase in the number of people seeking medical care has directly contributed to the frequency and severity of insurance claims. With improved access to healthcare and a growing population, more individuals are utilizing medical services, leading to a higher number of claims. The increased demand for healthcare services puts a strain on insurance companies, resulting in the need for higher premiums to cover the rising claims volume.
Higher number of catastrophic events
Natural disasters and catastrophic events such as hurricanes, earthquakes, and floods have also played a significant role in the increased frequency and severity of insurance claims. These events often cause substantial property damage and injuries, requiring insurance companies to pay out large sums of money for coverage. As the frequency and severity of these events increase due to climate change, insurance companies are forced to adjust their premiums accordingly to ensure they can meet the financial demands of these catastrophic events.
Expensive medical lawsuits
The rising costs of medical lawsuits have further driven up insurance premiums. When medical malpractice occurs, patients may file lawsuits seeking compensation for the damages they have suffered. The payouts from these lawsuits can be substantial, forcing insurance companies to increase premiums to cover the potential costs. Additionally, the legal fees associated with defending these lawsuits can also be significant, adding to the overall expenses of insurance companies and ultimately impacting the premiums for policyholders.


Insurance Fraud
Fake claims and staged accidents
Insurance fraud is a significant concern for insurance companies and policyholders alike. Fraudulent claims and staged accidents can cost insurance companies billions of dollars each year. When individuals make false claims or intentionally cause accidents to extract money from their insurance policies, the financial burden falls on the insurance company, which, in turn, impacts the premiums for all policyholders. To mitigate these fraudulent activities, insurance companies often have to allocate significant resources to investigate and prevent fraud, which further increases operational expenses and, consequently, insurance premiums.
Fraudulent billing practices
Fraudulent billing practices by healthcare providers also contribute to the increase in insurance premiums. Some providers may submit inflated or false bills to insurance companies, aiming to maximize their reimbursements. These fraudulent practices not only increase the costs for insurance companies but also affect premiums for policyholders. To combat fraudulent billing, insurance companies implement stringent auditing processes, which can drive up administrative costs and ultimately impact premiums.
Regulatory Requirements
Compliance costs
Insurance companies operate in a highly regulated environment, and compliance with regulatory requirements can be expensive. Complying with state and federal regulations, such as licensing, reporting, and monitoring, imposes additional costs on insurance companies. These compliance costs are ultimately passed on to policyholders through higher premiums.
Mandatory coverage provisions
Mandatory coverage provisions mandated by the government also contribute to the increase in insurance premiums. For example, laws requiring coverage for certain types of healthcare services or imposing restrictions on coverage limitations can increase the costs for insurance companies, leading to higher premiums. While these requirements aim to provide more comprehensive coverage for policyholders, they come with a cost that policyholders have to bear.

Aging Population and Longer Life Expectancy
Increased healthcare demand from older adults
The aging population and longer life expectancy have significantly contributed to the increased healthcare demand, ultimately affecting insurance premiums. As older adults tend to require more frequent medical care and have a higher likelihood of developing chronic conditions, insurance companies are faced with higher costs to cover their healthcare needs. This increased demand for healthcare services leads to an upward pressure on premiums to ensure that insurance companies can meet the financial demands of an aging population.
Higher prevalence of chronic diseases
The higher prevalence of chronic diseases among the aging population also impacts insurance premiums. Chronic conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and cancer require ongoing medical management and treatment, resulting in higher healthcare costs for insurance companies. To cover these costs, insurance companies may need to raise premiums for policyholders, particularly those who are more at risk of developing chronic diseases.
Adverse Selection
Insured individuals with higher risk profiles
Adverse selection occurs when individuals with higher risk profiles, such as those with pre-existing conditions, disproportionately seek insurance coverage. These individuals typically require more extensive healthcare services, leading to higher claims costs for insurance companies. To offset these higher costs, insurance companies often adjust their premiums to reflect the increased risk, resulting in higher premiums for all policyholders.
Unhealthy individuals disproportionately seeking coverage
In addition to individuals with pre-existing conditions, unhealthy individuals may also be more likely to seek insurance coverage. When individuals know they have health issues and require medical care, they are more likely to opt for insurance coverage. This disproportionately affects insurance companies, as they are required to provide coverage for these individuals. To cover the costs associated with higher healthcare utilization, insurance companies have to increase premiums for all policyholders.


Insurance Company Costs
Operational expenses
Insurance companies have substantial operational expenses, including staffing, technology, and administrative costs. These expenses include the salaries of insurance agents, claims adjusters, customer service representatives, and other staff members. Insurance companies also require robust technology infrastructure to manage policies, process claims, and provide customer support. The operational costs associated with running an insurance company inevitably impact premiums to cover these expenses.
Marketing and advertising costs
Insurance companies often invest heavily in marketing and advertising activities to attract new policyholders and retain existing ones. These costs include advertising campaigns, sponsorships, and agent commissions. Marketing and advertising expenses add to the overall costs borne by insurance companies, which are ultimately passed on to policyholders through higher premiums.
Profit margins
Like any business, insurance companies need to maintain profit margins to sustain their operations and provide returns to stakeholders. Profits generated by insurance companies help cover ongoing expenses, research and development costs, and other investments. When insurance companies experience increased costs, such as rising healthcare expenses or increased claims frequency, they may adjust their premiums to ensure a reasonable profit margin. This ultimately affects policyholders who must pay higher premiums.
Natural Disasters and Climate Change
Increased property and casualty claims
Natural disasters and climate change-related events often result in increased property and casualty claims. These events can cause significant damage to homes, businesses, and infrastructure, leading to substantial insurance payouts. When insurance companies incur higher claims costs due to natural disasters, they need to adjust their premiums to ensure they have enough funds to cover future claims. This can result in increased premiums for policyholders, particularly those living in areas prone to natural disasters.
Greater rebuilding and restoration costs
In addition to the immediate property and casualty claims, natural disasters also incur long-term costs associated with rebuilding and restoration. Insurance companies must factor in these costs when determining premiums, as they need to ensure they can cover the expenses of reconstruction and recovery. These additional costs contribute to the overall increase in insurance premiums for policyholders.

Lack of Competition in the Insurance Market
Fewer insurers leading to monopolistic practices
In some regions, the insurance market may lack competition, leading to monopolistic practices. When there are fewer insurers available, they have greater control over pricing and can dictate higher premiums. Limited competition prevents policyholders from having a variety of options to choose from, leaving them at the mercy of insurers who may charge higher premiums due to the lack of alternatives.
Limited options for consumers
A lack of competition also leads to limited options for consumers. When there are only a few insurance companies operating in an area, policyholders may not have access to policies that best suit their needs and budget. Consequently, they may have to settle for higher-priced policies or ones that offer less coverage. Limited options in the insurance market may result in policyholders having to pay higher premiums without enjoying the benefits of competitive pricing.
Changing Regulatory Environment
New legislation leading to higher premiums
The introduction of new legislation and regulatory changes can impact insurance premiums. Government regulations can impose new requirements on insurance companies or change existing ones, leading to increased costs. For example, legislation mandating coverage for certain healthcare services or increasing minimum coverage limits can result in higher premiums. These changes are often necessary to improve consumer protections or enhance the quality of coverage. However, they can also contribute to the rise in insurance premiums.
Additional coverage requirements
As the regulatory environment evolves, insurance companies may be required to offer additional coverage options. These additional coverage requirements can range from mandatory coverage for specific healthcare services to the inclusion of certain benefits. While these additional coverage options aim to provide more comprehensive protection for policyholders, they can lead to higher premiums. The costs associated with expanding coverage options are ultimately borne by policyholders through increased insurance premiums.
In conclusion, insurance premiums have seen a significant increase due to various factors. Rising healthcare costs, increased frequency and severity of claims, insurance fraud, regulatory requirements, an aging population, adverse selection, insurance company costs, natural disasters, lack of competition, and changing regulatory environments all contribute to the premium hikes. Understanding these factors helps policyholders comprehend the reasons behind the rising costs and make informed decisions when selecting insurance coverage.